Introduction
In the realm of investing, the ability to navigate the ever-changing financial markets is paramount. One potent tool that can amplify returns and mitigate risks is cash options trading. This intricate yet rewarding strategy has garnered widespread popularity, empowering traders to make informed decisions and capitalize on market opportunities. In this comprehensive guide, we will embark on a journey through the world of cash options trading, unraveling its intricacies and equipping you with actionable insights to enhance your financial acumen.
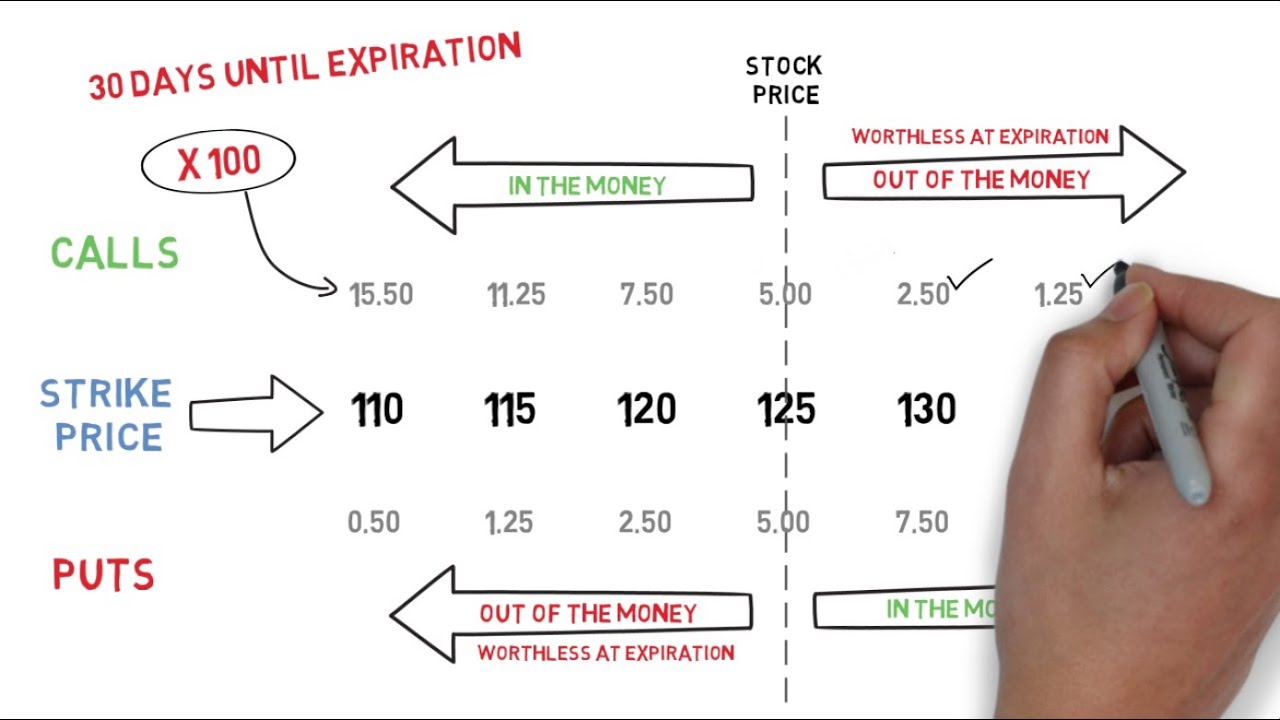
Image: www.youtube.com
Understanding Cash Options Trading
Cash options contracts represent a type of derivative that grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). These contracts are traded on standardized exchanges, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), providing a regulated and transparent marketplace.
Types of Cash Options
There are two primary types of cash options contracts: calls and puts. Call options grant the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price, while put options provide the right to sell. The versatility of cash options allows traders to speculate on market movements, hedge against risks, and generate income through various strategies.
Underlying Assets
Cash options can be based on a wide array of underlying assets, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies. This diversity enables traders to participate in various sectors and markets, catering to their specific investment objectives.
Image: www.learn-forextrading.org
Market Mechanics
The cash options market operates on the principles of supply and demand. The price of an option contract is determined by several factors, including the underlying asset’s price, the time remaining until expiration, the volatility of the underlying asset, and the current interest rate environment.
Option Premiums
When purchasing an option contract, traders pay a premium, which represents the cost of acquiring the right to exercise the option. The premium is determined by the interplay of the aforementioned factors.
Exercising and Assigning Options
The holder of a cash option has the right to exercise the option on or before the expiration date. Exercising a call option means buying the underlying asset at the strike price, while exercising a put option entails selling the underlying asset at the strike price. Options that are not exercised prior to expiration expire worthless.
Expert Insights
Seasoned traders and financial experts highly recommend understanding the inherent risks associated with cash options trading. Implied volatility, market sentiment, and unexpected events can significantly impact the value of option contracts. They advise traders to conduct thorough research, employ proper risk management strategies, and only trade with capital they can afford to lose.
Trading Strategies
Cash options trading opens up a world of investment strategies tailored to different market conditions and risk tolerances. From simple strategies like buying or selling naked options to complex strategies like spreads and straddles, traders can tailor their approach to meet their individual goals.
Cash Options Trading

Image: www.slideshare.net
Conclusion
Cash options trading is a sophisticated investment tool that can unlock a wide range of opportunities for those who possess a thorough understanding of its complexities. By embracing the principles outlined in this article, you can confidently navigate the financial markets, effectively manage risks, and harness the potential for substantial returns. Whether you are a seasoned trader or an aspiring investor, the knowledge and insights provided in this guide will empower you to make informed decisions and achieve financial success.






