Introduction: Delving into the Taxation Landscape
The world of finance beckons, with its allure of potential profits, but understanding the accompanying tax complexities is paramount. As you navigate the labyrinthine corridors of options trading in India, deciphering the intricacies of income tax laws becomes imperative.
Image: www.icicidirect.com
Like any savvy mariner braving the financial seas, I’ve encountered the enigmatic depths of options trading taxation firsthand. It’s a realm where knowledge serves as a beacon, guiding you through uncharted waters. In this comprehensive guide, I share my navigational aids, empowering you to grasp the intricacies of income tax on profit from options trading in India.
Understanding Options Taxation in India: A Holistic Overview
Definition and Mechanics of Options Trading
Before we delve into the nitty-gritty of tax implications, let’s unravel the fundamentals of options trading. An option is a contract that grants the buyer (holder) the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares or indices) at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specified date (expiry date).
There are two main types of options: calls and puts. A call option gives the buyer the right to buy, while a put option gives the buyer the right to sell. Option premiums are paid upfront by the buyer to the seller of the option in exchange for this right.
Taxation of Options Trading Profits: Unveiling the Fiscal Framework
The Indian tax authorities classify income from options trading as business income. This means that options trading profits are subject to income tax at the applicable slab rates. However, it’s important to note that certain nuances differentiate options trading taxation from regular stock trading.

Image: www.livemint.com
Exploring the Nuances of Options Trading Taxation
To unravel the intricacies of options trading taxation, let’s delve into the key aspects that distinguish it from other forms of financial market activities.
Short-Term Capital Gains Tax (STCG) and Long-Term Capital Gains Tax (LTCG)
The holding period determines whether the profits from options trading will be taxed as short-term capital gains (STCG) or long-term capital gains (LTCG). If the option is held for less than 365 days, the profit is considered STCG and taxed at a flat rate of 15%. On the other hand, if the option is held for more than 365 days, the profit is considered LTCG and taxed at the rate of 10% without indexation.
44AC Presumptive Taxation Scheme: Exploring An Alternative Avenue
In addition to the regular tax regime, traders can opt for the 44AC Presumptive Taxation Scheme. This scheme allows eligible traders to declare a specified percentage of their gross turnover as taxable income. Under this scheme, option trading profits are assumed to be 40% of the gross premium income. However, it’s important to note that traders opting for this scheme cannot claim any expenses against their income and must maintain proper books of accounts.
Expert Advice for Successful Options Trading Taxation Navigation
Navigating the complexities of options trading taxation requires strategic planning. Here are some invaluable tips to help you stay on the right side of the tax authorities:
Embrace Digital Record Keeping: Your Tax Audit Survival Kit
In today’s digital age, maintaining meticulous digital records of your options trading activities is not just a good practice; it’s a tax audit survival kit. Keep track of every trade, including the date, option type, strike price, expiry date, number of lots, and premium paid or received. Digital records simplify tax calculations and enhance accuracy, safeguarding you from potential audit headaches.
Strategic Holding Period Management: Unlocking Taxation Optimization
Timing is everything in options trading, and the same holds true for taxation. Carefully plan your holding period to optimize your tax liability. Short-term holding periods attract higher STCG rates, while long-term holding periods qualify for the LTCG tax benefit. By adjusting your trading strategies accordingly, you can minimize your tax burden and maximize your post-tax returns.
Frequently Asked Questions on Options Trading Taxation in India
To further illuminate the topic, let’s address some commonly asked questions on options trading taxation in India:
- Q: What is the tax treatment of premiums paid or received?
- A: Premiums paid for acquiring options are not tax-deductible and premiums received for selling options are taxable as business income.
- Q: Is losses from options trading tax-deductible?
- A: Losses from options trading can be set off against other business income under the regular tax regime. However, losses under the 44AC Presumptive Taxation Scheme cannot be set off.
Income Tax On Profit From Options Trading In India
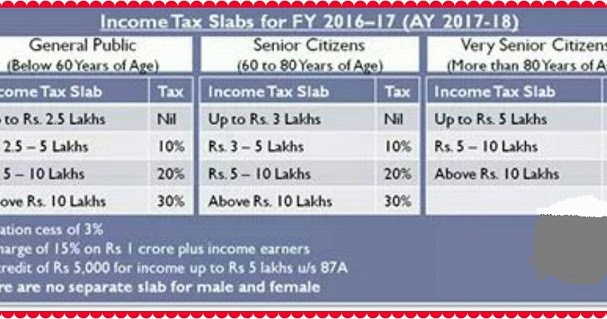
Image: laqenyberegi.web.fc2.com
Conclusion: Navigating Options Trading Taxation with Confidence
In the dynamic landscape of options trading, understanding the nuances of income tax laws empowers you to make informed decisions, optimize your tax liability, and maximize your profits. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting out, embrace these insights and embrace options trading with confidence.
Are you ready to delve deeper into the intricacies of options trading taxation in India? Reach out to us with any questions or for personalized guidance. Together, we’ll navigate the financial waters, ensuring that your options trading journey is not just profitable but also tax compliant.






