Imagine a world where you could potentially make significant returns on your investments, even in volatile markets. Imagine having the power to control risk and amplify potential gains. This is the world of options trading, a financial tool that has captivated investors for decades.
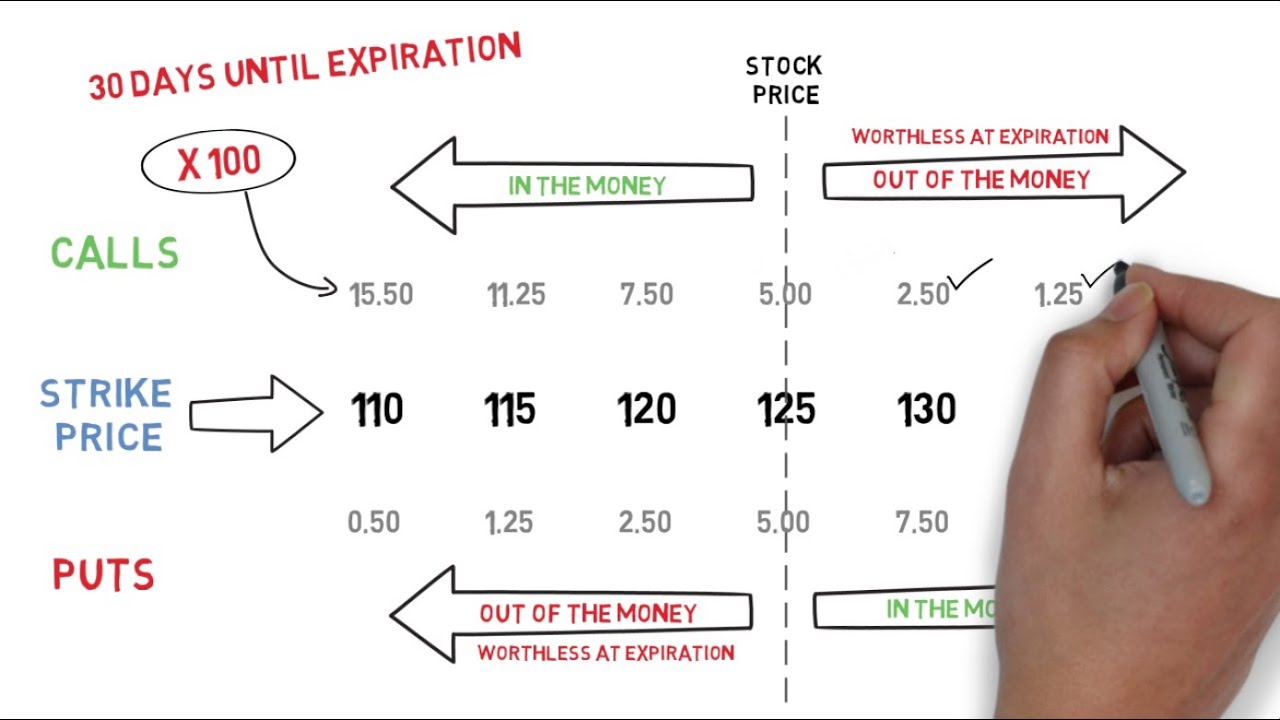
Image: www.youtube.com
While the allure of options trading is undeniable, it can also seem daunting, particularly for beginners. This guide will demystify the world of options trading, breaking down complex concepts into simple, digestible information. We’ll explore the fundamentals, discuss different strategies, and give you actionable tips to get started on your options trading journey. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how options work and be empowered to make informed decisions about whether this powerful tool is right for you.
Decoding the Options Enigma: Unveiling the Basics
At its core, an option is simply a contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. The underlying asset could be a stock, index, commodity, or even a currency. Think of it as a specialized insurance policy with the potential for lucrative returns.
There are two main types of options:
- Calls: A call option gives the buyer the right to purchase the underlying asset at a specific price, known as the strike price. This is particularly advantageous if the underlying asset’s price increases, allowing you to buy it at a discount from the market price.
- Puts: A put option gives the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. This is beneficial when the underlying asset’s price declines, enabling you to sell it at a higher price than what the market is currently offering.
Navigating the Option Landscape: Key Terminology
To truly grasp the nuances of options trading, it’s essential to understand the fundamental language of the options world. Here are a few key terms to familiarize yourself with:
- Strike Price: The predetermined price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Premium: The price you pay to acquire the option contract. It represents the value of the right granted by the option.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires, after which it becomes worthless.
- Underlying Asset: The asset being traded, such as a stock, index, commodity, or currency.
- In-the-Money: An option is “in-the-money” if it’s profitable to exercise it immediately.
- Out-of-the-Money: An option is “out-of-the-money” if it wouldn’t be profitable to exercise it immediately.
Unlocking the Secrets: Building Your Option Trading Strategy
Now that you understand the basic building blocks, it’s time to learn how to put them together to create a winning strategy. Options trading offers a multitude of approaches, each with its own risk and reward profile. Let’s explore some popular strategies for beginners:
1. Covered Calls: A covered call involves selling a call option on a stock you already own. This adds a potential income stream by collecting premiums. However, if the stock price rises significantly, your upside potential is capped by the strike price.
2. Cash-Secured Puts: A cash-secured put involves selling a put option and putting aside cash to cover the potential obligation if the option is exercised. This strategy can generate income, but you’re obligated to buy the stock at the strike price if the put buyer decides to exercise.
3. Protective Puts: Protective puts are a strategy to limit losses on a stock position. You buy a put option for the same stock you own. If the stock price falls, the put option can be exercised, allowing you to sell the stock at the strike price, mitigating potential losses.
4. Long Call: Buying a call option gives you the right to purchase the underlying asset at a specific price, enabling you to profit if the price rises. However, you’ll only make money if the stock price rises above the strike price plus the premium you paid.
5. Long Put: Buying a put option gives you the right to sell the underlying asset at a specific price, allowing you to profit if the price decreases. This strategy is beneficial when you expect the underlying asset to go down.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/BuyingCalls-7ff771dfbc724b95b8533a77948d7194.png)
Image: www.investopedia.com
Expert Insights: Unveiling the Wisdom of the Market
While theory is a great starting point, the real-world application of options trading demands guidance from experienced experts. Here’s what seasoned traders recommend for beginners:
- Start Small: Begin with a small initial investment and gradually increase your capital as you gain experience and confidence.
- Focus on Learning: Devote time to understanding the fundamentals of options trading, market dynamics, and risk management.
- Utilize Educational Resources: Take advantage of books, online courses, and webinars to enhance your knowledge base.
- Practice with Paper Trading: Simulate options trading with virtual money to hone your strategies without risking real capital.
- Embrace Patience: Options trading requires patience and discipline. Don’t chase quick profits; focus on long-term strategies.
Option Trading For Beginner
Charting Your Course: Embracing the Options Journey
Options trading can be an exhilarating and financially rewarding journey, but it requires a disciplined, strategic approach Remember: knowledge, patience, and a dedication to continuous learning are your most valuable assets. By harnessing the power of options, you can potentially turn your investment portfolio into a powerful force for financial freedom.
So, take the first step, explore the world of options, and discover the potential for unlocking your financial future. As you embark on this adventure, remember, the journey itself is as valuable as the destination.






