In the bustling world of financial markets, options trading stands out as a mesmerizing labyrinth of opportunities and risks. An options contract, akin to a financial chameleon, grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified time frame. Options trading offers a tantalizing blend of strategic precision and the potential for exponential gains, captivating the minds of traders seeking to master this financial chess match.
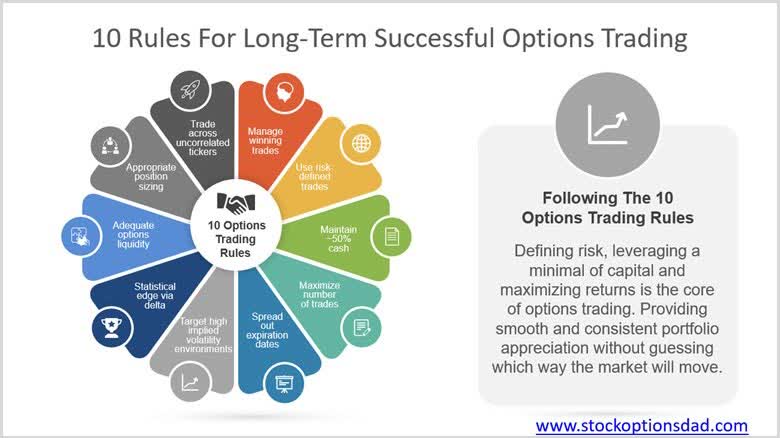
Image: seekingalpha.com
At its core, an options contract is a derivative instrument whose value is tethered to the price movements of the underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or even currencies. This intricate dance between the option and its underlying asset unlocks a realm of possibilities, from hedging risks to speculating on price fluctuations. Traders can choose between two primary types of options contracts: calls and puts. Call options grant the right to buy an underlying asset at a set price, while put options bestow the right to sell an underlying asset at a set price.
The allure of options trading lies in its versatility. Options can be employed as both offensive and defensive weapons in an investor’s financial arsenal. Whether seeking to bolster a portfolio with downside protection or to capitalize on anticipated price surges, options offer a tailored solution. The beauty of options trading lies in its adaptability to diverse investment strategies, empowering traders to mold the market to their vision.
To unravel the complexities of options trading, we must delve into the concept of time decay. As an options contract nears its expiration date, its value gradually diminishes. This steady erosion in value introduces an element of urgency, as traders must carefully calibrate their entry and exit points to maximize profits or minimize losses.
Furthermore, options trading introduces the notion of leverage, a double-edged sword that can magnify both gains and losses. By employing leverage, traders can control a larger position with a relatively smaller investment, potentially amplifying returns. However, this heightened leverage comes at a price, as losses can also be amplified, potentially eroding capital swiftly.
To navigate the treacherous waters of options trading, traders must arm themselves with a keen understanding of option pricing models. These models, such as the Black-Scholes model, factor in crucial variables like the underlying asset price, strike price, time to expiration, volatility, and risk-free interest rate to determine the fair value of an option contract. Mastery of these models empowers traders to make informed decisions, evaluating the potential risks and rewards with each trade.
The Mechanics of Options Trading
In the realm of options trading, the intricate interplay between key concepts orchestrates the symphony of market moves. To unravel this harmonious composition, let us dissect the fundamental mechanics that govern this financial dance.
At the heart of options trading lies the concept of the underlying asset. This is the financial instrument or commodity that forms the foundation upon which the option contract rests. Whether it be a stock, a bond, a commodity, or a currency, the underlying asset’s price fluctuations dictate the fortunes of the options contract.
Next in this intricate dance is the strike price, a pivotal determinant of an option’s value. This is the set price at which the holder of the option can buy (in the case of a call option) or sell (in the case of a put option) the underlying asset. The strike price serves as the epicenter around which the option’s value revolves.
Time, the inexorable force that governs all things, plays a crucial role in options trading. Each option contract carries a defined expiration date, marking the end of its trading life. The time value of an option, which represents the premium paid for the option, decays as the expiration date approaches. This time-sensitive nature adds an element of urgency to the trading process, as traders must carefully time their entries and exits to capture optimal returns.
Volatility, the ever-elusive measure of an asset’s price fluctuations, exerts a profound influence on the dynamics of options trading. High volatility, characterized by sharp price swings, often leads to higher option premiums, as investors are willing to pay more for the potential protection or profit opportunities that options offer. Conversely, low volatility, marked by relatively stable prices, typically results in lower option premiums.
Lastly, the risk-free interest rate, a benchmark against which all other interest rates are measured, adds another layer of complexity to the options trading equation. This rate influences the pricing of options, particularly long-term options, as it represents the opportunity cost of holding an option instead of investing in a risk-free asset.
These fundamental concepts intertwine to form the intricate tapestry of options trading. By mastering these mechanics, traders gain the tools to navigate this dynamic market landscape, crafting strategies that align with their risk tolerance and financial objectives.
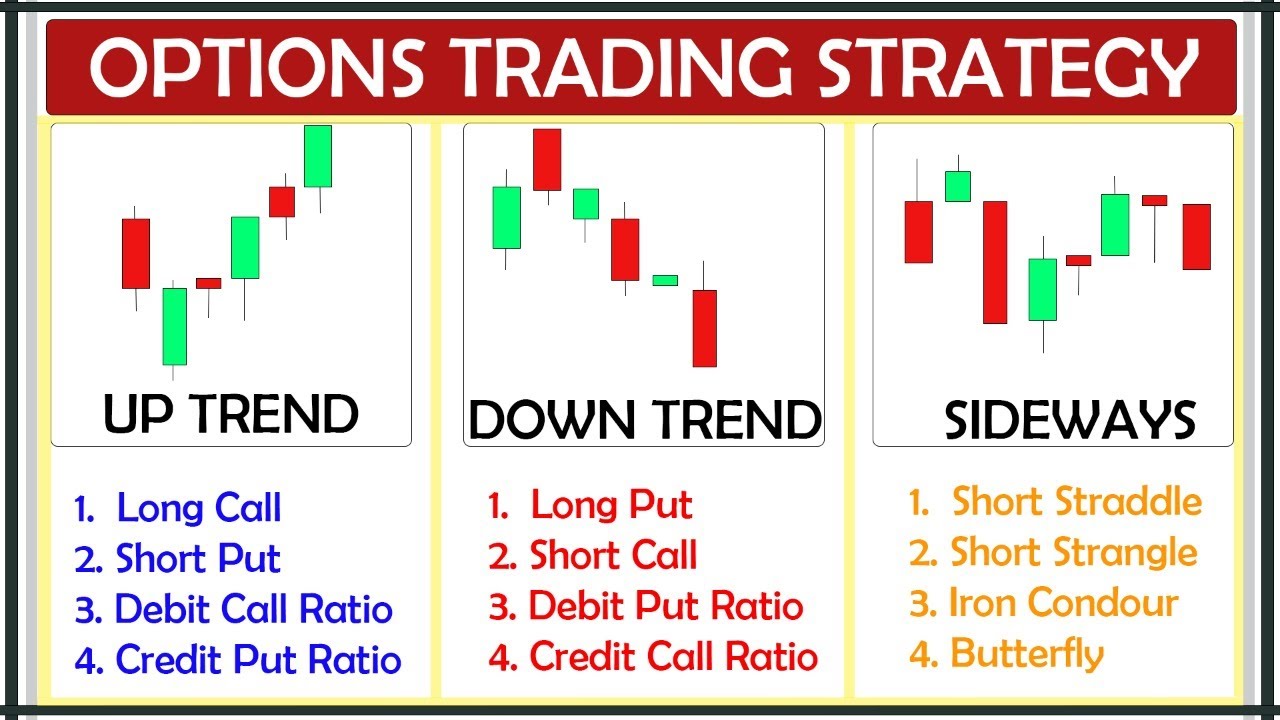
Image: www.youtube.com
What Are.Options Trading

Image: www.pinterest.com






