Introduction
Options trading may seem like a daunting concept, but it can be an effective tool for supplementing your investment portfolio. Options provide traders with the flexibility to leverage market movements and potentially generate significant收益, even in volatile markets. This beginner’s guide will break down the fundamentals of options trading, helping you understand the basics and enabling you to make informed investment decisions.

Image: www.barnesandnoble.com
Understanding Options
Options are financial instruments that derive their value from an underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies. They grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specified date (expiration date). This flexibility allows traders to tailor their investment strategies to different market scenarios and risk preferences.
Types of Options
There are two main types of options:
- Call Options: Give the holder the right to purchase the underlying asset at the strike price. They are typically used when traders expect the asset’s price to rise above the strike price.
- Put Options: Grant the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. Traders use them when they anticipate the asset’s price to fall below the strike price.
Call Option Example
Suppose Apple stock is trading at $150 per share, and you believe its price will increase. You could purchase a call option with a strike price of $160 that expires in one month. If Apple’s stock price rises to $170 within that month, you have the right to buy the stock at $160 and sell it at the market price of $170, generating a profit of $10 per share (excluding option premium and trading fees).

Image: www.linkedin.com
Put Option Example
Conversely, if you believe Apple’s stock price will decline, you could purchase a put option with a strike price of $140. If the stock price falls to $130, you have the right to sell your shares at $140, even though the market price is lower, allowing you to limit your losses.
Key Concepts in Options Trading
- Option Premium: The price of an option that is paid to the seller by the buyer.
- Breakeven Price: The price at which the option holder will neither gain nor lose money.
- Time Value: The portion of the option premium that represents the remaining time until expiration.
- Volatility: A measure of the expected price fluctuations of the underlying asset.
- Leverage: The ability of options to control a larger position in the underlying asset with less capital.
Strategies for Options Trading
There are numerous strategies that traders can employ using options. Some common approaches include:
- Covered Call: Selling a call option against underlying shares owned by the trader.
- Naked Call: Selling a call option without owning the underlying shares.
- Protective Put: Buying a put option to hedge against potential losses in the underlying asset.
- Straddle: Buying both a call and put option with the same underlying asset and strike price but different expiration dates.
- Strangle: Similar to a straddle, but the strike prices for the call and put options are different.
Risks of Options Trading
Like all investments, options trading carries inherent risks:
- Loss of Premium: If the underlying asset does not behave as expected, the option premium paid to the seller can be lost.
- Unlimited Risk: Some options, such as naked calls and puts, can expose traders to unlimited losses beyond their initial investment.
- Time Decay: The value of an option decreases over time until expiration.
- Volatility Risk: Options are sensitive to changes in the underlying asset’s volatility.
- Liquidity Risk: Some options may not have a liquid market, making it difficult to enter or exit positions.
Options Trading: Quick Start Guide
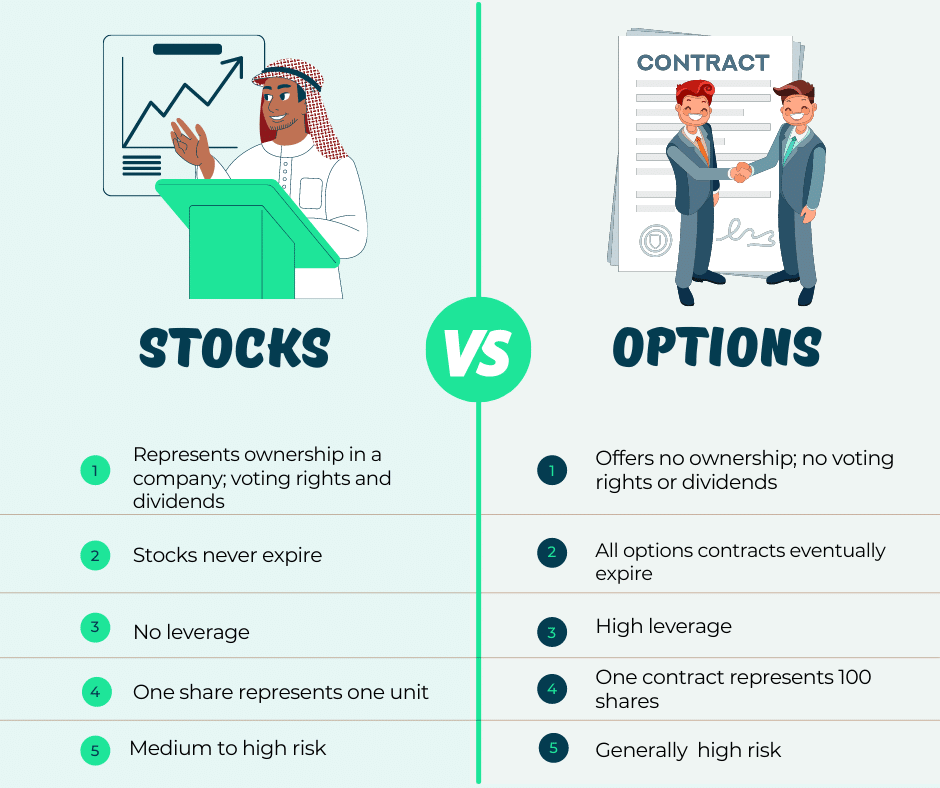
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Conclusion
Options trading can be a powerful tool for investors seeking to enhance their portfolio returns. However, it is essential to understand the fundamentals, risks, and strategies involved before investing. By thoroughly researching, carefully evaluating market conditions, and managing risk effectively, traders can harness the potential benefits of options trading while mitigating potential losses.






