Have you ever wished you could time the market, taking advantage of booming stocks or hedging against potential downturns? Imagine being able to profit from the volatility of the markets, even if you’re unsure which direction the price will move. This is the power of options trading, a unique and potentially lucrative investment strategy that can transform how you approach the financial world.
Image: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Options trading can seem daunting, a complex world of Greeks and premiums. But beneath the surface, it revolves around simple principles – the right to buy or sell an underlying asset (like a stock) at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. This guide will demystify options trading, unraveling its intricacies and empowering you with knowledge to make informed decisions.
Unveiling the World of Options: A Comprehensive Deep Dive
To grasp the essence of options, it’s essential to understand its history and core concepts.
The Origins of Options: From Ancient Markets to Modern Trading
Options have a long and fascinating history, dating back to ancient Greece. Farmers would use options contracts to secure a price for their crops, ensuring a stable income regardless of future market fluctuations. This concept evolved into modern options trading, which gained popularity in the 1970s with the advent of standardized options contracts and organized exchanges.
The Two Main Types of Options: Calls and Puts
Options are essentially contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price. There are two main types of options:
- Call Options: These give the holder the right to buy an underlying asset at a specific price (known as the strike price) within a certain timeframe (the expiration date). Think of it as an insurance policy against rising prices. If the price goes up, the call buyer can exercise their right and buy the asset at a lower price than the current market value, making a profit.
- Put Options: Conversely, put options offer the right to sell an underlying asset at a specific price within a certain timeframe. Picture it as a safety net against falling prices. If the price goes down, the put buyer can exercise their right and sell the asset at a higher price than the current market value, limiting their losses.
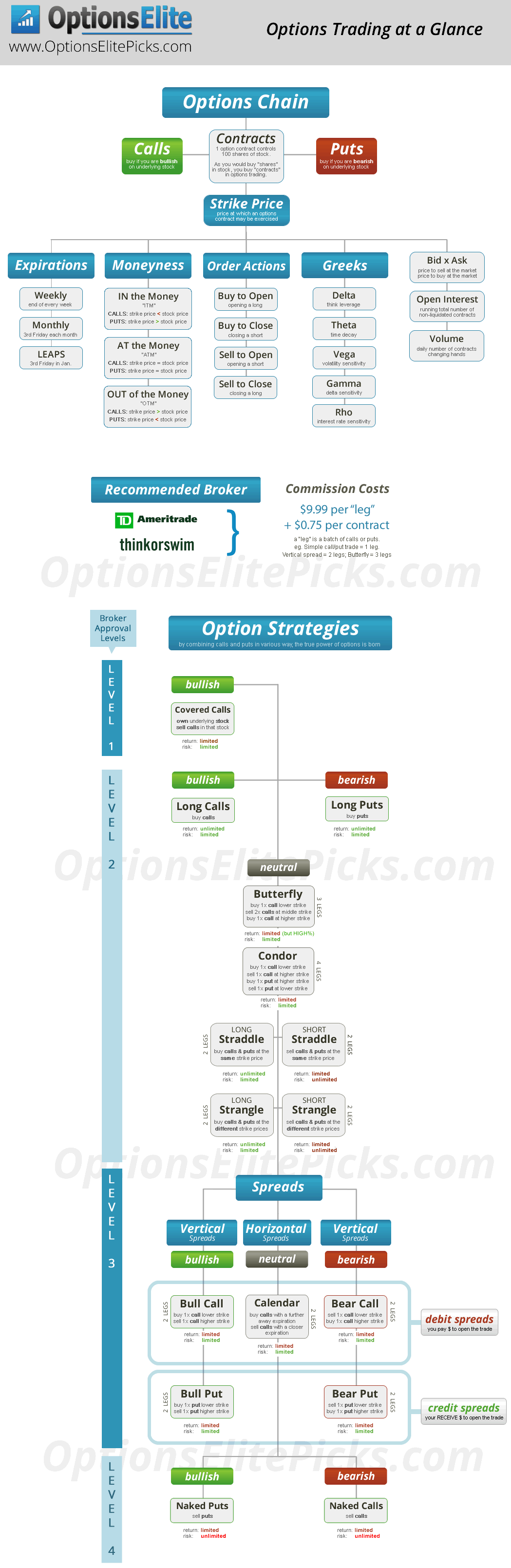
Image: thestockmarketwatch.com
Understanding the Anatomy of an Option
To truly comprehend options, it’s essential to understand their key components:
- Strike Price: The predetermined price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires.
- Premium: The price you pay to purchase the option. This is like a down payment for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Underlying Asset: The asset that the option contract is based on, such as stocks, indices, commodities, or currencies.
- Intrinsic Value: The difference between the strike price and the current market price of the underlying asset. It represents the immediate profit you’d make if you exercised the option right now.
- Time Value: The portion of the option premium that reflects the remaining time until expiration. Time value deteriorates as the expiration date approaches.
The Greeks: Unmasking the Forces Influencing Option Prices
Options prices are dynamic and constantly changing. Understanding the Greeks helps us analyze and predict these price fluctuations:
- Delta: A measure of how much an option’s price will change for every $1 change in the price of the underlying asset.
- Gamma: Measures the rate of change of delta. It tells us how much the delta will change for every $1 change in the price of the underlying asset.
- Theta: Represents the time decay of an option, indicating how much its value decreases as the expiration date approaches.
- Vega: Measures the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in implied volatility. Volatility refers to the magnitude of price fluctuations.
- Rho: Indicates how much an option’s price changes in response to interest rate fluctuations.
Unleashing the Power of Options: Applications and Strategies
The beauty of options lies in their flexibility and diverse applications. Here are some common uses of options:
- Income Generation: Covered call writing allows investors to generate income by selling call options on stocks they already own.
- Hedging: Options can protect your portfolio from potential losses in declining markets. For example, a put option on a stock can shield you from price drops.
- Speculative Trading: Options can amplify your potential gains or losses, making them attractive to traders looking to capitalize on strong market movements.
- Leverage: Options offer leverage, allowing you to control a larger amount of underlying assets with a smaller investment.
Diverse Options Strategies: Navigating the Market Landscape
Options offer an array of strategies tailored to specific goals:
- Bullish Strategies: Strategies designed to profit from rising prices, such as buying call options or selling put options.
- Bearish Strategies: Strategies that aim to profit from declining prices, such as buying put options or selling call options.
- Neutral Strategies: Strategies that aim to profit from volatility regardless of the direction of the underlying asset, such as straddles and strangles.
- Combinations: Complex options strategies that combine multiple options contracts to achieve specific risk and reward profiles.
Understanding the Risks: The Potential Downside of Options
While options offer exciting possibilities, they also carry inherent risks.
- Limited Risk: Options allow you to control a larger position with a smaller investment, but also limit your losses.
- Unlimited Risk: Options can potentially lead to unlimited losses if the trade goes against you.
- Expiration: Options have limited lifespans, and their value can rapidly decline as they approach their expiration date.
- Volatility: Options prices are heavily influenced by market volatility, which can make them difficult to predict.
Mastering the Market: Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
To succeed in options trading, it’s vital to learn from those who have already navigated the terrain:
- Start with a solid foundation: Understand the core concepts of options trading before diving into complex strategies.
- Embrace continuous learning: The options market is dynamic, so constant learning is crucial.
- Manage your risk: Risk management is paramount in options trading. Define your risk tolerance and implement strategies to minimize potential losses.
- Practice with a paper trading account: Test your strategies and gain experience in a risk-free environment before committing real capital.
- Seek professional guidance: Consider consulting with a financial advisor or experienced options trader for personalized advice.
Whats Options Trading
Embarking on Your Options Journey: A Final Word
Options trading can be a rewarding experience, but it requires careful research, planning, and risk management. As you delve deeper into this exciting world, remember that knowledge is power. The best way to gain mastery is through continuous learning, responsible experimentation, and a commitment to seeking expert guidance. The journey to becoming a successful options trader begins with a single step – embrace the opportunity and start exploring the world of options!






