Image: laqenyberegi.web.fc2.com
Introduction
In the realm of stock market investments, options trading has emerged as a powerful tool for risk management and profit generation. However, understanding the intricacies of taxation associated with options trading can be a daunting task, especially in India. This comprehensive guide delves into the taxation framework surrounding options trading in India, providing a clear roadmap for investors to navigate the complexities of this domain.
**Understanding Options Trading**
Options are financial contracts that provide the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specific date (expiration date). There are two types of options: calls and puts. Call options give the buyer the right to buy, tandis que put options give the buyer the right to sell.
**Taxation of Options Trading**
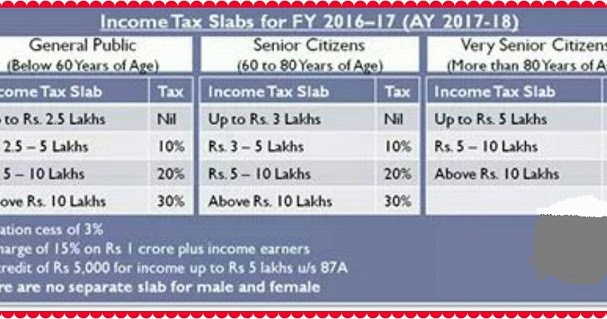
The Income Tax Act of India categorizes options trading income as either speculative income or business income. The tax treatment of these two categories differs significantly.
-
Speculative Income: Options trading is deemed speculative if the transactions are carried out for short-term profits and are not part of a regular business activity. Profits from speculative options trading are taxed at a flat rate of 30%, regardless of the holding period.
-
Business Income: If options trading is carried out as a regular part of a business, the income is considered business income and is taxed according to the slab rates applicable to the business’s overall income. However, to qualify as business income, the taxpayer must demonstrate that options trading is integral to the core activities of their business and is not merely an ancillary activity.
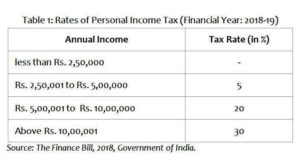
Image: www.cbgaindia.org
**Exemption for Qualified Hedge Transactions**
Hedging is a financial strategy used to reduce risk by offsetting potential losses from one investment with corresponding gains from another. In certain cases, hedge transactions involving options may qualify for an exemption from the 30% speculative tax rate and be taxed as business income. To qualify, the hedging transaction must meet the following criteria:
- The underlying asset of the option must be the same or substantially similar to the hedged asset.
- The purpose of the transaction must be to reduce the risk of price fluctuations in the hedged asset.
- A direct relationship must exist between the hedged asset and the option.
**Calculating Tax Liability**
The tax liability for options trading income is calculated based on the difference between the selling price (in the case of call options) or the purchase price (in the case of put options) and the strike price. The resulting profit or loss is then taxed as per the applicable tax rates.
- Call Options: Taxable Profit = (Selling Price – Strike Price)
- Put Options: Taxable Profit = (Strike Price – Purchase Price)
**Record-Keeping and Reporting**
It is crucial for options traders to maintain accurate records of all their transactions, including the date, strike price, expiration date, and profit or loss. These records should be maintained for a minimum of six years, as prescribed by the Indian tax authorities.
The details of options trading income must be reported in the annual income tax return filed with the Income Tax Department. Failure to accurately report options trading income can lead to tax penalties or prosecution.
**Expert Insights**
“Options trading can be a powerful tool, but it is essential to understand the tax implications before entering into any transactions,” advises Mr. Ashutosh Kapur, a respected financial advisor. “Consulting with a tax professional can help you optimize your tax strategy and minimize your tax liability.”
Ms. Meera Gupta, a Chartered Accountant, emphasizes the importance of record-keeping. “Accurate and up-to-date records are crucial for proper tax compliance and can help avoid unnecessary tax disputes,” she says.
Income Tax On Options Trading In India
https://youtube.com/watch?v=g_4TmzND1ks
**Conclusion**
Navigating the tax landscape of options trading in India requires a thorough understanding of the relevant regulations and tax rates. This comprehensive guide has provided an overview of the key concepts, tax treatment, and record-keeping requirements. By adhering to the guidelines outlined herein, options traders can minimize their tax liability, optimize their trading strategies, and achieve financial success.






