Introduction:
Imagine a world where you can harness the potential of the stock market to multiply your wealth, but every triumph carries a silent shadow: the tax implications. Options trading, a dynamic instrument for advanced investors, brings with it a unique set of tax considerations that can impact your financial journey. Fear not, for this comprehensive guide will lead you through the intricacies of capital gains tax for options trading, empowering you to make informed decisions and minimize tax liability.
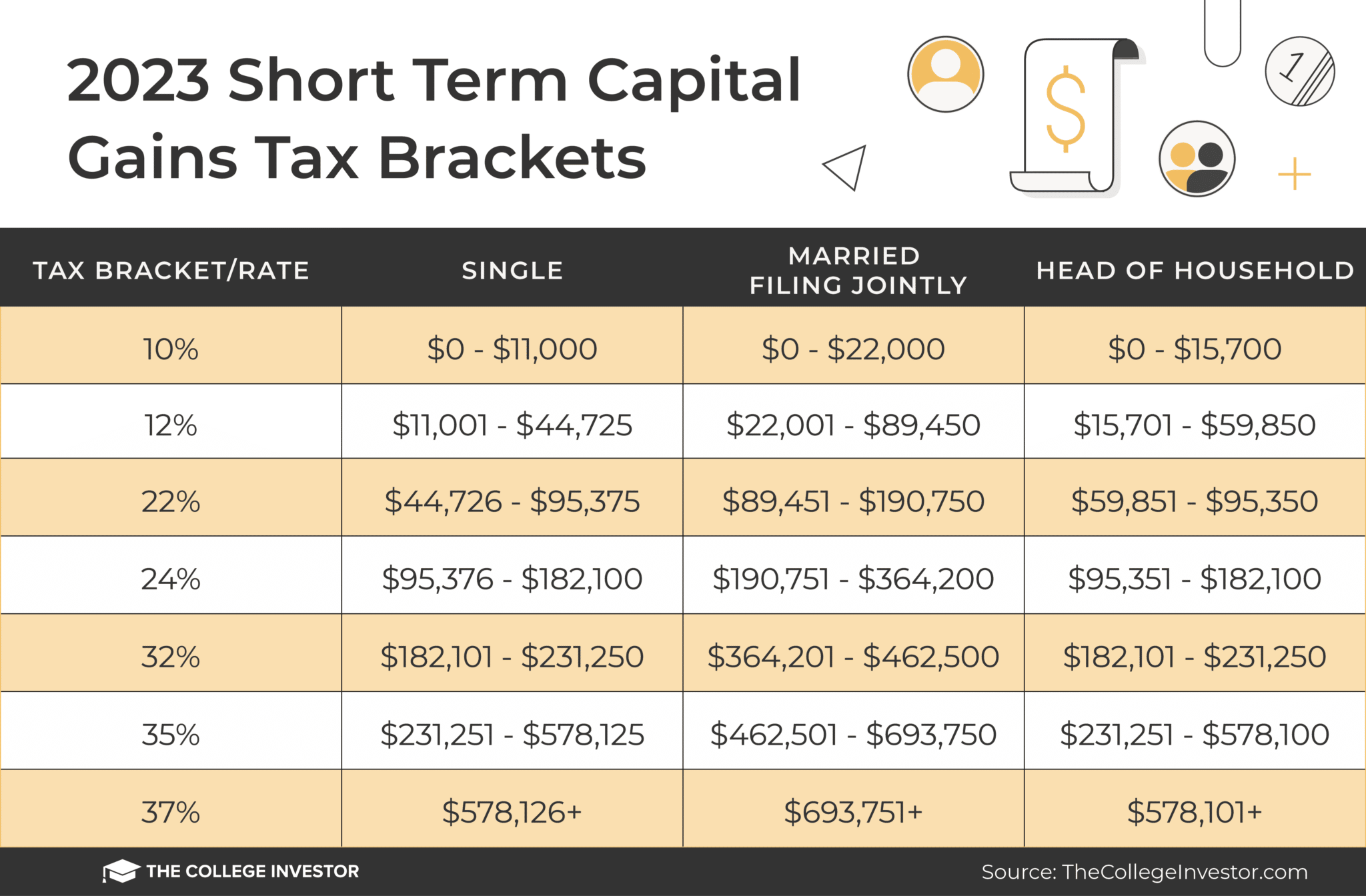
Image: investguiding.com
Demystifying Capital Gains Tax:
Capital gains tax is a levy imposed on the profit derived from selling an asset, such as stocks or options. Options, contracts that grant the right to buy or sell an underlying security at a specific price and time, can generate capital gains or losses depending on their performance against the market. Understanding the types of capital gains taxes, their rates, and how they apply to options trading is crucial for prudent financial planning.
Taxation Based on Holding Period:
The holding period, the time elapsed between acquiring and selling an option, plays a significant role in determining capital gains tax. Options held for less than a year (short-term) are taxed as ordinary income, typically at higher rates, while those held for a year or longer (long-term) are taxed at more favorable rates.
Types of Capital Gains:
-
Long-Term Capital Gains: Apply to options held for over a year and are generally taxed at lower rates, providing tax savings for patient investors.
-
Short-Term Capital Gains: Imposed on options held for less than a year and are taxed at ordinary income rates, potentially reducing your profit margin.

Image: www.taxpolicycenter.org
Maximizing Your Returns:
-
Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Consider utilizing tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s, where investment earnings, including options trading gains, can grow tax-deferred until withdrawal.
-
Harvesting Losses: When options incur a loss, you can offset those losses against your gains, reducing your overall tax liability. Strategic loss harvesting can create financial flexibility.
Expert Advice:
“Options trading, while potentially lucrative, requires a deep understanding of capital gains tax implications,” advises financial expert Dr. Mark Hanson. “Consult with a tax advisor to tailor your strategy for optimal tax efficiency.”
Actionable Tips:
-
Keep meticulous records of option purchases and sales for accurate tax reporting.
-
Utilize tax software or online calculators for precise tax calculations.
-
Monitor tax laws and seek professional guidance for timely updates.
Capital Gains Tax For Options Trading

Image: equitymultiple.com
Conclusion:
Capital gains tax for options trading is a complex but manageable aspect of your financial strategy. By navigating this guide, you gain the knowledge and tools to maximize your profits. Remember, the path to financial success often involves understanding the tax implications that shape your investments. Embrace this knowledge, consult expert guidance when needed, and let options trading propel you towards your financial aspirations.






