Introduction
In the realm of financial markets, there are a myriad of paths investors can take to capitalize on market movements. Two popular approaches that often draw comparisons are option trading and margin trading. While both involve leverage and can yield significant rewards, their underlying mechanisms and risk profiles are vastly different. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of option trading vs. margin trading, guiding readers through the complexities of these financial instruments.
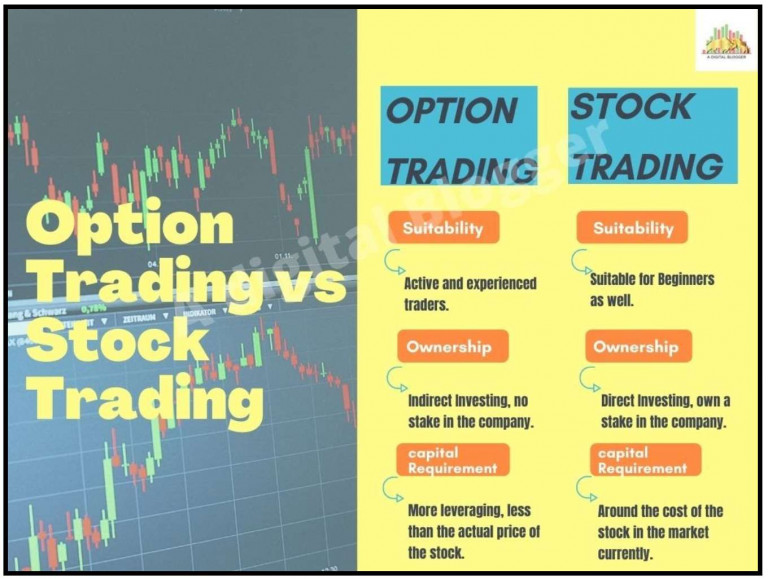
Image: www.adigitalblogger.com
Option Trading: Unveiling the Power of Derivatives
Option trading involves the exchange of financial instruments known as “options.” Options are contracts that convey the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specified date. Option traders pay a premium to acquire these contracts, which gives them the potential to profit from price fluctuations in the underlying asset.
There are two main types of options: calls and puts. Call options confer the right to buy the underlying asset, while put options grant the right to sell it. The strike price is the predetermined price at which the option can be exercised, and the expiration date denotes the final day when the option can be used.
The allure of option trading stems from the leverage it provides. By paying a relatively small premium, traders can control a much larger amount of the underlying asset. This can amplify potential profits, but it also magnifies potential losses.
Margin Trading: Borrowing to Enhance Returns
Contrarily, margin trading entails borrowing money from a brokerage firm to purchase securities. This increases the investor’s potential purchasing power, enabling them to enter larger positions than their account balance would ordinarily allow. The borrowed funds are secured by the investor’s existing assets or cash on deposit, which serve as “collateral.”
Margin trading effectively allows investors to control more shares of a stock or other financial instrument than they actually own. This leverage can significantly magnify both profits and losses, as investors can reap the benefits of price appreciation without having to fully fund the position. However, it also magnifies potential losses, particularly in declining markets.
Unveiling the Key Differences
Despite their shared characteristic of leverage, option trading and margin trading differ significantly in several key aspects:

Image: blog.cctip.io
1. Underlying Assets
In option trading, the underlying assets can vary widely, including stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, and market indices. In contrast, margin trading is typically limited to stocks and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
2. Risk Profile
Option trading can offer more flexibility in managing risk compared to margin trading. Options provide a range of strategies that allow traders to cap their potential losses while defining the potential reward. Margin trading, on the other hand, exposes investors to potentially unlimited losses that can exceed their initial investment.
3. Complexity
Option trading is a complex financial instrument that requires considerable knowledge and skill to navigate successfully. Margin trading, while less intricate, still carries its own set of risks that investors must fully understand before employing it.
4. Suitability
Option trading is generally more suited for experienced traders who are comfortable with complex financial instruments and willing to take on higher risks. Margin trading, while potentially accessible to a broader range of investors, should only be considered by those who comprehend the inherent risks and have the necessary knowledge to manage it responsibly.
Maximizing Profits While Minimizing Risks
Successful option trading and margin trading hinge on a thorough understanding of these financial instruments and their respective risks. Here are some strategies to optimize profits while mitigating risks:
- Option Trading:
- Use defined risk strategies such as covered calls or cash-secured puts to limit potential losses.
- Diversify your portfolio by trading options on various underlying assets to spread risk.
- Set realistic profit targets and avoid chasing quick gains that can lead to excessive losses.
- Margin Trading:
- Begin with small margin positions to familiarize yourself with the risks before increasing leverage.
- Maintain a healthy margin call ratio to avoid margin calls in volatile markets.
- Monitor market conditions closely and adjust positions as necessary to manage risk.
Option Trading Vs Margin Trading

Image: app-aws-useast1.cryptohopper.com
Conclusion
Option trading and margin trading present distinct opportunities for investors seeking to amplify their returns. By leveraging the power of derivatives or borrowing capital, these strategies can enhance the potential for profits. However, it is crucial to recognize that these instruments also carry significant risks. Investors should carefully assess their individual circumstances, tolerance for risk, and level of financial expertise before engaging in option trading or margin trading. By approaching these markets with a clear understanding of their complexities and risks, investors can maximize their chances of success while safeguarding their financial well-being.






