Options trading, the dynamic art of leveraging market volatility to secure financial gains, has gained immense popularity in India. However, as with any financial venture, it’s crucial to understand the tax implications associated with this exciting arena. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of taxes on options trading in India, empowering you to optimize your strategies and navigate the regulatory landscape.

Image: www.forbesindia.com
Understanding Options Trading and Taxation
Options, financial instruments that grant the holder the right (but not the obligation) to buy (call options) or sell (put options) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specified date (expiry date), offer a versatile means of profiting from market movements. The taxation of options trading in India adheres to specific principles, shaping the tax liability of traders.
Classifying Options: Capital Assets or Business Income
The tax treatment of options trading hinges upon the classification of the options as capital assets or business income. Options held for less than 12 months from their purchase are considered short-term capital assets, while those held for longer than 12 months qualify as long-term capital assets. Profits or losses from short-term capital assets are taxed at the applicable slab rate, whereas profits from long-term capital assets are subject to a concessional tax rate of 10%. Options trading that forms part of regular business activity, such as for hedging purposes, is classified as business income and taxed accordingly.
Taxation of Options Premiums
Options premiums, the price paid to acquire an option, are generally non-taxable. However, if an option expires worthless, the premium paid is treated as a loss and can be offset against other gains from options trading. Premiums received from selling options, on the other hand, are taxable as business income or capital gains, depending on the classification of the option as discussed earlier.

Image: thesisprinters.web.fc2.com
Taxation of Options Profits
Profits from options trading are taxed based on the nature of the option (call or put) and the underlying asset (equity, index, or commodity). Profits from trading equity options are taxed as capital gains, following the classification and tax rates mentioned above. Profits from trading index or commodity options are taxed at a flat rate of 30%.
Advance Tax and TDS Applicability
Traders in options are required to pay advance tax on an estimated basis, similar to other sources of income. Additionally, a 10% Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is applicable on settlement of option contracts, further adjusting the tax liability.
Tax Exemptions and Deductions
Certain exemptions and deductions may be available for options trading, including:
- Set-off of losses from options trading against profits from other similar transactions
- Exemption for agricultural commodity options used for hedging price risk
- Carry forward and set-off of losses from options trading in subsequent financial years
Taxes On Options Trading India
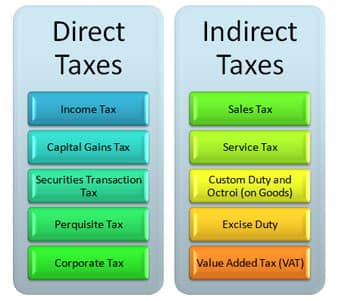
Image: 45.153.231.124
Conclusion
Navigating the tax implications of options trading in India requires a comprehensive understanding of the applicable laws and regulations. By familiarizing oneself with the classification of options, taxation of premiums and profits, advance tax and TDS provisions, and available exemptions, traders can optimize their stratégies, minimize their tax liability, and maximize their returns. Consulting with a tax professional is always advisable to ensure compliance and tailor tax planning to individual circumstances.






