Embarking on the Options Trading Journey
Venturing into the realm of options trading often evokes a sense of intrigue, as it unveils a path to amplify financial prospects. Options bestow upon traders the power to harness market trends and orchestrate strategic maneuvers. Yet, alongside the captivating potential for gains lies a fiscal aspect that commands our attention—the interplay between options trading and taxation. Delving into this intricate realm, we shall illuminate the nuances of tax obligations associated with options trading, ensuring that your financial endeavors are navigated with prudence and clarity.
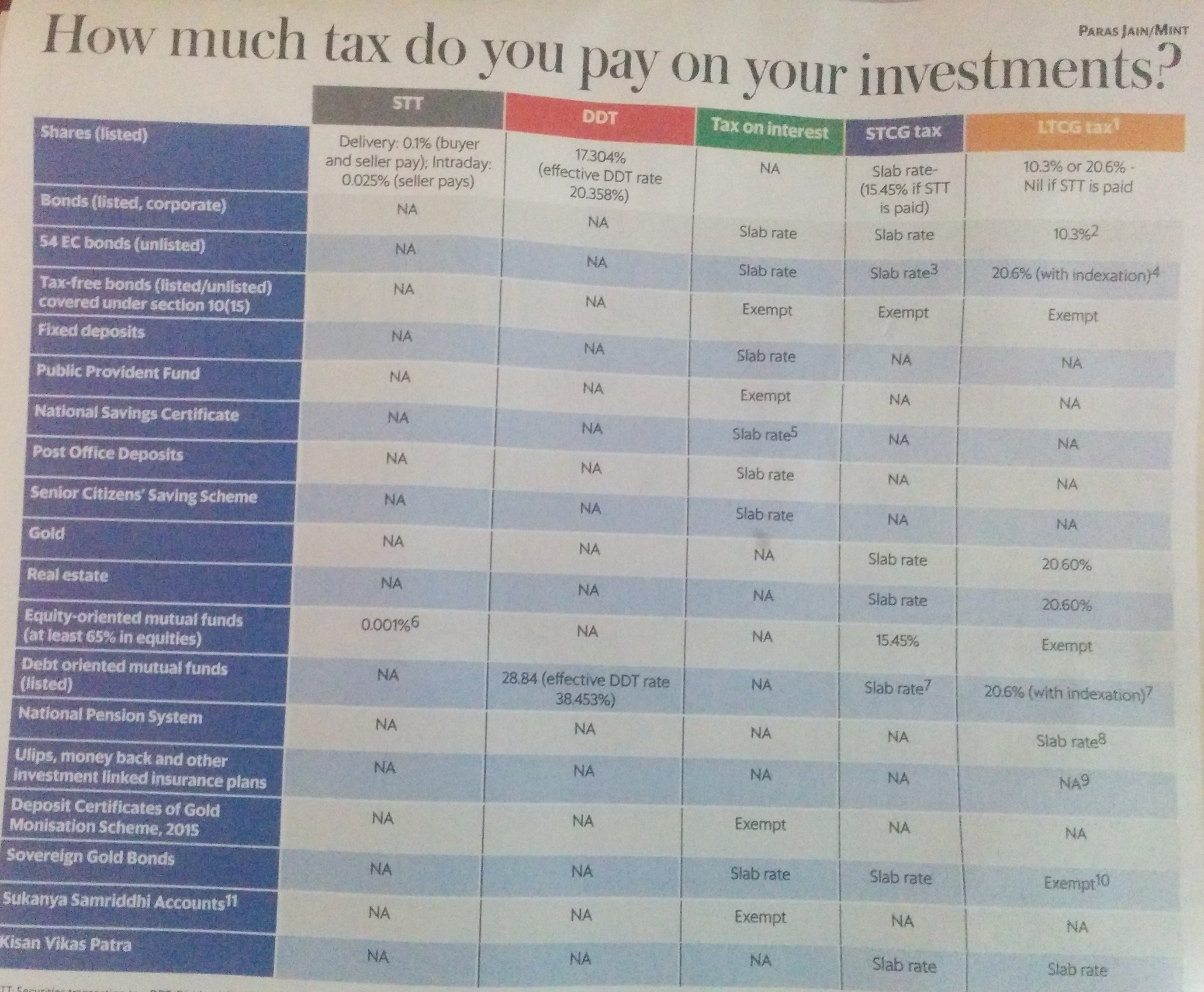
Image: alphaideas.in
Deciphering Options Taxation: A Comprehensive Overview
Options, an integral component of the financial landscape, confer the right—although not the obligation—to either purchase (in the case of call options) or sell (in the case of put options) an underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price. These versatile instruments empower traders with the flexibility to capitalize on market movements without the burden of direct ownership. However, it is imperative to delve into the intricacies of tax implications that accompany such transactions.
When an options contract is exercised, resulting in the purchase or sale of the underlying asset, the transaction is subject to capital gains tax. The tax treatment of your gains will depend on the duration of the period you held the option. If you held the option for one year or less, your gains will be taxed as short-term capital gains, which are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. However, if you held the option for more than one year, your gains will be taxed as long-term capital gains, which are taxed at a lower rate.
It is worth noting that options contracts that expire worthless are not subject to capital gains tax. However, if you sell an options contract before it expires, the proceeds from the sale will be taxed as ordinary income.
Exploring the Nuances of Taxation Strategies
Understanding the subtleties of taxation strategies associated with options trading unlocks the gateway to optimized financial outcomes. One such strategy involves the diligent tracking of your cost basis for each options contract. The cost basis represents the initial investment made to acquire the contract and serves as a crucial element in determining your taxable gains or losses. By maintaining accurate records of your cost basis, you arm yourself with the necessary information for precise tax calculations.
Additionally, astute traders leverage the power of tax-advantaged accounts, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, to shield their options trading gains from taxation. By executing options trades within these accounts, traders can harness the potential for tax-deferred or even tax-free growth on their investment returns.
Seeking Expert Guidance: Tips for Navigating the Tax Labyrinth
As you navigate the complexities of options trading taxation, enlisting the expertise of a seasoned tax professional or financial advisor can prove invaluable. These experienced individuals possess a profound understanding of tax laws and can provide tailored advice specific to your financial situation. By tapping into their knowledge, you can optimize your tax strategy, ensuring that your options trading endeavors align seamlessly with your overall financial objectives.
Furthermore, continuous engagement with reputable sources of tax information and updates keeps you abreast of evolving tax regulations and industry best practices. Forums and social media platforms dedicated to options trading often serve as valuable knowledge hubs, offering insights from experienced traders and tax professionals alike.

Image: dividendonfire.com
Comprehensive Q&A: Unraveling Options Trading Taxation
Q: Can I deduct losses incurred from options trading against my other income?
A: Yes, losses from options trading can be deducted against your other income, subject to certain limitations.
Q: What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains?
A: Short-term capital gains are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, while long-term capital gains are taxed at a lower rate. The duration of the period you held the option determines whether your gains are short-term or long-term.
Q: How can I minimize the tax impact of my options trading activities?
A: Employing tax-advantaged accounts, optimizing your cost basis, and seeking expert guidance can help minimize the tax impact of your options trading endeavors.
Do You Pay Tax On Options Trading

Image: dividendonfire.com
Conclusion: Navigating the Interplay of Options Trading and Taxation
Understanding the interplay between options trading and taxation is an essential facet of successful financial planning. By delving into the complexities of capital gains tax, employing effective tax strategies, and harnessing expert advice, you can confidently navigate the options trading landscape while optimizing your returns. Remember, the journey into options trading is an ongoing exploration, and continuous engagement with tax-related information and updates empowers you to adapt seamlessly to evolving regulations and industry best practices. Embrace the challenge, master the intricacies, and reap the rewards of informed, tax-advantaged options trading.
Are you eager to delve further into the captivating realm of options trading and taxation? Share your thoughts and questions below, and let us ignite a vibrant dialogue that illuminates the path toward financial empowerment.






