In the world of options trading, volatility is a key concept that plays a crucial role in determining the value and risk associated with an option contract. Understanding volatility is essential for investors looking to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the options market.

Image: www.dailyfx.com
What is Volatility?
Volatility measures the degree to which the price of an underlying asset fluctuates over time. It is typically expressed as an annualized percentage and indicates the potential range of price movements over a given period. Higher volatility signifies that the asset’s price is more likely to experience significant swings, while lower volatility suggests a more stable price environment.
Volatility is a dynamic concept that can change over time, influenced by a wide range of factors, including economic conditions, geopolitical events, and company-specific news. Options traders closely monitor volatility trends as they can significantly impact the value of their contracts.
Historical Volatility vs. Implied Volatility
Options traders utilize two primary types of volatility measures: historical volatility and implied volatility.
Historical volatility measures the realized volatility of an asset’s price over a specific past period, typically 6 months to a year. It provides a basis for assessing the asset’s normal price movements.
Implied volatility, on the other hand, measures the market’s expectation of future volatility. It is derived from the prices of options contracts with various expiration dates and strike prices. Implied volatility is often seen as a forward-looking indicator and can provide insights into investor sentiment towards an asset.
Impact of Volatility on Option Prices
Volatility has a significant impact on option prices. In general, options become more expensive when volatility is higher and cheaper when volatility is lower. This is because higher volatility increases the probability of significant price swings, which in turn increases the potential value of the option.
For example, if the implied volatility of a stock’s options is 20%, there is a higher likelihood that the stock’s price will move significantly over the life of the option. As a result, the option premium (price) will be higher to reflect this potential for greater price fluctuations.

Image: www.tradingfuel.com
Managing Volatility in Options Trading
Recognizing the importance of volatility in options trading, investors employ various strategies to manage its impact:
- Vega Trading: Vega measures the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in implied volatility. Traders can use vega to adjust their portfolio exposure to volatility by buying or selling options with high or low vega, respectively.
- Implied Volatility Trading: This involves trading options based on their implied volatility in relation to their historical volatility. Traders can sell options when implied volatility is high and buy options when implied volatility is low, to capitalize on potential mispricing.
- Hedging with Volatility: Investors can use options to hedge against volatility risks. By selling options with low vega and buying options with high vega, a balanced portfolio can be created that provides protection against extreme price fluctuations.
FAQs on Volatility in Options Trading
Q: What factors can affect volatility?
A: Economic conditions, geopolitical events, company-specific news, and investor sentiment can all influence volatility levels.
Q: How can I measure volatility?
A: Historical and implied volatility are two primary measures that provide insights into the realized and expected volatility of an asset.
Q: How does volatility impact option pricing?
A: Higher volatility generally corresponds with higher option premiums, while lower volatility leads to lower premiums due to the increased probability of significant price movements.
What Is Volatility In Options Trading
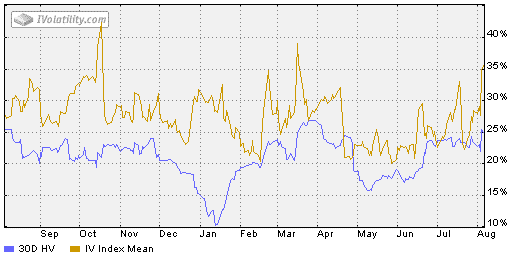
Image: www.optionstradingiq.com
Conclusion
Understanding and managing volatility are critical for success in options trading. By grasping its concept, monitoring its trends, and employing appropriate strategies, traders can better navigate market fluctuations and optimize their trading returns. Recognizing the importance of volatility empowers investors to make informed decisions and enhance their overall trading performance.
If you have any further questions or would like to delve deeper into the topic of volatility in options trading, please don’t hesitate to contact your financial advisor or engage with other experts in the field.






