Options trading holds the allure of leveraging potential financial gains. This tutorial will lead you through the intricacies of options trading, helping you understand its nuances. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced trader, this guide aims to simplify the concepts and enhance your knowledge.
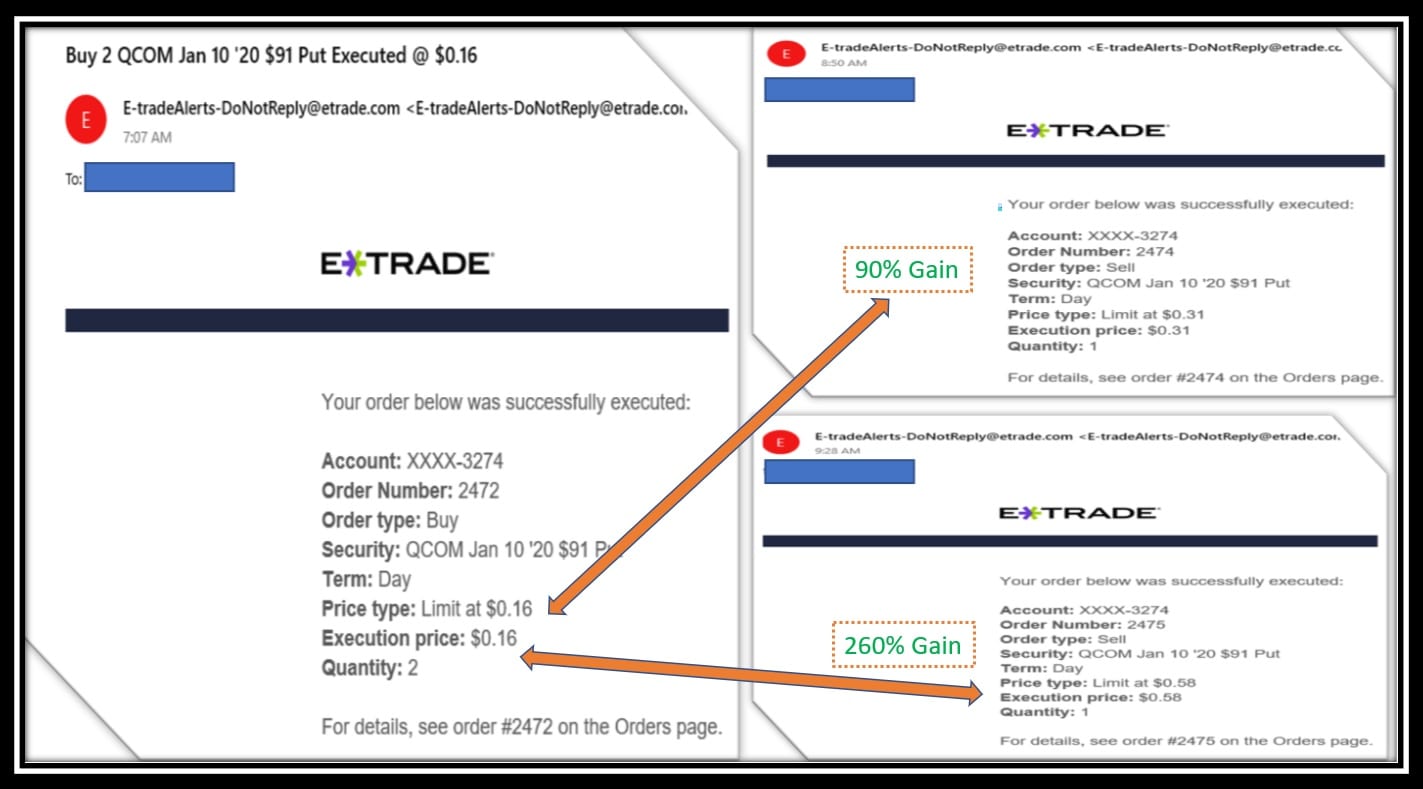
Image: successfultradings.com
Today, options trading is an increasingly popular way of investing and hedging. By comprehending this financial tool, you’ll be able to navigate market uncertainties and make informed decisions.
Understanding Options Trading: The Fundamentals
Options trading involves contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) on or before a set date (expiration date). As a buyer, you have the flexibility to exercise your right or let the option expire worthless.
The seller (writer) of the option has the corresponding obligation. They must facilitate the sale or purchase of the underlying asset if the buyer chooses to exercise their right. For this commitment, the writer receives a premium, the price paid by the buyer for the option contract.
Anatomy of an Option Contract
Each option contract is characterized by specific parameters:
- Type: Call or put, denoting the option to buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Strike Price: The agreed-upon price for the transaction if the option is exercised.
- Expiration Date: The set date by which the option can be exercised.
- Premium: The price the buyer pays to the seller for the option contract.
- Underlying Asset: The security or commodity subject to the option contract.
Deciphering Option Pricing
Option contracts are not static; their value changes based on various factors:
- Underlying Asset Price: The price of the underlying asset directly impacts the option’s value. An increase in the price usually increases the value of a call option and decreases the value of a put option.
- Time to Expiration: The closer an option gets to its expiration date, the more its time value decays. This decay is more significant for out-of-the-money options.
- Volatility: Higher volatility in the underlying asset tends to increase the option’s premium.
- Interest Rates: Interest rate changes can influence the value of options, especially long-term options.
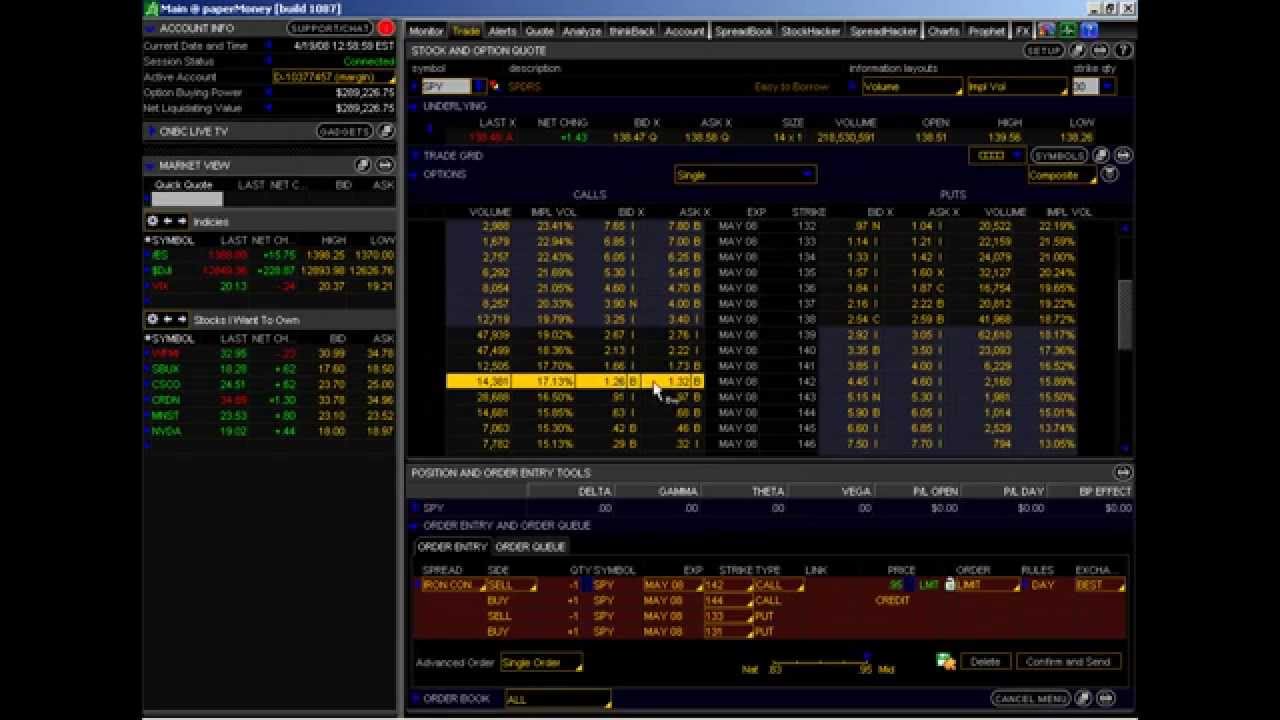
Image: listwithsage.com
Mastering Options Trading Strategies
Options trading offers a wide spectrum of strategies, cater to diverse investment goals and appetite for risk:
- Covered Call: A strategy where a trader sells a call option while owning the underlying asset, aiming to generate income.
- Protective Put: A strategy where a trader buys a put option to hedge the potential downside risk of an existing portfolio.
- Long Call: A strategy where a trader buys a call option with the expectation of the underlying asset price rising.
- Short Put: A strategy where a trader sells a put option with the expectation of the underlying asset price rising or staying steady.
- Collar: A strategy combining a long put with a short call to limit the potential loss and income.
Expert Tips and Advice for Options Trading Success
Become a more empowered options trader by following these expert tips:
- Educate Yourself: Continuously expand your knowledge of options trading concepts and strategies. Attend webinars, read books, and engage with industry experts.
- Practice with Paper Trading: Before risking real capital, gain experience and test your strategies with paper trading platforms that simulate real-world markets.
- Manage Your Risk: Carefully assess and limit your risk exposure. Use stop-loss orders and avoid overleveraging your positions.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends, economic data, and company announcements that may impact the value of your options.
Frequently Asked Questions about Options Trading
Q: What are the benefits of options trading?
A: Options trading can offer opportunities for income generation, hedging, and portfolio diversification.
Q: What are the risks involved in options trading?
A: Options trading involves substantial risk. Options can expire worthless, resulting in a loss of the premium paid.
Q: What is the difference between call and put options?
A: Call options give the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset, while put options give the buyer the right to sell.
Options Trading Tutorial Video

Image: www.hahn-tech.com
Conclusion
Options trading can be a powerful financial tool if approached with knowledge and strategy. This guide has furnished you with a comprehensive framework to understand its mechanics and explore its possibilities. Remember, the universe of options trading is ever-evolving; stay curious, continue learning, and practice prudent risk management to navigate this dynamic field.
Embark on your options trading journey with confidence, knowing that the knowledge gained from this guide will empower your decision-making and enhance your financial acumen. We encourage you to explore further, engage with industry professionals, and continue the pursuit of becoming a successful options trader.






