Options trading involves the purchase or sale of options contracts, which provide the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price within a determinada period of time. Margins, on the other hand, enable traders to control a larger position in an underlying asset using a deposit that is generally equal to a percentage of the total value.
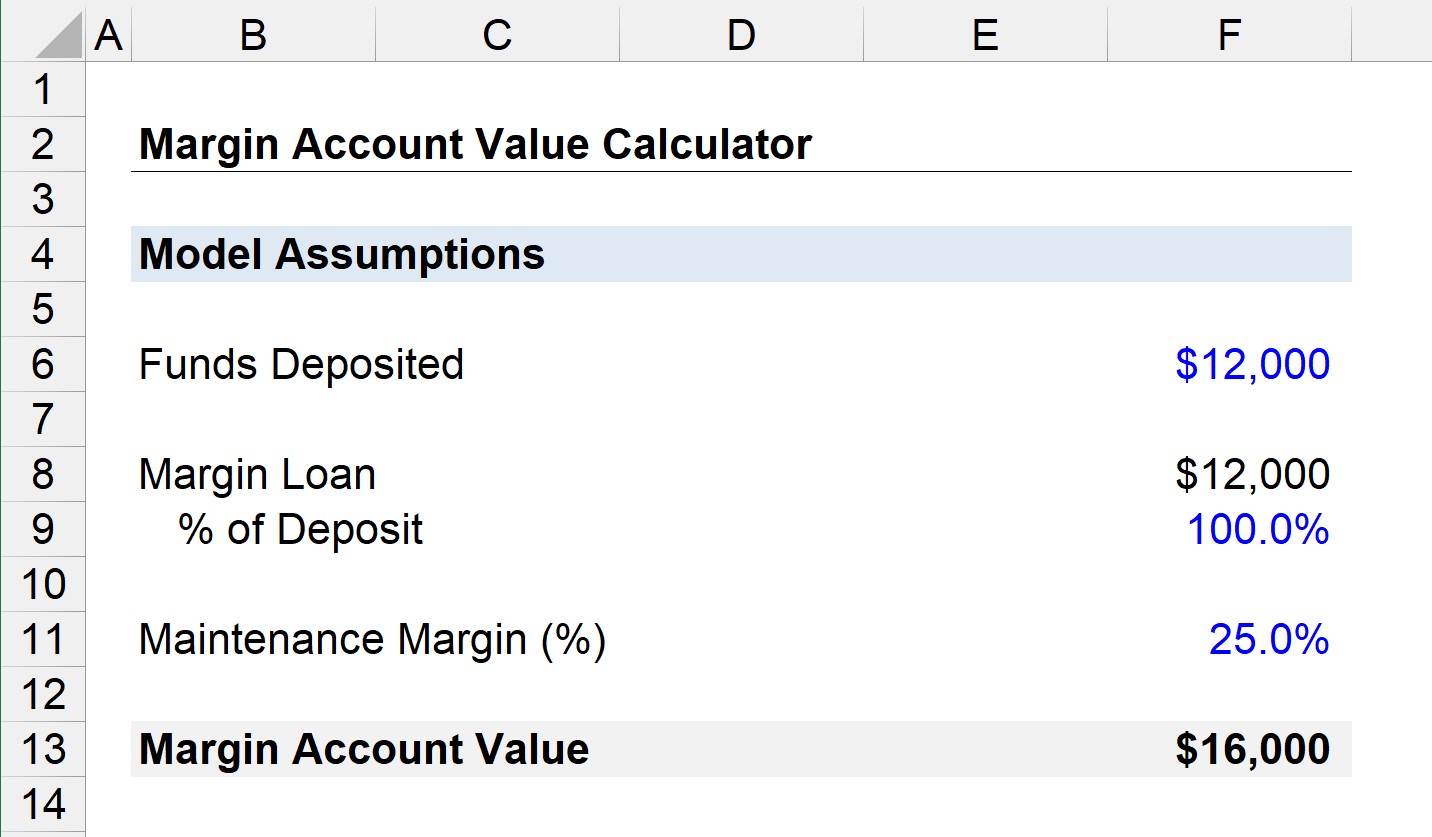
Image: www.wallstreetprep.com
The intertwining of margins and options trading creates a potent combination that can magnify both the potential gains and risks. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of margins and options trading, shedding light on their workings and exploring their implications for investors at every level.
Origins and Evolution: A Historical Perspective
The genesis of margin trading can be traced back to the late 19th century, where traders sought creative methods to increase their capital without tying up significant amounts in cash. The concept gained prominence in the United States, where it ultimately became an integral aspect of the securities markets.
Options trading, too, gained momentum in the early 20th century, with the first standardized options contract being traded on the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) in 1973. Since then, this financial instrument has evolved tremendously, with the emergence of various types and strategies.
Understanding Margins: The Gateway to Leveraging Positions
Margins serve as a bridge between investors’ capital and their investment opportunities, allowing them to trade with more capital than they possess in cash accounts. By depositing a margin of generally 50% or more of the contract value, traders can gain control over larger positions, enhancing their potential profit margins.
The availability of margin trading has transformed the financial landscape, enabling investors to access greater market exposure and potentially earn higher returns. However, it is pivotal to remember that the increased potential for rewards comes hand in hand with the potential for amplified losses.
Options Trading: Navigating the World of Contracts
Options contracts are agreements that grant the holder the choice, albeit not the obligation, to enter into a transaction involving an underlying asset. The contract stipulates the asset type, the target price, and the expiration date. Options trading encompasses two main categories:
-
Call Options: These allow the holder to buy an underlying asset at a preset price before the expiration date. They are ideal when investors anticipate a rise in asset prices.
-
Put Options: These empower the holder to sell an underlying asset at a specified price before the expiration date. They are preferred in scenarios where investors foresee a decline in asset values.
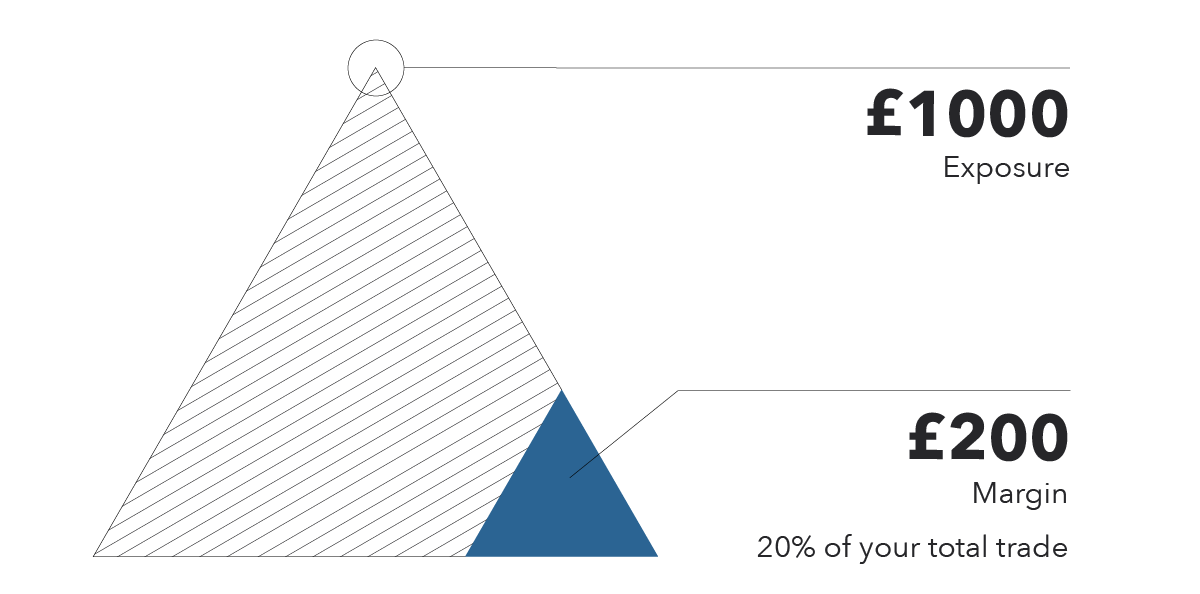
Image: www.ig.com
Varieties of Margin Accounts: Suiting Different Needs
There are diverse types of margin accounts tailored to specific objectives. Some notable examples include:
-
Standard Margin Account: This is the account type where traders are most likely to initiate their interaction with margin trading, designed as a conventional margin trading account with its associated requirements and regulations.
-
Portfolio Margin Account: Advanced traders who trade with diversified portfolios may opt for portfolio margin accounts that grant access to specialized margin calculations based on their overall portfolio.
-
Day Trading Margin Account: Day traders engage in quick trades within the same business day. This specialized margin account provides them with the agility to fulfill their unique trade patterns.
Maximizing Returns and Mitigating Risks: A Balancing Act
The powerful conjunction of margins and options trading offers immense opportunities for profit augmentation. Yet, investors must be cognizant of the risks that accompany such elevated rewards. It is quintessential to adopt a vigilant strategy that emphasizes risk management to avoid potential pitfalls.
By implementing robust risk management practices, including establishing clear trading objectives, diligently tracking positions, and vigilantly seeking professional advice when needed, investors can mitigate risks while capturing the potential benefits of this potent financial fusion.
Margins And Options Trading

Image: phemex.com
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Margins and Options
Margins and options trading present exciting avenues for investors seeking heightened market exposure and potential returns. By comprehending the workings of both concepts and exercising judicious risk management, investors can unlock the true potential of this strategic combination. Remember, the allure of higher rewards must be perpetually balanced with a sound understanding of the inherent risks. By cautiously venturing into the realm of margins and options trading, investors can empower themselves to maximize opportunities while safeguarding their financial well-being.






