Imagine yourself staring at a screen filled with numbers, graphs, and the constant ticking of a clock. The air hums with the possibility of both colossal gains and crushing losses. This, my friends, is the world of option trading. It’s a high-stakes game where astute strategy can reap immense rewards, but a lack of preparation can lead to devastating consequences. In this guide, we’ll navigate the intricacies of option trading, unraveling the best strategies to harness its power and guide you toward profit.
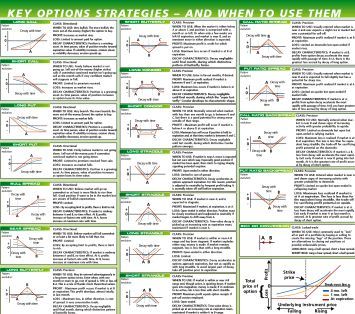
Image: kumeyuroj.web.fc2.com
Option trading, simply put, grants you the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset, like a stock, at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. Its allure lies in its leverage – the potential for amplified profits with comparatively small investments. But this leverage also doubles as a double-edged sword, magnifying potential losses if not managed carefully. So, how do you strike the right balance, maximizing your potential while minimizing risk? This is where the art of strategy comes in; the compass guiding you through the volatile waters of the options market.
Fundamental Navigation Tools: Unveiling the Building Blocks of Option Strategies
Before diving into specific strategies, we must lay the groundwork: understanding the terminology and building blocks of this intricate world.
1. The Anatomy of an Option
- Call Option: Grants the right to buy an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified period.
- Put Option: Grants the right to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified period.
2. Key Determinants of Option Value
- Underlying Asset: The value of the underlying asset directly impacts the option’s price.
- Strike Price: The price at which you can buy or sell the asset.
- Expiration Date: The date when the option expires.
- Volatility: The degree of price fluctuation in the underlying asset. Higher volatility generally translates to higher option prices.
- Time Value: The value derived from the time remaining until expiration. As time passes, the time value of an option decays.
Image: marketxls.com
Charting a Course: A Spectrum of Option Strategies
Armed with the basic understanding, let’s explore various strategies, each with its unique risk and reward profile:
1. Covered Calls
- Strategy: Selling a call option on an asset you already own.
- Objective: Generate income while limiting potential losses.
- Risk/Reward: Limited potential profit, but potentially capped losses.
- Example: You own 100 shares of Apple stock. You sell a call option on those shares, giving someone else the right to buy them from you at a specific price by a set date. If the stock price rises, the buyer will exercise their option, and you’ll be obligated to sell your shares for the strike price. If the stock price remains below the strike price, the option expires worthless, and you keep the premium collected.
2. Cash Secured Puts
- Strategy: Selling a put option while holding enough cash to buy the underlying asset if the option is exercised.
- Objective: Generate income with the potential to acquire the underlying asset at a discount.
- Risk/Reward: Limited potential loss, but potential to buy the asset at a discounted price.
- Example: You have $1,000 in cash. You sell a put option on 100 shares of Amazon stock with a strike price of $100. If the stock price drops, the buyer could exercise their option, forcing you to buy 100 shares at $1,000. However, you also keep the premium collected for selling the put option. This allows you to buy shares at a lower price than the market if the stock drops.
3. Bullish Call Spreads (Debit/Credit)**
- Strategy: Buying a call option with a lower strike price and selling a call option with a higher strike price, both with the same expiration date.
- Objective: Profit if the underlying asset price increases, with limited risk.
- Risk/Reward: Limited profit potential, but also limited risk.
- Example: You buy a call option on 100 shares of Tesla stock with a strike price of $200 and sell a call option on 100 shares with a strike price of $250, both expiring in one month. This strategy profits if Tesla’s stock price rises above $200, but your risk is limited because you’ve sold a higher strike price call option.
4. Bearish Put Spreads (Debit/Credit)**
- Strategy: Buying a put option with a higher strike price and selling a put option with a lower strike price, both with the same expiration date.
- Objective: Profit if the underlying asset price decreases, with limited risk.
- Risk/Reward: Limited profit potential, but also limited risk.
- Example: You buy a put option on 100 shares of Google stock with a strike price of $120 and sell a put option on 100 shares with a strike price of $100, both expiring in one month. This strategy profits if Google’s stock price falls below $100, but your risk is again limited because you’ve sold a lower strike price put option.
Steering Through Volatility: Mastering Risk Management
Option trading thrives on volatility, but it also becomes its Achilles’ heel. Therefore, managing risk is paramount. Here are some guiding principles:
1. Understand the “Greeks”:
Greek letters like Delta, Gamma, Theta, and Vega quantify the sensitivity of an option’s price to various factors like price movement, time, and volatility. By understanding them, you gain insights into how your positions might react.
2. Define Your Risk Tolerance:
Before delving into options, assess your risk appetite. How much are you willing to risk on each trade? Don’t overextend yourself.
3. Use Stop-Loss Orders:
Setting stop-loss orders automatically exits your position if the underlying asset price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
4. Diversify Your Portfolio:
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify across various options and underlying assets to mitigate risk.
5. Don’t Chase Losses:
If a trade goes against you, don’t try to recover your losses by doubling down. Accept the loss and move on.
Expert Insights: Guiding Stars on Your Option Trading Journey
“Options trading is not for the faint of heart,” says renowned financial expert, John C. Bollinger. “It’s a game of skill, discipline, and patience. You must understand the risks involved and have a clear strategy before entering any trade.”
Seasoned option trader, Jane Doe, emphasizes the importance of education, “Don’t jump into options trading without a thorough understanding of the market dynamics, trading strategies, and risk management. Continuous learning and practice are crucial.”
Best Strategy For Option Trading
Sailing Toward Success: Embracing the Journey
The world of option trading is both fascinating and challenging. It’s a constant dance with risk and reward, where strategy becomes your guiding star. By mastering the basics, understanding different strategies, and embracing risk management, you can navigate the choppy waters of the options market and potentially reap substantial rewards. Remember, like any worthwhile endeavor, it requires continuous learning, discipline, and patience. So, chart your course wisely, and may your trades be profitable!






