Introduction
In the ever-evolving realm of financial markets, investors are constantly on the lookout for innovative and lucrative ways to navigate the complexities of the trading landscape. Among the diverse array of investment strategies, credit spread options trading stands out as a sophisticated yet potent technique that offers the potential to amplify returns and manage risk effectively. Whether you’re a seasoned veteran or a burgeoning market enthusiast, understanding the mechanics of credit spread options trading can open up a world of opportunities and empower you to make informed decisions in pursuit of your financial goals.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Understanding Credit Spread Options
At its core, a credit spread option strategy involves the simultaneous purchase of an “out-of-the-money” option and the sale of an “in-the-money” option with the same underlying asset but different strike prices. The “out-of-the-money” option has a strike price above (in the case of a call spread) or below (in the case of a put spread) the current market price of the underlying asset, while the “in-the-money” option has a strike price below (for call spreads) or above (for put spreads) the market price. By employing this strategy, traders can potentially reap profits from the price movement of the underlying asset while mitigating potential losses. However, it’s crucial to note that, as with any investment endeavor, credit spread options trading carries its inherent risks, and investors must approach it with caution and a thorough understanding of its dynamics.
Types of Credit Spread Strategies
The realm of credit spread options encompasses a spectrum of strategies, each tailored to suit distinct investment objectives and risk preferences. Some of the most commonly employed credit spreads include:
Bull Call Spread
A bull call spread is a bullish strategy that involves buying an “out-of-the-money” call option and selling an “in-the-money” call option with the same underlying asset but a higher strike price. A bull call spread is usually employed when traders anticipate a significant upswing in the price of the underlying asset and are seeking to capitalize on that potential gain while limiting their risk exposure.
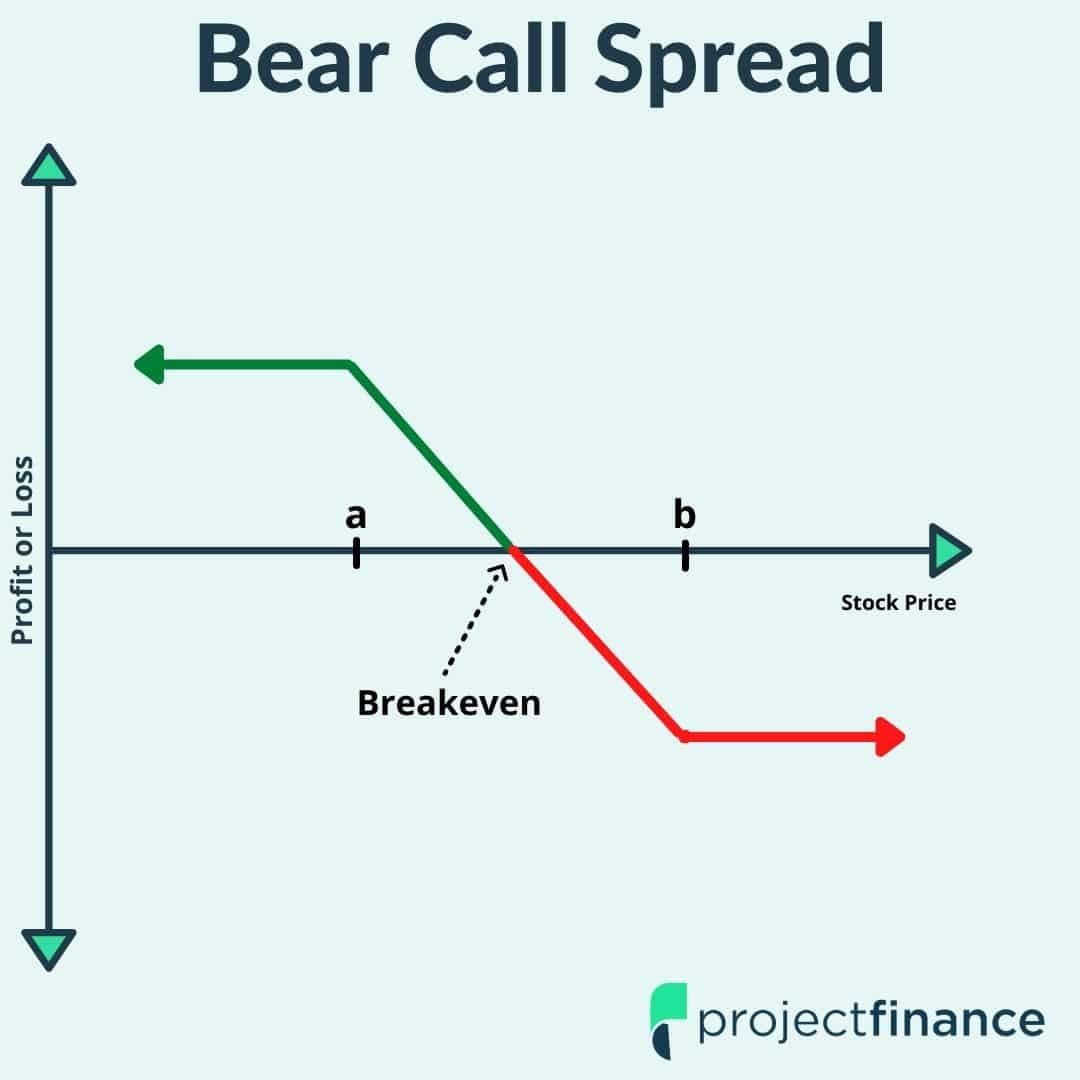
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Bear Put Spread
Conversely, a bear put spread is a bearish strategy that entails selling an “out-of-the-money” put option and buying an “in-the-money” put option with the same underlying asset but a lower strike price. This strategy is typically employed when traders expect a downturn in the price of the underlying asset and aim to benefit from that anticipated decline while limiting their downside risk.
Calendar Spread
A calendar spread strategy involves buying an “out-of-the-money” option with a longer-term expiration date and selling an “in-the-money” option with a shorter-term expiration date. This strategy is often implemented when traders anticipate a sustained movement in the price of the underlying asset but are unsure of the exact timing of that movement.
Benefits and Risks of Credit Spread Trading
Like any investment strategy, credit spread options trading offers both potential benefits and inherent risks that traders must carefully consider before embarking on this path.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Returns: Credit spread options trading offers the potential to amplify returns compared to simply holding the underlying asset. By leveraging the option premiums, traders can potentially generate significant profits from relatively small price movements.
- Risk Management: Credit spread strategies allow traders to manage their risk exposure by simultaneously buying and selling options with different strike prices. This approach helps to define potential losses and protect against substantial downturns in the underlying asset’s price.
- Defined Profit Potential: The maximum profit potential for a successful credit spread trade is predefined at the outset and is determined by the difference between the premiums received and paid when entering the trade.
Risks:
- Limited Upside Potential: The profit potential of a credit spread strategy is capped, especially in the case of bull call and bear put spreads. If the underlying asset’s price movement exceeds the predefined parameters, the trader’s profit will be limited.
- Loss of Premium: If the underlying asset’s price moves against the trader’s expectations, both the purchased and sold options may expire worthless, resulting in a loss of the premium paid.
- Complexity: Credit spread options trading involves sophisticated strategies and requires a thorough understanding of options pricing and market dynamics. Beginners may find it challenging to navigate the complexities and risks involved.
Credit Spread Options Trading
Conclusion
Harnessing the power of credit spread options trading can empower investors to explore advanced investment strategies and potentially enhance their returns. By meticulously planning and carefully managing risk, traders can leverage this technique to navigate market fluctuations and pursue their financial aspirations. However, it’s imperative to approach credit spread options trading with a deep understanding of the dynamics at play, a realistic assessment of the risks involved, and a commitment to ongoing education. By embracing this approach, investors can unlock the potential of credit spread options trading and expand their investment horizons.






