Introduction
In the ever-volatile world of financial markets, investors are constantly seeking strategies to capitalize on price fluctuations while minimizing risk. One such strategy is the strangle, a versatile options trading technique that allows traders to profit from both upward and downward movements in the underlying asset’s price. Understanding the intricacies of a strangle can provide a significant advantage in the pursuit of financial gains.

Image: www.youtube.com
What is a Strangle?
A strangle is a neutral options strategy involving the simultaneous purchase of a call option and a put option with the same expiration date but different strike prices. The call option grants the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at a predetermined strike price, while the put option grants the right to sell the underlying asset at a lower strike price. By purchasing both options, the trader creates a range of potential profitability.
Benefits of Using a Strangle
-
Profit Potential: A strangle allows traders to profit from both bullish and bearish market movements. If the underlying asset’s price rises, the call option gains value, and vice versa for the put option if the price falls.
-
Flexibility: Unlike directional options strategies, a strangle does not require the trader to predict the direction of the price movement. As long as the price moves significantly in either direction, the trader can profit.
-
Risk Management: The purchase of both a call and a put option creates a defined risk profile. The maximum potential loss is limited to the premium paid for both options.
Components of a Strangle
-
Call Option: An option contract that gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at a predetermined strike price.
-
Put Option: An option contract that gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at a predetermined strike price.
-
Strike Price: The price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold using the option.
-
Expiration Date: The date on which the option contracts expire.
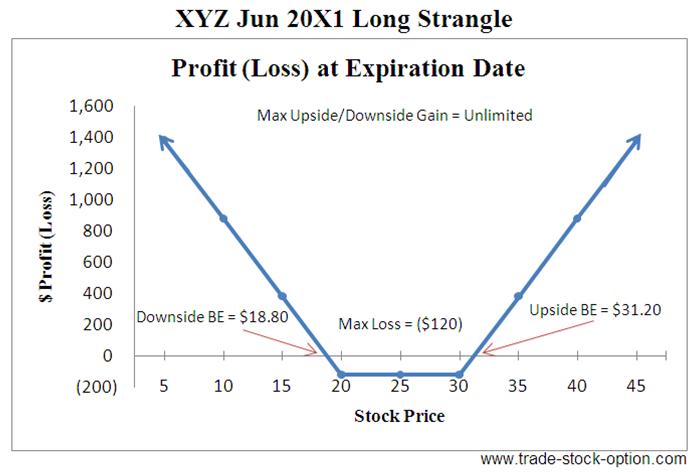
Image: ejizajif.web.fc2.com
Trading Strategies using a Strangle
Traders can implement various strategies using a strangle:
-
Long Strangle: Buying both a call and a put option with strike prices above and below the current market price. This strategy is appropriate when the trader expects high volatility but is uncertain about the direction of price movement.
-
Short Strangle: Selling both a call and a put option with strike prices above and below the current market price. This strategy is suitable when the trader anticipates low volatility and expects the price to remain within a specific range.
Example
Suppose an investor purchases a call option with a strike price of $105 and a put option with a strike price of $100 for the same expiration date on a stock currently trading at $102. If the stock price rises to $110, the investor profits from the call option, and if it falls to $95, the investor profits from the put option. However, if the stock price remains within the range of $100-$105, the investor loses the premium paid for both options.
What Is A Strangle In Trading Options

Image: www.options-trading-mastery.com
Conclusion
A strangle is a valuable options trading strategy that allows investors to profit from volatility while managing risk. By understanding the components and mechanics of a strangle, traders can effectively implement this strategy as part of their overall investment portfolio. Remember to conduct thorough research, manage risk, and consider market conditions before executing any options trades.






