The world of financial trading offers a myriad of opportunities for investors seeking to capitalize on market fluctuations. Among the most popular instruments are contracts for difference (CFDs) and options. Both CFDs and options provide traders with unique advantages and risks, making it crucial to understand their key differences to make informed investment decisions.
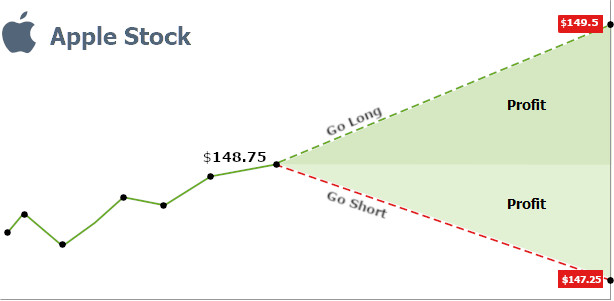
Image: www.ifcm.co.uk
Defining CFDs and Options
A contract for difference (CFD) is a financial instrument that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of an underlying asset without owning the asset itself. When entering a CFD contract, the trader agrees to exchange the difference between the opening and closing prices of the underlying asset. CFDs can be traded on a wide range of financial instruments, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies.
An option, on the other hand, is a derivative contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (in the case of a call option) or sell (in the case of a put option) an underlying asset at a specified price (known as the strike price) on or before a specified date (known as the expiration date). The buyer of an option pays a premium to the seller in exchange for this right.
Key Differences:
1. Ownership of the Underlying Asset: CFDs do not involve ownership of the underlying asset, while options give the buyer the option to purchase or sell it at the strike price.
2. Leverage and Margin: CFDs typically offer leverage, allowing traders to control a larger notional value of the underlying asset with a smaller initial investment. Options, on the other hand, usually do not provide leverage.
3. Expiration Dates: CFDs do not have expiration dates, while options have predetermined expiration dates, beyond which they become worthless if not exercised.
4. Settlement: CFDs are cash-settled contracts, while options can be cash-settled or physically settled (involving the delivery of the underlying asset).
5. Risk and Reward: CFDs carry the risk of potentially unlimited losses as there is no maximum loss limit. Options, however, have a limited profit potential, as profits are capped by the difference between the option premium and the underlying asset’s price movement.
Advantages of CFDs:
- Leverage: CFDs allow traders to gain greater exposure to the underlying asset, potentially amplifying their profits (or losses).
- Flexibility: CFDs can be traded on a wide range of markets, including those that may not be accessible directly.
- Short-selling: CFDs enable traders to take a short position (betting on the decline of an asset’s price), while this may not be possible with traditional stock ownership.
- Cost-effective: CFD trading fees can be lower than those of options trading, making it more cost-effective for smaller trades.

Image: rwrant.co.za
Advantages of Options:
- Limited Risk: Options offer limited risk as the maximum loss is capped by the option premium paid.
- Versatility: Options can be used to create sophisticated trading strategies, allowing traders to hedge risks, speculate, and generate income.
- Income generation: Options can be bought or sold to generate income from market volatility or time decay.
- Expiration Dates: The finite nature of options can help traders manage risk by setting clear profit and loss limits.
Cfd Vs Options Trading
Conclusion:
Whether CFDs or options are a more suitable choice for traders depends on their individual trading objectives, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. CFDs offer greater leverage and flexibility, while options provide more controlled risk and the potential for income generation. By carefully considering the differences between these two instruments, traders can make informed decisions that align with their specific trading goals.






