Understanding the Basics
In the realm of finance, options trading stands as a multifaceted and versatile financial instrument that empowers investors with the opportunity to hedge risk, enhance returns, and speculate on the price direction of underlying assets. Fundamental to grasping the intricacies of options trading lies the distinction between call and put options. A call option grants the buyer the right (but not the obligation) to purchase the underlying asset at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a specified date (the expiration date). Conversely, a put option confers upon the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
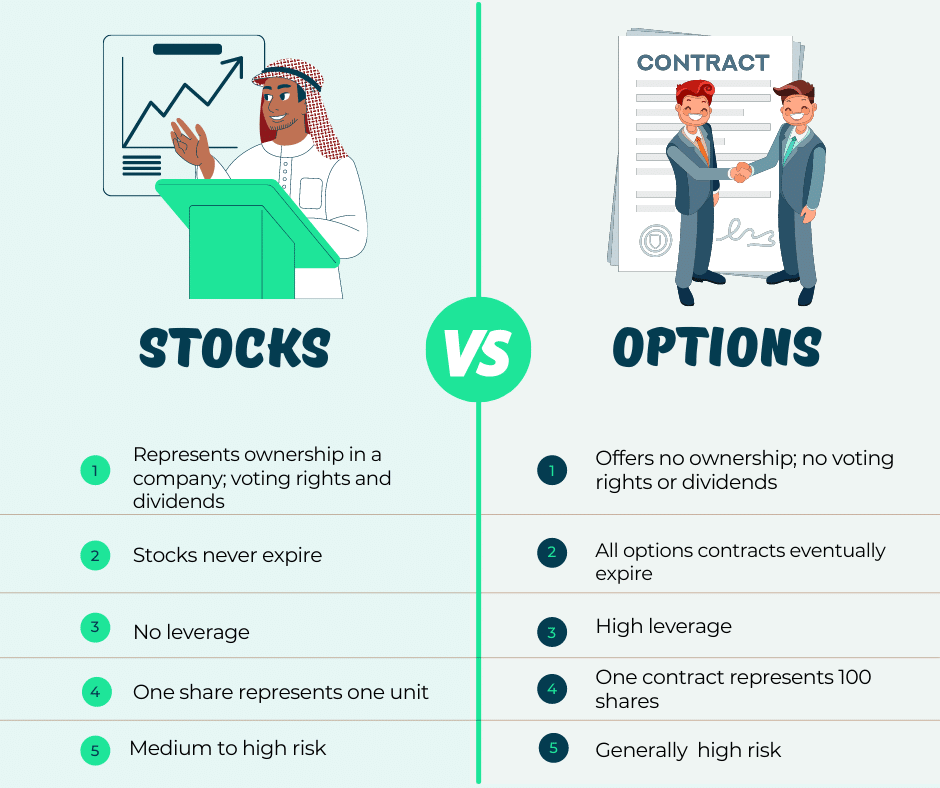
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Factors Influencing Option Pricing
Understanding the factors that influence the pricing of options is crucial for savvy trading decisions. Predominant among these factors is the underlying asset’s current price relative to the strike price. The closer the underlying asset’s price is to the strike price, the more valuable the option. Moreover, the amount of time until the expiration date impacts option pricing. Options with longer time until expiration generally cost more than those with shorter time frames. Volatility, a measure of the underlying asset’s price fluctuations, also exerts a significant influence. Options on more volatile assets tend to be more expensive than those on less volatile assets.
Call vs. Put Options: Understanding the Applications
The choice between call and put options hinges on the investor’s anticipations regarding the underlying asset’s price movements. Call options are employed when investors expect the underlying asset’s price to rise, as they provide the right to purchase the asset at a fixed price in the future. Conversely, put options are utilized when investors foresee a decline in the underlying asset’s price.
Options Trading Strategies
The versatility of options trading allows for a wide range of strategies tailored to diverse investment objectives and risk tolerances. Some popular options strategies include covered calls, protective puts, call spreads, and put spreads. Covered calls involve selling a call option while owning the underlying asset, generating income while potentially limiting upside potential. Protective puts provide downside protection by purchasing a put option while holding the underlying asset. Call and put spreads involve buying and selling options at different strike prices, creating a defined risk and reward profile.

Image: www.investchannels.com
Options Trading Financial Product

Image: www.pinterest.com
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Options Trading
Mastering options trading requires a comprehensive understanding of the concepts, factors, and strategies involved. By thoroughly researching and carefully evaluating options, investors can harness their power to enhance their investment portfolios. Whether hedging risk, generating income, or speculating on market movements, options trading offers a sophisticated tool for informed investors seeking financial advantage.






