In the realm of investing, two distinct financial tools – Margin Trading and Options – stand as gateways to amplifying returns. However, understanding the intricacies and risks associated with these strategies is paramount before venturing into their transformative potentials. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of both methods, contrasting their mechanisms, advantages, and drawbacks to empower investors with informed decision-making.
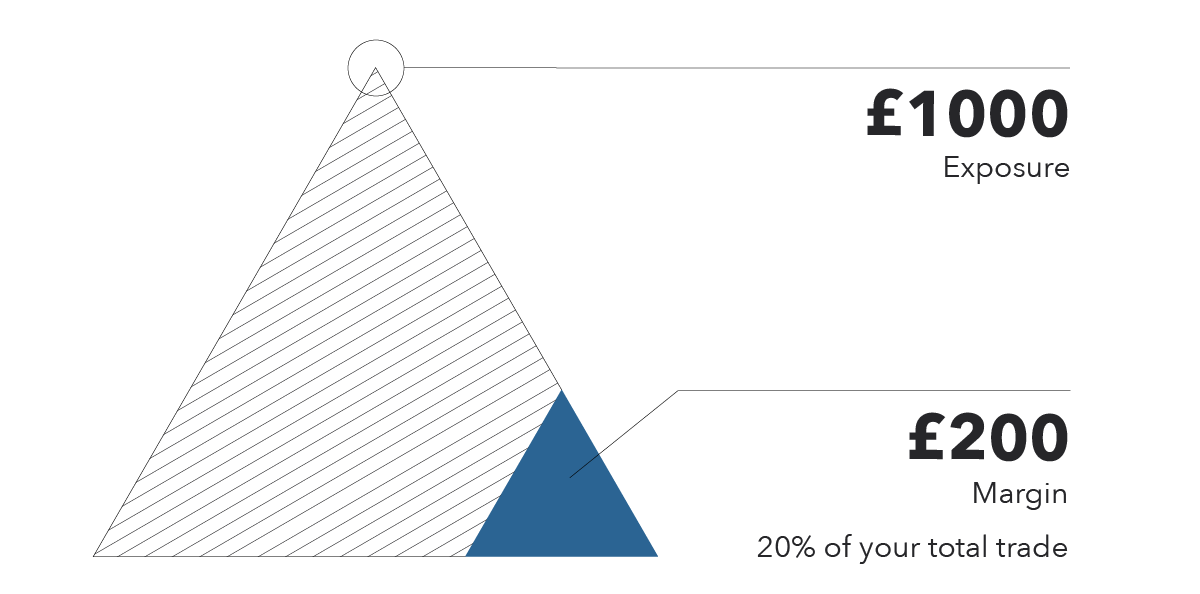
Image: balrajsufyaan.blogspot.com
Unveiling Margin Trading: Borrowing Power with Enhanced Returns
Simply put, Margin Trading empowers investors to borrow capital from their broker, enabling them to purchase a larger number of shares than their account balance alone would permit. By leveraging this borrowed capital, investors can amplify their gains if the underlying asset appreciates in value. Mathematically, their Return on Investment (ROI) becomes the sum of their original investment multiplied by their ROI if no leverage were used and the ROI on the borrowed amount.
Take, for instance, an investor with $5,000 in their account. Without margin trading, they could only purchase 100 shares of a stock priced at $50 each. However, with margin trading, they could potentially buy 200 shares using a 50% margin, which means borrowing an additional $5,000 from their broker. If the stock price rises to $60, the investor would have profited by $2,000 compared to only $1,000 without leverage.
Options: Diversifying Portfolios and Managing Risk
In contrast to Margin Trading, Options offer a distinct approach to financial maneuvering. These contracts provide investors with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a set price within a predetermined time frame. This flexibility allows investors to either capitalize on potential price movements or hedge against unfavorable market conditions.
Purchasing a Call Option, for example, bestows upon the investor the right to buy an underlying asset at a specified price, irrespective of its actual market price at the time of expiration. By exercising this option, the investor can potentially profit if the asset’s value surpasses the strike price. Conversely, selling a Put Option grants the investor the right to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price. This option can prove lucrative if the asset’s value depreciates below the strike price.
A Tale of Leverage: Amplification of Returns but Heightened Risk
As with any financial endeavor, both Margin Trading and Options carry inherent risks that investors must judiciously evaluate before committing their capital. Margin Trading, by virtue of its inherent leverage, can amplify both profits and losses. Should the underlying asset’s value decline, the investor may face the dreaded “Margin Call,” demanding immediate repayment of the borrowed funds. In extreme cases, the broker may liquidate the investor’s holdings to cover the loan, potentially resulting in substantial losses.
Options, too, are not immune to risk. Incorrectly predicting price movements or erroneous timing can lead to significant financial losses. The time decay in the value of options contracts can also diminish returns or even render them worthless if the underlying asset’s price fails to move as anticipated.

Image: www.fibogroup.com
Adapting Strategies to Investment Goals
Selecting the appropriate financial strategy hinges on a thorough understanding of one’s risk tolerance and investment goals. For investors seeking aggressive growth, Margin Trading can potentially magnify returns beyond what is achievable through unleveraged trading. However, those with a lower risk appetite should proceed with caution, fully comprehending the potential consequences of margin calls.
Options, on the other hand, offer a versatile tool for sophisticated investors. Through a multitude of strategies, experienced traders can manage risk and enhance returns by speculating on price movements or hedging against potential losses. Yet, it is crucial to recognize that options trading entails a higher degree of knowledge and experience to navigate the complexities of these contracts.
Margin Trading Vs Options
Conclusion: Navigating the Financial Landscape with Knowledge and Prudence
In the vast landscape of financial strategies, both Margin Trading and Options serve as powerful tools for astute investors. Margin Trading can amplify returns through leveraging borrowed capital, while Options provide flexibility for capitalizing on price movements or mitigating risk. However, unlocking the full potential of these strategies demands a thorough understanding of their mechanisms, risks, and suitability for one’s individual circumstances.
By wielding knowledge as their guiding force and exercising prudence in their financial endeavors, investors can harness the transformative power of Margin Trading and Options to achieve their investment aspirations. The path to financial success may be paved with complexity, but with informed decisions and a measured approach, investors can navigate the complexities with confidence, reaping the rewards that lie ahead.






