Have you ever wished you could profit from a stock’s rise or fall without actually owning it? Have you ever dreamt of limiting your potential losses while still participating in the market’s upswing? Enter the realm of options trading, a complex yet powerful financial instrument that allows investors to manage risk and potentially amplify their returns.
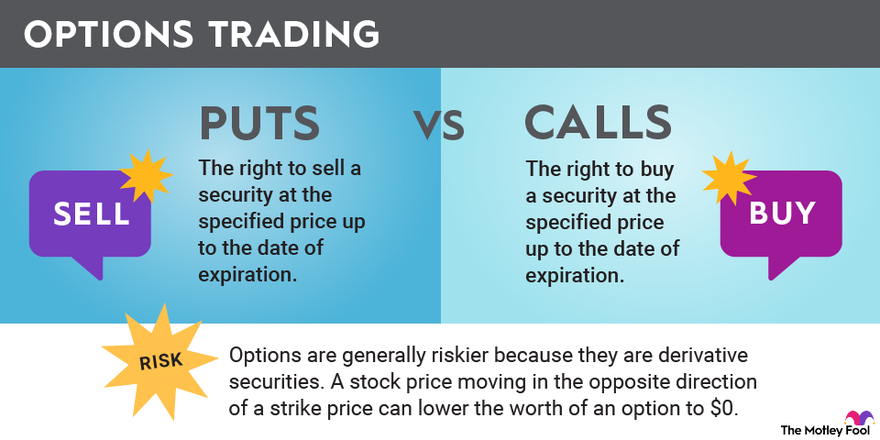
Image: runacrosscongo.org
Options, in essence, are contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset, such as a stock, at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). They are often considered “derivatives” because their value is derived from the price movements of the underlying asset. But why delve into this intricate world? The answer lies in the unique opportunities options offer, allowing for diverse strategies tailored to different market outlooks and risk tolerance levels.
Understanding the Basics: Calls, Puts, and More
Before diving into the complexities of options trading, let’s grasp the fundamental concepts. There are two primary types of options:
Call Options
A call option grants the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price. Imagine you believe a certain stock will rise in value. By purchasing a call option, you’re essentially betting on that stock’s increase. If the stock price climbs above the strike price, your call option gains value, potentially generating a profit. However, if the stock price falls below the strike price, you lose your premium, the price you paid for the option.
Put Options
A put option grants the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. If you anticipate a stock’s decline, purchasing a put option allows you to profit from that drop. If the stock price falls below the strike price, your put option gains value, potentially generating a profit. But if the stock price rises above the strike price, you lose your premium.
Beyond basic call and put options, various variations exist, including:
- Covered Options: Call options where the seller owns the underlying asset.
- Naked Options: Options sold without owning the underlying asset, involving higher risk.
- Spread Options: Combinations of options with different strike prices or expiration dates.
- Straddle Options: Simultaneous purchase of a call and a put with the same strike price and expiration date.

Image: www.projectfinance.com
The Advantages and Risks of Options Trading
Options trading presents a plethora of potential benefits, but it comes with its own set of risks. Understanding both sides is crucial for making informed decisions:
Advantages
- Leverage: Options trading allows investors to control a larger position in the underlying asset than they would with traditional stock purchases, magnifying potential profits (and losses).
- Flexibility: Options offer diverse strategies to suit various market views and risk profiles, from bullish to bearish, conservative to aggressive.
- Limited Risk: Options contracts have a defined maximum loss, unlike buying shares directly. You can only lose the premium paid, regardless of the underlying asset’s price fluctuations.
- Time Decay: Option prices decrease over time as expiration approaches, making it a factor in strategic planning and profit generation.
Risks
- Complexity: Options trading involves a steep learning curve, requiring a grasp of pricing models, volatility, and time value.
- Time Decay: While beneficial for some strategies, time decay can also lead to losses if the option expires worthless.
- Volatility Amplification: Options prices are highly sensitive to price movements in the underlying asset, amplifying both potential gains and losses.
- Potential for Loss: Though limited, the premium paid is still a potential loss if the option expires worthless.
Navigating the World of Options: Strategies and Applications
Options trading extends far beyond simple call and put purchases. Various strategies cater to different market conditions and risk appetites. Let’s explore some common approaches:
Income Generation
- Covered Call Writing: Selling a call option on a stock you own, generating premium income while potentially limiting future upside gains.
- Cash Secured Put Writing: Selling a put option on a stock you wish to purchase, generating premium income while potentially acquiring the stock at a discounted price.
Profiting from Volatility
- Straddle: Buying a call and a put with the same strike price and expiration date, profiting from large price movements regardless of direction.
- Strangle: Buying a call and a put with different strike prices and the same expiration date, profiting from more significant price movements while requiring less premium.
Hedging and Risk Management
- Protective Put: Buying a put option on a stock you own, protecting against potential losses in the underlying asset while still allowing for potential upside.
- Covered Put: Selling a put option on a stock you own, potentially generating premium income while simultaneously potentially acquiring the stock at a lower price.
Understanding Option Pricing
Option pricing is crucial for determining fair value and assessing potential returns. Various factors influence option prices, including:
- Underlying Asset Price: When the underlying asset price increases, call option prices rise, while put option prices decrease. Conversely, a falling underlying asset price increases put option prices and lowers call option prices.
- Strike Price: As the strike price increases, call option prices decrease, and put option prices increase.
- Time to Expiration: Options with longer durations have higher prices, reflecting the longer period for the underlying price to move in their favor.
- Volatility: Higher volatility in the underlying asset increases option prices, as there is greater uncertainty and a higher chance of large price movements.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates generally decrease call option prices and increase put option prices.
The Evolution of Options Trading: Technology and Accessibility
The options trading landscape has undergone a significant transformation. With the advent of online brokerage platforms and sophisticated trading tools, access to this powerful market has become more accessible than ever. This evolution has led to several notable trends:
- Increased Retail Participation: Online platforms and educational resources have lowered the barriers to entry, enabling individual investors to delve into options trading.
- Automated Trading: Algorithmic trading and automated strategies have become more common, incorporating complex option pricing models and analysis.
- Mobile Trading: Trading platforms are now seamlessly integrated into smartphones, allowing for market access on the go.
- Data Analysis and Visualization: Advanced software delivers real-time market data, charts, and analytics, enhancing trading decisions.
Options In Trading
Conclusion: A World of Opportunities Awaits
Options trading offers a multifaceted world of opportunities, allowing investors to explore diverse strategies, manage risk, and potentially magnify returns. But remember, this power comes at a cost: complexity and inherent risks. It’s vital to approach options trading with meticulous preparation, a solid understanding of its intricacies, and a commitment to learning. With the right knowledge, you can unlock the potential of options and navigate this exciting market with confidence.
This article has merely scratched the surface of this dynamic field. Continued exploration, seeking guidance from experienced traders, and actively engaging with the ever-evolving options landscape are integral for success. As you delve deeper into this arena, always prioritize a thorough understanding of options contracts, pricing models, and relevant risk management strategies. The path to mastery in options trading is a continuous journey of learning and adaptation, fueled by passion, discipline, and a thirst for knowledge.






