Trading financial instruments offers a diverse landscape of opportunities to generate profits. Two prominent investment vehicles in this realm are options trading and CFD (Contract for Difference) trading. However, understanding their distinct characteristics is paramount before embarking on either path. This comprehensive guide delves into the depths of options trading versus CFDs, illuminating their mechanisms, advantages, and drawbacks to guide informed decisions.
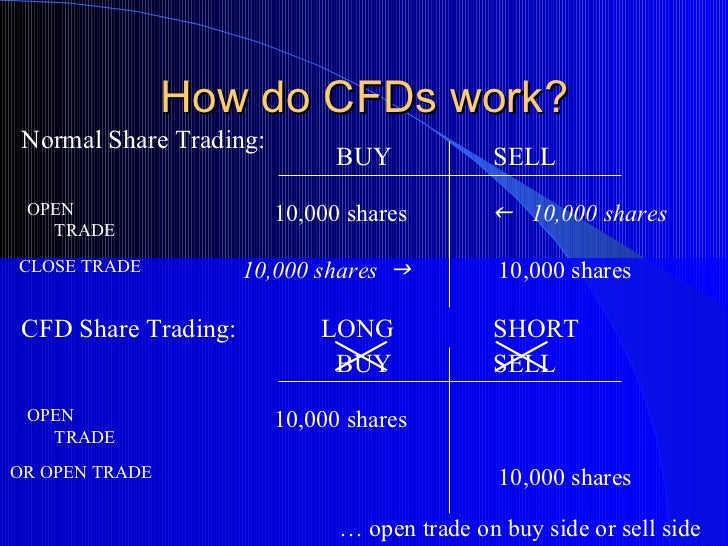
Image: klfx.blogspot.com
Navigating Options Trading: Understanding Contracts and Leverage
Options contracts bestow upon investors the right but not the obligation to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specified date (expiration date). Traders can utilize options to hedge risk, speculate on price movements, or generate income through option premiums.
One of the salient features of options trading lies in its leverage. By posting a small fraction of the underlying asset’s value as a margin, traders can control significant positions, potentially amplifying their profits. However, this leverage also magnifies potential losses, emphasizing the importance of diligent risk management strategies.
CFDs vs. Options: Exploring Key Distinctions
Stepping into the arena of CFDs reveals inherent differences from options trading. CFDs are contracts between two parties to exchange the difference between the opening and closing price of an underlying asset, irrespective of ownership. Unlike options, CFDs offer no right to buy or sell the underlying asset.
Another notable distinction lies in the settlement of positions. Options contracts have a finite lifespan, expiring on the specified date. In contrast, CFDs can be held indefinitely, allowing traders to maintain positions for as long as they deem fit. This extended flexibility may appeal to investors seeking longer-term market exposure.
Harnessing the Advantages of Options Trading
Options trading presents several benefits that resonate with traders of all levels. For risk-averse investors, options serve as a protective mechanism against adverse price fluctuations, allowing them to hedge their underlying asset holdings.
Speculators, on the other hand, leverage options to capitalize on predicted price movements. By correctly anticipating market trends, traders can generate substantial profits through well-executed options strategies.
Moreover, options trading offers a high degree of flexibility, empowering investors to tailor strategies to their individual risk tolerance and investment goals. Whether seeking income generation, risk mitigation, or speculative opportunities, options trading provides a versatile platform for financial maneuvers.

Image: www.manners-biz.com
Comprehending CFDs: Leveraging the Benefits
CFDs, with their unique characteristics, also offer a range of advantages to traders. Their ability to go long or short on an underlying asset without ownership simplifies market navigation and expands profit potential in both rising and falling markets.
The extended flexibility of CFDs grants traders the freedom to hold positions indefinitely, enabling them to ride market trends for potentially significant long-term gains. Additionally, CFD trading eliminates the need for physical delivery or settlement, reducing transaction complexities.
Weighing the Pitfalls: Disadvantages of Options Trading and CFDs
Despite the merits of both options trading and CFDs, it is imperative to acknowledge their potential drawbacks. Options trading involves the decay of option premiums over time, known as theta decay, which can erode profits if trades are not executed swiftly or held for extended periods.
Furthermore, options trading may not be suitable for all investors, especially those with limited trading experience or low risk tolerance. The complexities of options strategies and the potential for substantial losses warrant careful consideration before engaging in this market segment.
Conversely, CFDs are not exempt from their own set of challenges. The unregulated nature of CFD trading in certain jurisdictions exposes investors to potential risks associated with unscrupulous brokers or market manipulation.
Margin trading inherent in CFDs magnifies both profits and losses, amplifying the significance of disciplined risk management practices. Additionally, CFDs may incur overnight financing charges, which can accumulate over time and impact profitability.
Selecting the Ideal Investment Vehicle: Options Trading vs. CFDs
The choice between options trading and CFDs hinges on the individual investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and trading style. For risk-averse investors seeking hedging strategies or income generation, options trading presents a viable option.
Speculators and experienced traders may find CFDs more suitable, given their flexibility and potential for long-term profit maximization. However, careful consideration of potential risks and diligent risk management strategies are paramount in either investment endeavor.
Options Trading Vs Cfd
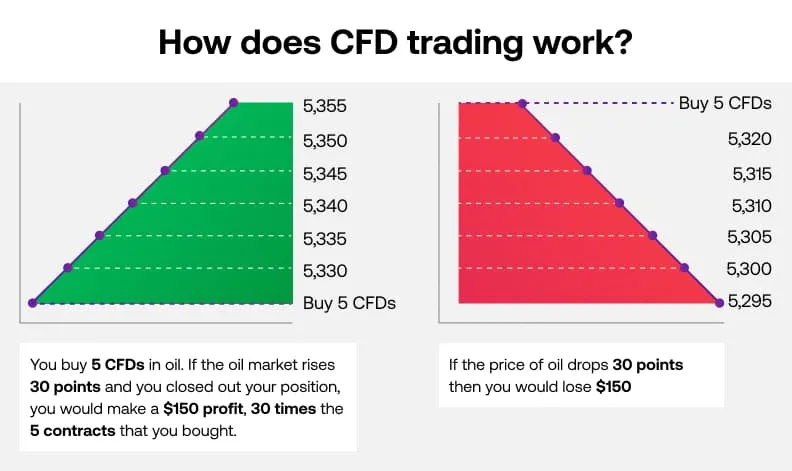
Image: www.cityindex.com
Conclusion
The realm of financial trading encompasses a diverse tapestry of instruments, each carrying its unique advantages and drawbacks. Options trading and CFDs stand out as popular investment vehicles, offering distinct mechanisms, benefits, and risks. By thoroughly comprehending their nuances and aligning investment strategies with individual risk tolerance and goals, investors can harness these financial instruments to navigate markets and pursue their financial objectives.






