Introduction
In the realm of financial markets, options trading presents a captivating blend of risk and reward. At the heart of this complex yet lucrative endeavor lies the concept of intrinsic value, a fundamental tenet that forms the cornerstone of calculating the potential profitability of an options contract.
Intrinsic value quantifies the inherent worth of an option based on the difference between the underlying asset’s current market price and the option’s strike price. Understanding this critical metric is tantamount to maximizing your options trading strategy’s effectiveness, enabling you to navigate the ever-fluctuating market landscape with confidence.

Image: www.simplertrading.com
Strikes, Options, and the Anatomy of Intrinsic Value
Delving into the mechanics of intrinsic value, we encounter two fundamental elements: strike prices and option types. Strike price represents the predetermined price at which the underlying asset can be bought (call option) or sold (put option).
Call options, granting the holder the right to buy the underlying asset, possess intrinsic value only when the market price exceeds the strike price. Conversely, put options, conferring the right to sell the underlying asset, hold intrinsic value when the market price dips below the strike price.
Calculating Intrinsic Value
The formula for calculating intrinsic value is straightforward, yet profound in its implications:
Call Option Intrinsic Value: Market Price – Strike Price
Put Option Intrinsic Value: Strike Price – Market Price
By meticulously applying this formula, you can ascertain the exact amount of premium an option is worth based on its intrinsic value at any given time.
Expiration and Intrinsic Value: A Matter of Time
Intrinsic value is not a static entity; its magnitude ebbs and flows in concert with time’s passage. As options approach their expiration date, their intrinsic value undergoes a dramatic transformation.
Call options tend to lose intrinsic value as expiration nears, while put options typically gain intrinsic value. This temporal dance underscores the time-sensitive nature of options trading, amplifying the importance of strategic execution.

Image: danilacalise.blogspot.com
Trading Strategies that Leverage Intrinsic Value
- Buying Deep In-the-Money Options: These options possess significant intrinsic value, making them ideal for capturing sizable profits if the underlying asset’s price moves favorably. However, they command a higher premium, demanding greater precision in market timing.
- Buying At-the-Money Options: At-the-money options, with intrinsic value hovering around zero, offer a balance of potential reward and risk. Their lower premium makes them more forgiving of timing errors, but their profit potential is more modest.
- Selling Out-of-the-Money Options: Out-of-the-money options, devoid of intrinsic value, involve selling the option’s right to someone else. This strategy can generate income through premium collection, but it carries the risk of unlimited losses if the underlying asset’s price moves against you.
Options Trading Intrinsic Value
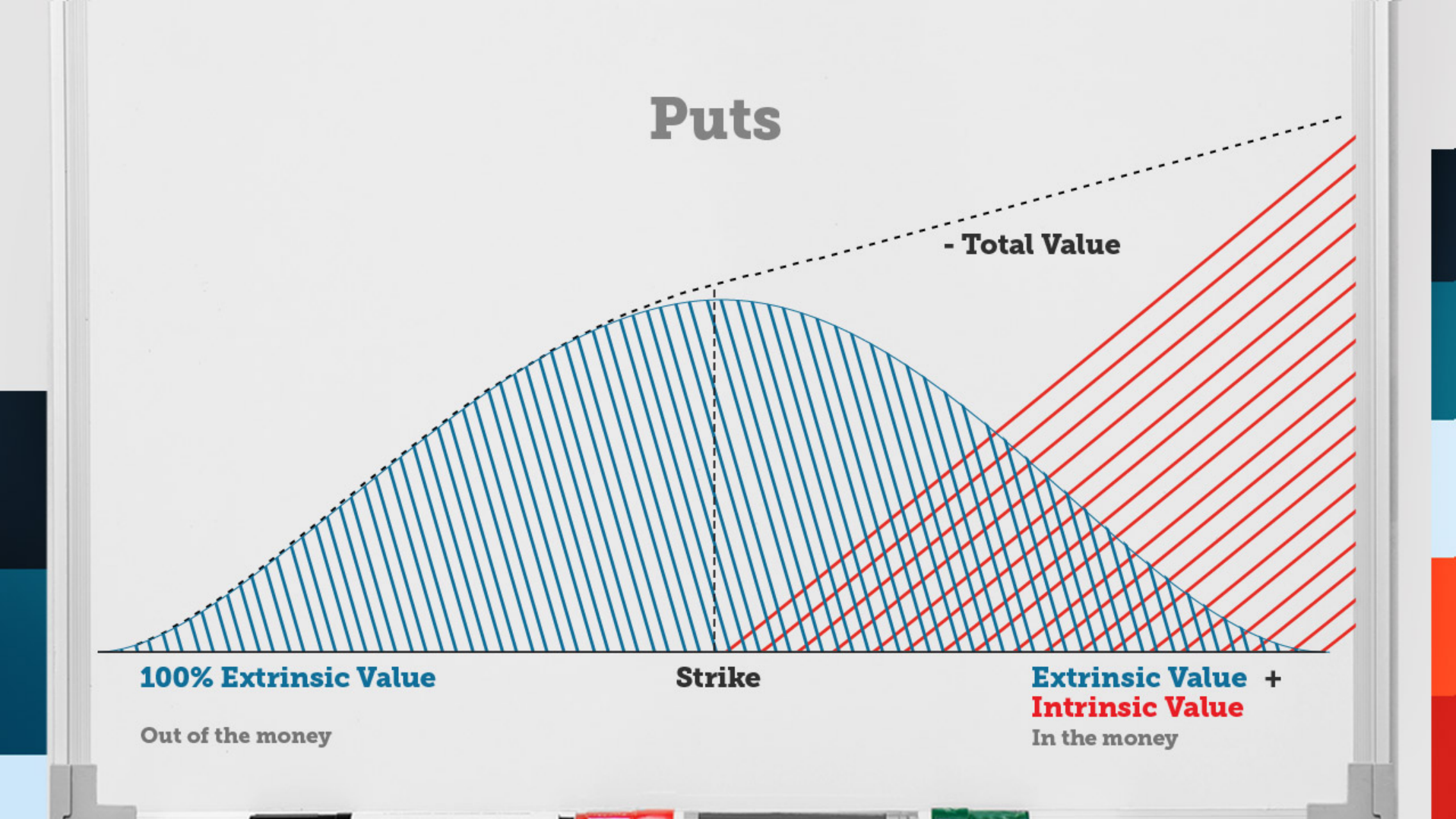
Image: www.tastylive.com
Conclusion
Intrinsic value is the quintessential foundation of options trading, providing a tangible measure of an option’s inherent worth and guiding traders in making informed decisions. By mastering the intricacies of intrinsic value, traders can harness its power to enhance their strategies and maximize their chances of success in the dynamic and ever-evolving financial markets.






