In the intricate world of financial markets, where uncertainty and opportunity intertwine, the art of options trading has emerged as a powerful tool for investors seeking to enhance their portfolio performance or mitigate risks. Among the diverse trading strategies available, spreads, a unique combination of buying and selling multiple options contracts, stand out as a valuable technique. This article will explore an example of a spread in options trading, delve into its components, and uncover the strategic advantages it offers.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/10OptionsStrategiesToKnow-02_2-c1aed6a1ee3545068e2336be660d4f81.png)
Image: pureherbs-egy.com
What is a Spread in Options Trading?
In options trading, a spread refers to the simultaneous buying and selling of two or more options contracts, typically with the same underlying asset but different strike prices or expiration dates. The purpose of using a spread is to create a customized position that aligns with the trader’s specific risk tolerance and profit goals. By combining different options contracts, investors can engineer desired risk-reward profiles or capitalize on market inefficiencies.
An Example of a Vertical Spread
One common type of spread is the vertical spread, where the options contracts have the same expiration date but different strike prices. For instance, consider an investor who believes a stock will continue to rise in value but wants to limit their downside risk. They could create a bull call spread by buying one call option with a lower strike price and simultaneously selling one call option with a higher strike price.
In this example, let’s say the stock is currently trading at $50. The investor buys a call option with a strike price of $45 and sells a call option with a strike price of $55, both expiring in two months. This would create a vertical bull call spread.
Benefits and Advantages of Using Spreads
Spreads offer several advantages over trading individual options contracts:
- Risk Management: Spreads, particularly vertical spreads, can reduce the risk of holding a single option contract by diversifying the position. The investor in the bull call spread has a limited loss potential up to the difference between the strike prices, even if the stock price falls below the lower strike price.
- Profit Potential: Well-crafted spreads allow investors to define their profit potential while controlling risk. Depending on the type of spread, traders can benefit from both bullish or bearish market movements, or target fluctuations within a specific range.
- Flexibility: Spreads provide a high degree of customization. Traders can tailor spread positions to their risk tolerance, capital level, and market outlook. With various spread combinations available, investors can adapt their strategies to changing market conditions.

Image: www.schwab.com
Example Of A Spread In Options Trading
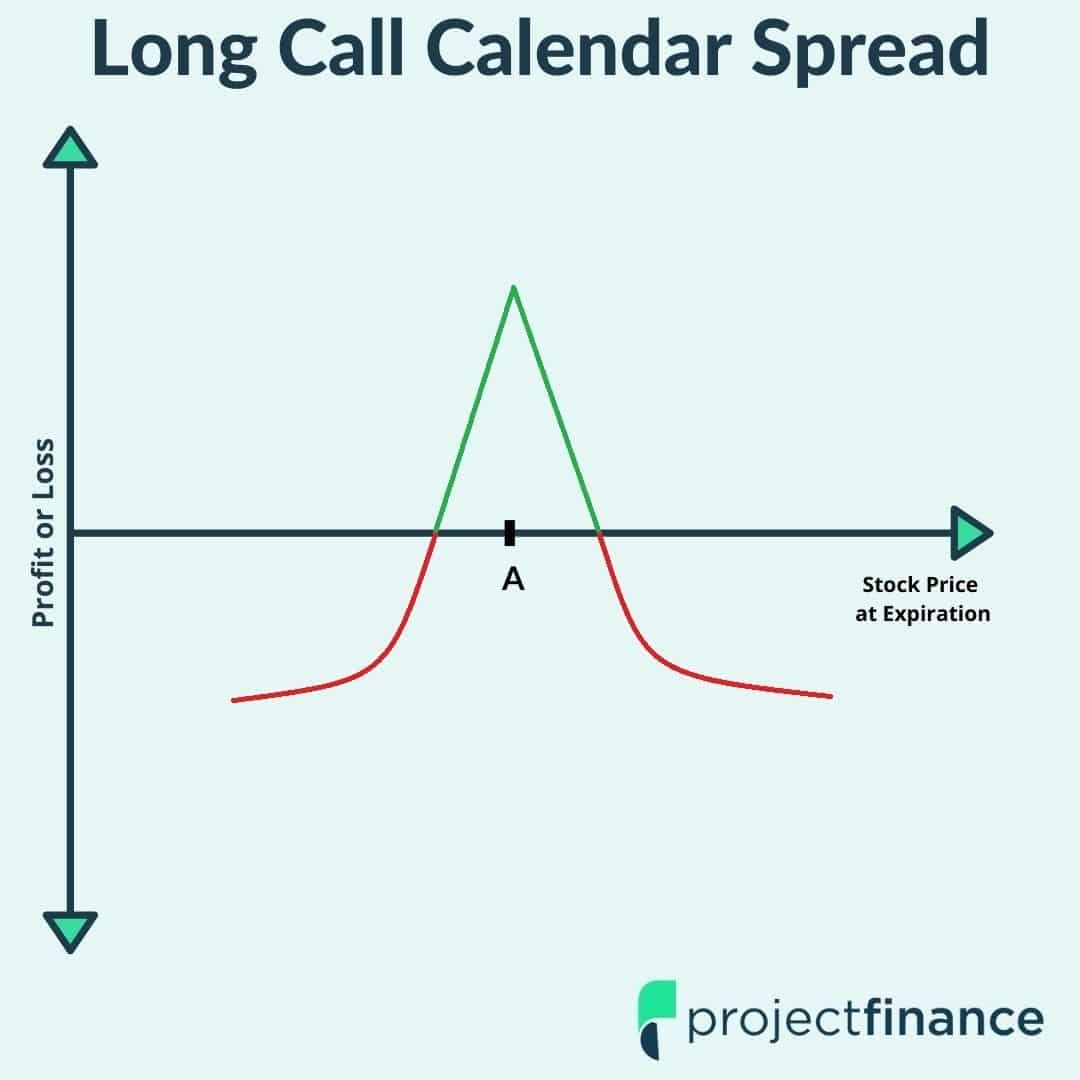
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Conclusion
Spreads, as exemplified by the vertical bull call spread, are a powerful tool in the options trading toolkit. By combining different options contracts, investors can create custom positions that align with their investment goals and risk appetites. While options trading involves inherent risk, spreads offer a versatile approach to potentially enhance portfolio returns or manage uncertainty. Whether you are a seasoned trader or just starting to explore options strategies, understanding spreads and their applications can empower you to navigate the financial markets with greater confidence and efficiency.






