Introduction
The world of finance is multifaceted and constantly evolving, offering a range of investment options that cater to diverse financial goals. Among the various investment instruments, options trading has gained considerable popularity in recent years. If you’re eager to delve into the realm of options trading, this comprehensive guide will provide you with the fundamental knowledge and insights necessary to understand this exciting and potentially lucrative market.

Image: tradebrains.in
Understanding Options
An option contract is a financial instrument that grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specified date (expiration date). This flexibility provides traders with the opportunity to speculate on the future price movements of the underlying asset without the obligation to complete the transaction.
Types of Options
There are two primary types of options: call options and put options. Call options give the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price, while put options grant the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. Additionally, options can be categorized based on their expiration date: American options can be exercised anytime before their expiration date, whereas European options can only be exercised on their expiration date.
Mechanics of Options Trading
To initiate an options trade, the trader purchases an options contract from an options exchange. The premium paid for the option represents the cost of acquiring the contract. If the underlying asset’s price moves in a favorable direction, the value of the option contract increases, and the trader can potentially sell it for a profit. However, if the underlying asset’s price moves against the trader’s position, the value of the option contract decreases, resulting in a potential loss.
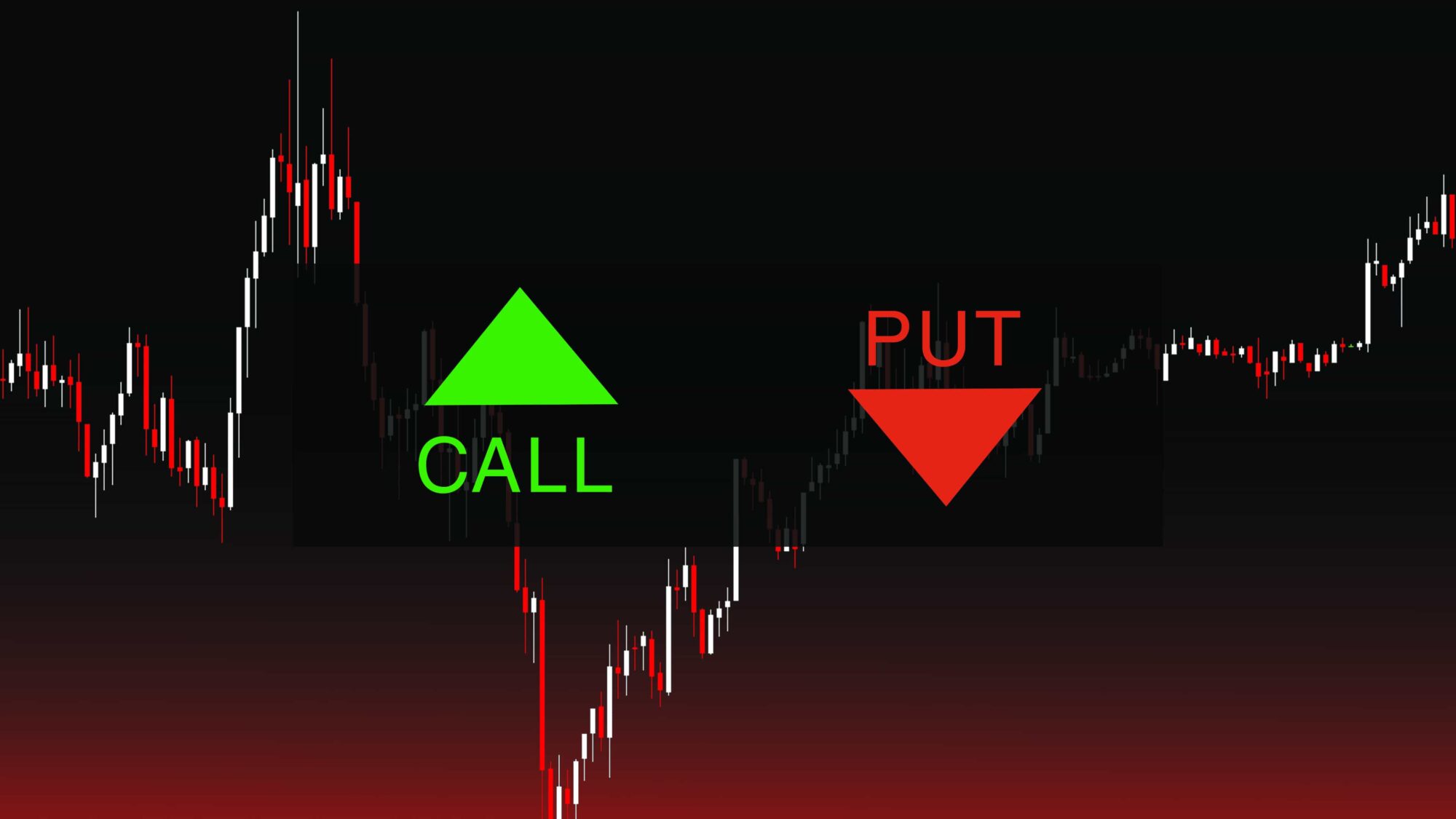
Image: www.asktraders.com
Leverage and Risk in Options
Options trading offers significant leverage, as a relatively small investment in an options contract can control a much larger amount of the underlying asset. This leverage can amplify potential profits but also magnifies potential losses. Understanding and managing risk is paramount in options trading, as traders should only commit capital they can afford to lose.
Tips and Expert Advice for Options Trading
Embarking on options trading requires a combination of knowledge, skill, and strategic planning. Here are some tips and expert advice to enhance your trading experience.
- Conduct Thorough Research: Before entering any options trade, thoroughly research the underlying asset and market conditions. Understand the potential risks and rewards associated with the trade.
- Manage Risk Prudently: Develop a robust risk management strategy that involves setting stop-loss orders, diversifying your portfolio, and using appropriate position sizing techniques.
- Utilize Technical Analysis: Technical analysis tools can provide valuable insights into market trends and help identify potential trading opportunities.
- Stay Updated on Market News and Events: Monitor financial news and events that may impact the value of the underlying asset and adjust your trading strategy accordingly.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If necessary, consider consulting with a financial advisor or broker with expertise in options trading to obtain personalized guidance and support.
Frequently Asked Questions About Options Trading
Here are a few common questions related to options trading, along with concise and informative answers:
Q: What is the difference between a bull call spread and a bear put spread?
A: A bull call spread involves buying a call option at a higher strike price and simultaneously selling a call option at a lower strike price. A bear put spread involves selling a put option at a lower strike price and simultaneously buying a put option at a higher strike price. The former strategy benefits from a rise in the underlying asset’s price, while the latter strategy benefits from a decline in the underlying asset’s price.
Q: Can I lose more money than I invested in options trading?
A: Yes, in options trading, the potential loss is limited to the premium paid for the option contract. However, if the underlying asset’s price moves significantly against the trader’s position, they could lose the entire investment and potentially incur additional losses.
Q: What are the tax implications of options trading?
A: Options trading is subject to taxation, and the specific tax treatment varies depending on the holding period and other factors. Consult with a tax professional for specific guidance on the tax implications of your options trades.
Options Trading Basic
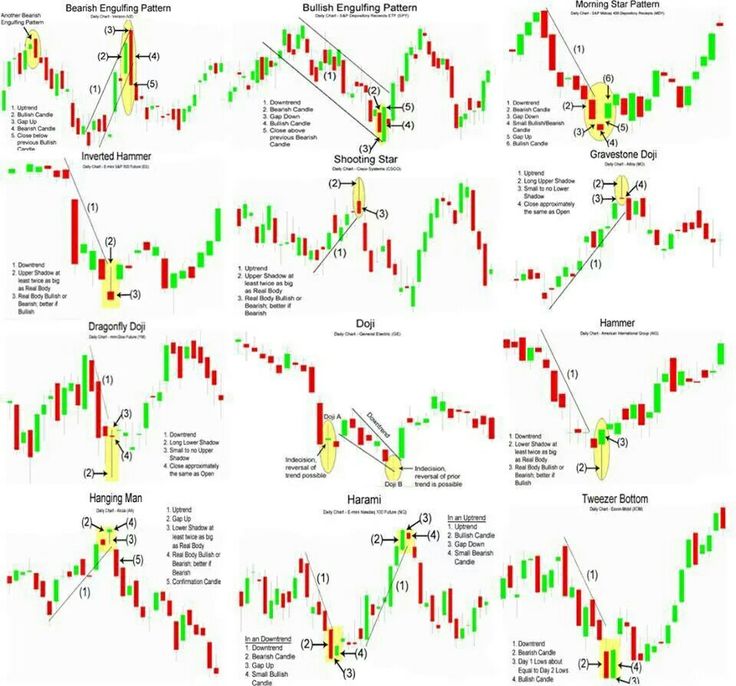
Image: ritholtz.com
Conclusion
Options trading provides a dynamic and potentially lucrative avenue for savvy investors to enhance their financial portfolios. However, it’s essential to approach this market with a solid understanding of its mechanics, risks, and potential rewards. By implementing sound trading strategies, managing risk effectively, and staying abreast of market trends, traders can navigate the complexities of options trading and increase their chances of achieving success.
Would you like to learn more about options trading and explore the opportunities it presents?






