Introduction
Options trading can often seem like a daunting concept for beginners in the financial markets. The intricate strategies and terminology associated with options can be intimidating, deterring many from exploring this powerful financial tool. However, with a simplified approach, beginners can navigate the world of options trading and harness its potential benefits. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of simple options trading strategies, empowering beginners to confidently step into the arena.
Options are financial contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as a stock, index, or commodity) at a specified price (known as the strike price) on or before a specified date (known as the expiration date). Options trading involves speculating on the future price movements of the underlying asset to profit from those price fluctuations.
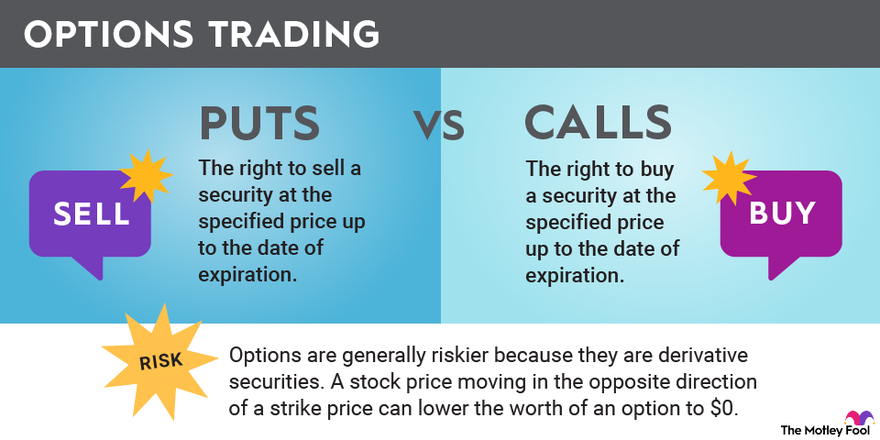
Image: www.fool.com
Types of Simple Options Strategies
Call Option: A call option gives the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date. Call options are employed when the trader anticipates an increase in the underlying asset’s price.
Put Option: A put option grants the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date. Put options are used when the trader expects a decrease in the underlying asset’s price.
Covered Call Strategy
This strategy is designed to generate income from an underlying asset the trader already owns, known as the underlying security. By selling a call option at a strike price higher than the current market price of the underlying security, the trader receives a premium for granting another trader the right to potentially buy their shares at the higher price. Should the underlying security’s price rise above the strike price, the call option will likely be exercised, obligating the trader to sell their shares at the strike price.
Protective Put Strategy
This strategy aims to protect the trader’s portfolio from potential losses arising from a decline in the underlying asset’s price. The trader buys a put option with a strike price below the current market price of the underlying security, paying a premium to acquire this protection. If the market takes a downturn, and the underlying security’s price falls below the strike price, the put option can be exercised, allowing the trader to sell the relevant shares at a preferable price, mitigating the impact of the market decline.

Image: stockforexstrategy.blogspot.com
Bull Call Spread
This strategy combines buying one call option at a lower strike price with simultaneously selling one call option at a higher strike price while ensuring both options have the same expiration date. Both options are based on the same underlying asset. The net premium paid by the trader is the difference in premiums between the two options. The strategy positions the trader to benefit from moderate increases in the underlying asset’s price while limiting both potential profits and losses.
Bear Put Spread
Similar to the bull call spread, this strategy involves buying a put option at a higher strike price and selling a put option at a lower strike price, both with the same underlying asset and expiration date. The trader stands to profit if the underlying asset experiences a significant decline in price. This strategy is intended to capitalize on substantial price drops.
Benefits of Simple Options Trading Strategies for Beginners
– Income Generation: Options can generate income through premiums, particularly suitable for covered call strategies.
– Risk Management: Options strategies such as the protective put provide downside protection, helping limit losses in unfavorable market conditions.
– Increased Leverage: Options offer greater leverage compared to directly purchasing the underlying asset, allowing for potentially significant returns with a smaller capital outlay.
– Adaptability: Options strategies can align with diverse market views and risk tolerance levels, catering to both bullish and bearish market outlooks.
– Simplicity: Simple options strategies are straightforward and accessible to beginners, avoiding overwhelming complexities.
Considerations for Simple Options Trading
– Time Decay: Options lose value over time, which means traders need to manage the time frame of their strategies carefully.
– Volatility: Market volatility significantly impacts options pricing, which can lead to substantial gains or losses.
– Risk Management: Options should be traded with defined risk parameters to prevent excessive losses in adverse market conditions.
– Broker Selection: Choose brokers offering options trading platforms and support suitable for beginners.
– Continuous Education: Stay abreast of ongoing market developments, strategies, and risk management techniques.
Simple Options Trading For Beginners Filetype Pdf

Image: www.pinterest.com
Conclusion
Simple options trading strategies provide an accessible entry point for beginners into the world of financial markets. By understanding the fundamentals of call and put options and utilizing basic strategies, beginners can unlock the potential benefits of options trading. However, it is crucial to proceed cautiously, manage risk prudently, and continually educate oneself to navigate the complexities of the options market successfully. With careful planning and execution, simple options trading strategies can enhance investment strategies and yield significant returns.






