In the realm of financial markets, options trading stands out as a potent tool for investors seeking to enhance returns and manage risk. However, navigating the complexities of options trading requires a deep understanding of the underlying analytics, which empower traders to make informed decisions and maximize profitability.
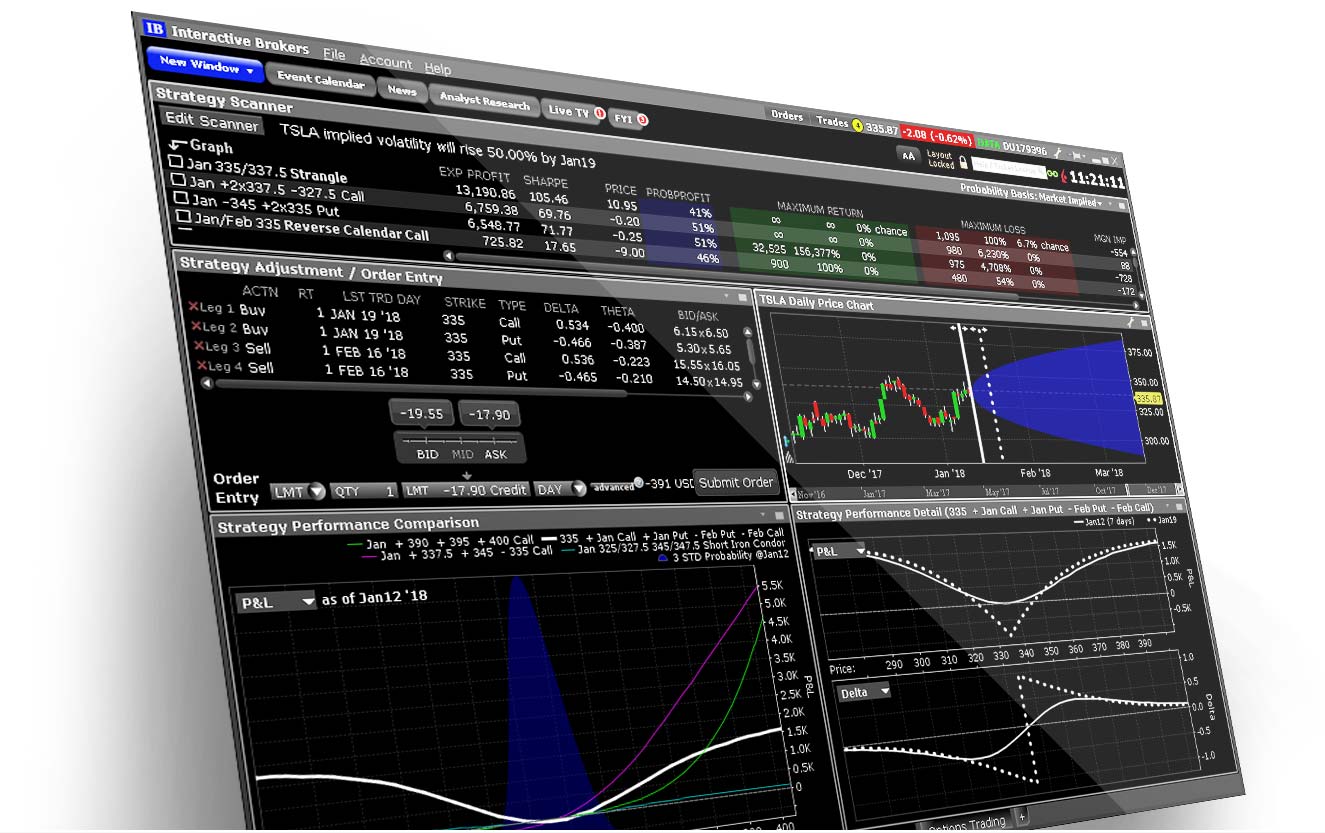
Image: www.interactivebrokers.com.au
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of options trading analytics, providing a clear roadmap for investors to decipher the market’s dynamics and unlock its hidden opportunities. From historical data to volatility measures and pricing models, we unveil the secrets that empower successful options traders.
Historical Data: A Window into the Past
Options trading analytics begins with a thorough examination of historical data, which offers invaluable insights into the market’s behavior over time. By studying historical price charts, traders can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that can inform future trading decisions.
Historical data also enables traders to calculate key statistical measures, such as the mean, median, standard deviation, and skewness. These metrics shed light on the distribution of returns and volatility, empowering traders to assess the potential risks and rewards associated with different options strategies.
Volatility Measures: Gauging Market Uncertainty
Volatility, a measure of the uncertainty or fluctuation in asset prices, plays a pivotal role in options trading analytics. Higher volatility translates into greater potential returns but also increased risk. Traders employ various volatility measures to gauge the market’s current and future uncertainty.
The most widely used volatility measure is the implied volatility (IV), which is derived from the prices of options contracts. IV reflects market expectations of future volatility and is an important factor in determining options premiums. Other volatility measures include historical volatility and realized volatility, which provide insights into the past and current market conditions.
Pricing Models: Valuing Options
At the core of options trading analytics lies the ability to accurately value options contracts. A range of pricing models, each with its own assumptions and complexity, enables traders to determine the fair value of options based on market parameters.
One of the most fundamental pricing models is the Black-Scholes model, which assumes constant volatility and a lognormal distribution of returns. While it offers a simplified approach, the Black-Scholes model may not fully capture the complexities of real-world markets. More sophisticated models, such as the Heston model and the Bates model, account for stochastic volatility and non-normal returns, providing greater accuracy in some circumstances.

Image: nvder.com
Options Trading Analytics
Image: www.inuvest.tech
Conclusion
Options trading analytics empowers investors with the tools and knowledge to navigate the complexities of options markets with greater confidence and success. By harnessing the power of historical data, volatility measures, and pricing models, traders can unlock the secrets of profitable options trading, enhancing returns while managing risk effectively.
We encourage you to delve deeper into this fascinating topic by exploring further resources and sharing your experiences and insights with the trading community. The world of options trading awaits your exploration, where analytics becomes your compass and profitability your destination.






