In the intricate world of financial markets, options trading stands as a powerful strategy for investors seeking to harness the volatility of underlying assets. At the heart of this strategy lies the enigmatic concept of the underlying price, a pivotal determinant of option value. Embark on a captivating journey as we delve into the intricate details of options trading, exploring the fundamental principles, real-world applications, and the profound impact of the underlying price on this captivating financial instrument.

Image: www.samco.in
Understanding Options Trading: A Gateway to Opportunity
Options trading, a derivative strategy, empowers investors with a unique opportunity to speculate on the future price movements of an underlying asset without owning it outright. These versatile contracts grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset at a predefined price on or before a predetermined date. By meticulously studying market dynamics and harnessing predictive analytics, investors can make informed decisions about whether to exercise their option or not, creating potential for lucrative returns while mitigating risk.
The Underlying Price: A Catalyst for Option Value
The price of the underlying asset, whether it be a stock, commodity, or currency, plays a pivotal role in determining the value of an option. This relationship hinges on the type of option being traded. Call options, which grant the holder the right to buy the underlying asset, tend to appreciate in value as the underlying price rises. Conversely, put options, which bestow the right to sell the underlying asset, gain value as the underlying price declines. Understanding this fundamental correlation empowers investors to make strategic decisions about option selection, positioning for potential profit from favorable price movements.
As the underlying price fluctuates, so too does the intrinsic value of an option. Intrinsic value represents the difference between the underlying price and the strike price, the predetermined price at which the option can be exercised. When an option is in-the-money, meaning its intrinsic value is positive, it holds both intrinsic and time value. Conversely, when an option is out-of-the-money, with negative intrinsic value, its value is solely derived from time value, which diminishes as the expiration date approaches.
Navigating the Intricacies of Time Value: A Ticking Clock
In the realm of options trading, time is of the essence. Options have a finite lifespan, with each contract expiring on a specific date. As this expiration date nears, the time value of an option gradually erodes, with its rate of decay accelerating closer to maturity. This temporal constraint adds a dynamic element to options trading, compelling investors to carefully consider the time decay factor when evaluating potential investments.
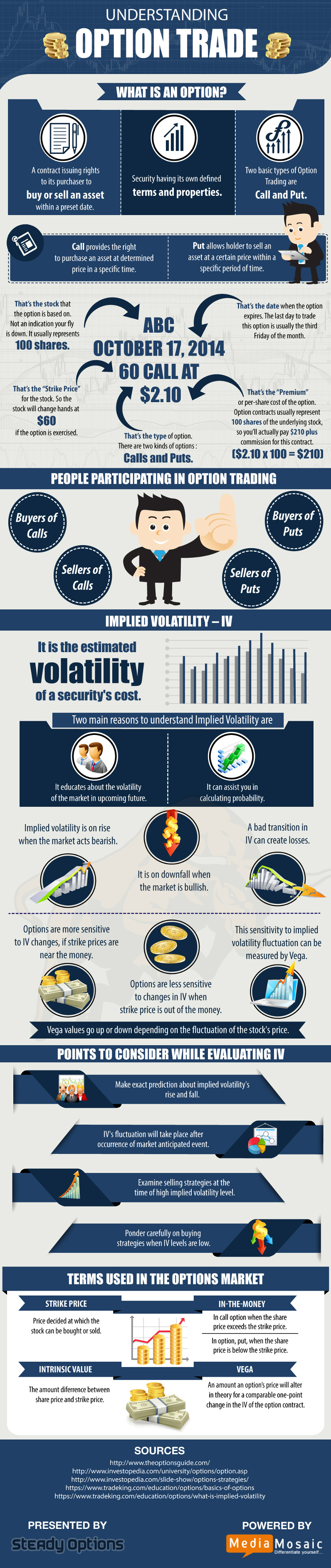
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
Real-World Applications: Unlocking Options Trading’s Power
Options trading finds widespread application in a myriad of financial scenarios. Speculators leverage options to capitalize on predicted price movements, while hedgers utilize options to mitigate portfolio risk. Income-oriented investors can employ covered call strategies to generate additional income, while sophisticated traders engage in complex multi-leg option strategies to optimize returns and manage risk exposure.
Options Trading Price Of The Underlying

Image: purepowerpicks.com
Conclusion: Empowering Investors through Options Trading
By mastering the intricacies of options trading and comprehending the profound impact of the underlying price, investors gain a potent financial tool that can enhance their portfolio strategies. Whether seeking speculative returns, hedging against risk, or pursuing income generation, options trading offers a versatile path to financial success. As the markets continue to evolve, investors who embrace continuous learning and hone their trading skills will be well-positioned to leverage the power of options trading for their financial benefit.






