The world of finance can be a captivating and often intimidating landscape. For many, the allure of potentially large returns draws them to the realm of trading, but navigating the complexities of financial instruments can be daunting. Among the many tools available to traders, options contracts stand out as a versatile and potentially powerful tool, capable of offering both significant profits and substantial risk. My own journey into the world of options trading began with a mix of curiosity and trepidation. I had heard countless tales of traders making fortunes, but also stories of those who lost everything. This led me on a quest to understand the intricacies of options contracts, a journey that ultimately transformed my approach to trading.
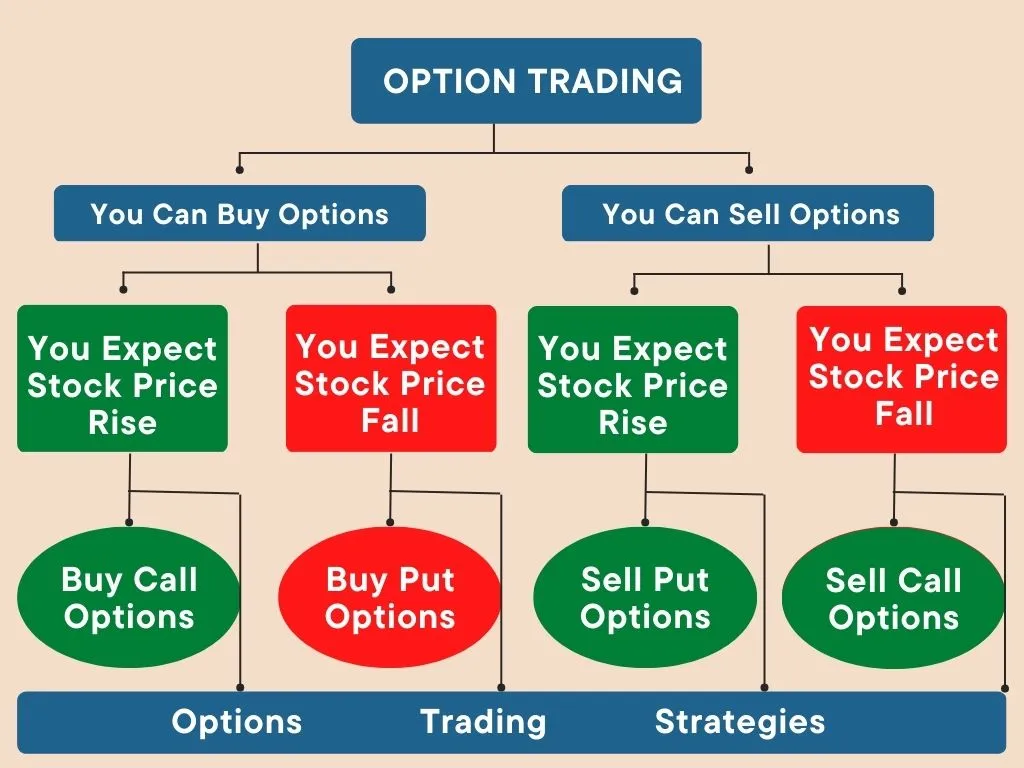
Image: changehero.io
The key to navigating options trading lies in understanding their fundamental principles and applying them strategically. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of options contracts, exploring their origins, how they work, their various applications, and the key considerations for traders entering this exciting, yet potentially risky, market.
Understanding the Basics of Options Contracts
What is an Options Contract?
An options contract is a financial instrument that grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). This right comes at a cost, known as the premium, which the buyer pays to the seller. Options contracts offer traders a unique opportunity to leverage their capital and potentially generate significant returns, but they also involve inherent risks.
Types of Options Contracts
There are two primary types of options contracts: call options and put options. Call options give the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price, while put options give the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price.

Image: www.wordstemplates.org
Key Terminology
Several key terms are crucial to understanding options contracts:
- Strike Price: The price at which the underlying asset can be bought (call) or sold (put) as defined by the contract.
- Expiration Date: The date by which the option must be exercised or it expires worthless.
- Premium: The price paid by the buyer to purchase the option contract.
- Underlying Asset: The asset being traded with the option, such as a stock, index, or commodity.
Exploring the Mechanics of Options Trading
How Options Contracts Work
Imagine you want to buy a stock that you believe will rise in value. Instead of purchasing the stock outright, you could consider buying a call option. This allows you to purchase the stock at a predetermined price (the strike price) before the expiration date, giving you the potential to profit from an increase in the stock’s value. The premium you paid for the call option acts as a buffer, limiting your potential loss but also reducing your potential gains.
The Profit and Loss Potential
The potential profit and loss associated with options trading depend on several factors:
- The type of option (call or put)
- The strike price
- The premium paid
- The price movement of the underlying asset
Leverage and Risk
Options trading offers leverage, which means you can control a larger amount of underlying asset with a smaller investment. While this can amplify your potential profits, it also magnifies your potential losses. It’s crucial to manage risk effectively by choosing appropriate options and implementing strategies to mitigate potential losses.
Real World Applications of Options Contracts
Hedging Strategies
One of the most common uses for options is hedging, a strategy designed to reduce or eliminate risk. For example, a company holding shares of a stock could buy put options to protect against a decline in the stock’s price.
Income Generation
Traders can also use options to generate income. For example, by selling covered call options, they can collect premiums while maintaining the potential for growth in their underlying asset.
Speculation
Options can also be used for speculation, where traders aim to profit from anticipated price movements. For example, a trader might buy call options on a stock they believe will increase in value.
Modern Trends and Developments in Options Trading
The Rise of Options Trading Platforms
Technological advancements have made it easier than ever to trade options. Numerous online platforms offer a wide range of options trading tools and resources, enabling both novice and experienced traders to participate in this market.
Increasing Interest in Options Strategies
The ever-increasing popularity of options among individual investors often drives discussions within online communities and social media platforms, further fueling interest in this asset class.
Expert Tips and Advice for Options Trading
Start Small and Learn
Take the time to learn the fundamentals of options trading before diving into the market headfirst. Start with a small amount of capital and gradually increase your investment as your understanding grows.
Focus on Risk Management
Options trading comes with inherent risks. Always have a clear risk management plan in place, including stop-loss orders and exit strategies, to protect your capital.
Stay Informed
The options market is constantly evolving. Stay updated on market trends, news affecting the underlying assets, and any changes in regulations or trading policies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Are options contracts suitable for all investors?
A: No, options trading carries significant risk and may not be suitable for all investors. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research and have a strong understanding of options contracts before you trade.
Q: How can I minimize my risk when trading options?
A: Use stop-loss orders, diligently manage your position sizes, and employ hedging strategies to mitigate potential losses.
Q: What are some good resources for learning about options trading?
A: There are numerous online resources, books, and courses available. Consider exploring platforms like Investopedia, The Options Industry Council (OIC), and reputable online brokers offering educational tools.
Trading Options Contracts
Conclusion
In conclusion, options contracts offer a powerful tool for traders seeking to leverage their capital, manage risk, or speculate on market movements. By understanding the underlying mechanics of options trading, diligently managing risk, and staying informed about market trends, you can unlock the potential of these financial instruments and potentially achieve your trading goals. Remember, options trading is not for the faint of heart, but with careful research, practice, and a disciplined approach, it can be a potentially rewarding trading endeavor.
Are you interested in learning more about options trading? Share your thoughts and any specific questions you have in the comments below!






