The high-stakes world of options trading not only offers opportunities for financial gain but also brings forth a complex tax landscape that can confound even seasoned traders. Understanding the tax implications is crucial to maximizing your returns while staying compliant with the law. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of options tax rates, providing you with an authoritative and accessible roadmap to navigate this intricate terrain.

Image: www.simpletaxindia.net
Navigating the Options Tax Maze: A Comprehensive Overview
Before venturing into options trading, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of taxation. Options, financial instruments derived from underlying assets, are subject to taxation based on their specific characteristics and the trader’s objectives. Understanding these nuances is paramount to avoiding costly surprises down the road.
Upon exercise, options are categorized as either short-term or long-term, with each category carrying distinct tax treatment. Short-term options, held for less than a year, are taxed at ordinary income rates, while long-term options, held for a year or more, benefit from favorable capital gains rates. It’s worth noting that these rates vary depending on your individual tax bracket.
Decoding the Tax Treatment of Covered and Uncovered Options
The tax treatment of options further hinges on whether they are classified as covered or uncovered. Covered options are options secured by the underlying asset, while uncovered options lack such collateral. This distinction holds significant implications for tax purposes.
Premiums received from selling covered options are generally not taxable until the underlying asset is sold. However, if the options expire unexercised, the premiums may be considered ordinary income subject to taxation. Conversely, premiums from selling uncovered options are immediately taxed as ordinary income. Remember, the tax implications also extend to option buyers, with premiums paid for purchasing options being considered capital losses or deductions against future capital gains.
Straddling the Line: Tax Considerations for Qualified and Nonqualified Options
The complexities of options taxation extend beyond the basic framework, with qualified and nonqualified options presenting unique considerations. Qualified options, granted to employees as part of compensation, enjoy preferential tax treatment under certain conditions. In contrast, nonqualified options are subject to ordinary income tax rates upon exercise, irrespective of holding period.
Navigating the nuances of options taxation can be a daunting task, but armed with the right knowledge, you can confidently navigate this intricate landscape. Seek professional advice from tax experts or financial advisors who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific trading strategies and financial situation.

Image: www.angelone.in
What Is The Tax Rate For Options Trading
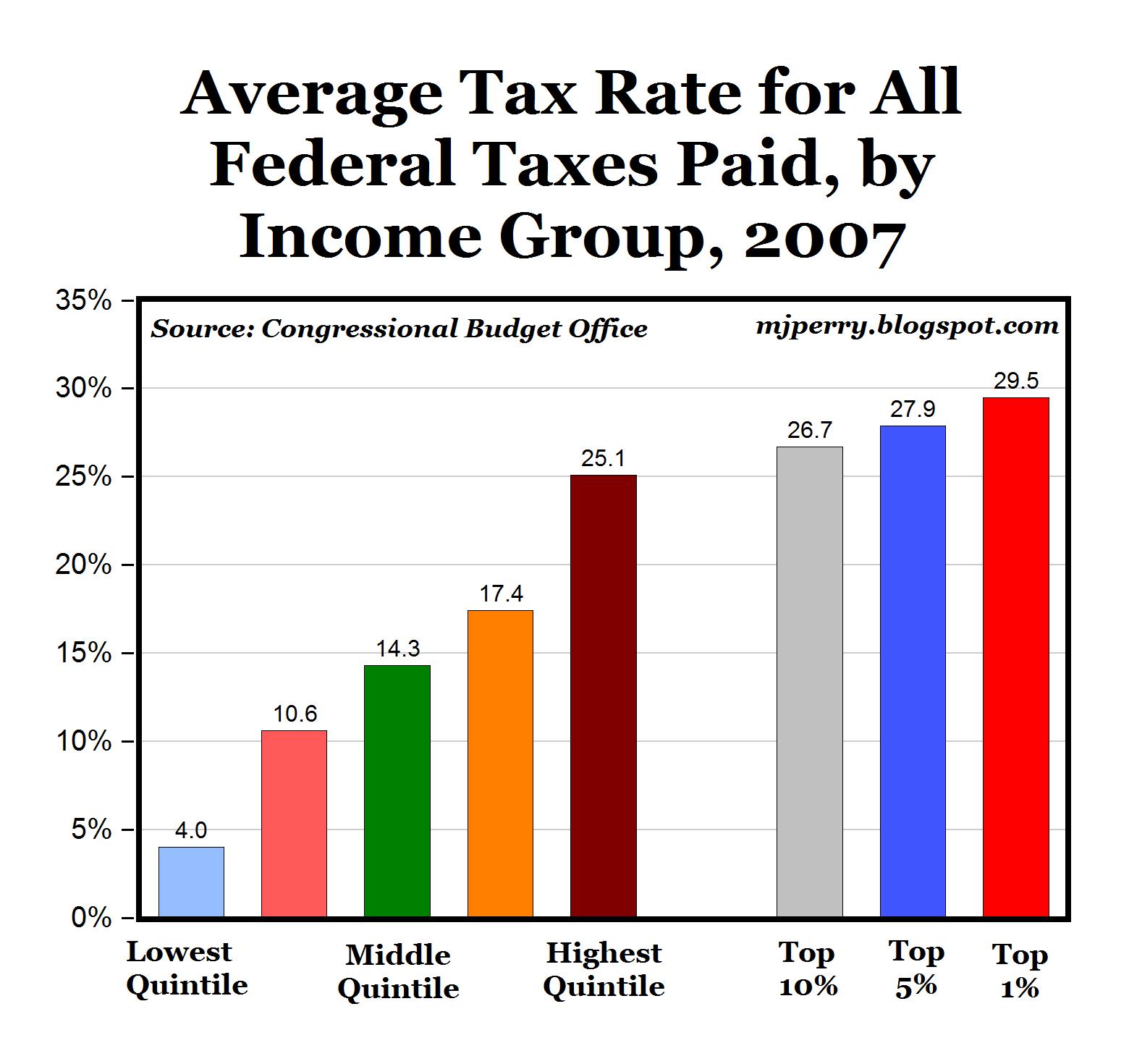
Image: mjperry.blogspot.com
Empowering Your Options Trading Journey: The Value of Informed Decision-Making
As you embark on your options trading expedition, a comprehensive understanding of tax implications is essential. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions, maximizing your financial outcomes while adhering to legal requirements. Remember, staying abreast of the latest tax laws, regulations, and market trends is crucial to navigating the ever-evolving landscape of options trading.
By embracing this guide’s insights, you gain an invaluable advantage in your options trading endeavors. The clarity and depth of the information provided equip you to confidently navigate the tax implications, allowing you to trade with greater confidence and optimize your financial strategies. Remember, education is the cornerstone of successful investing, enabling you to maximize returns while minimizing risks.






