Trading options can be a lucrative way to potentially increase your returns, but it’s important to understand the associated charges that come with it. Understanding charges on options trading will help ensure that you make informed decisions before entering into any trades.
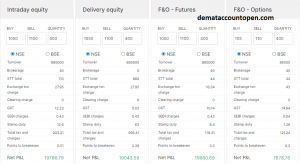
Image: demataccountopen.com
There are various costs involved in options trading, such as the option premium, commissions, exercise fees, and assignment fees. Knowing these charges will help account for them in your trading strategy, enabling you to maximize profits.
The Option Premium
The option premium is the price you pay to purchase an option contract. It represents the cost of the option’s potential profit. The premium is determined by several factors, including the strike price, time to expiration, volatility, and the underlying asset’s price.
Commissions
Commissions are the fees charged by your broker for executing your trades. The commission structure varies among brokers, with some charging a flat fee per trade while others charge a percentage based on the contract size. Consider your trading volume and the broker’s commission rates when choosing a broker.
Exercise Fees
Exercise fees are charged when you exercise an option contract, which is when you buy the underlying asset (in the case of a call option) or sell the underlying asset (in the case of a put option). Exercise fees vary between brokers, so it’s important to check with your broker.

Image: www.youtube.com
Assignment Fees
Assignment fees are charged when your option contract is assigned, which means that the buyer of your call option exercises their right to buy the underlying asset from you, or the buyer of your put option exercises their right to sell the underlying asset to you. Assignment fees are typically charged by the OCC (Options Clearing Corporation) and are usually a small fee.
Other Considerations
In addition to these charges, there are other factors to consider when trading options, such as margin requirements, margin interest rates, and regulatory fees. Make sure you have a solid understanding of these factors before engaging in options trading.
Tips for Minimizing Charges
- Choose the right broker: Compare commission structures and other fees charged by different brokers to find the one that best suits your trading needs.
- Trade during off-peak hours: Options trading is more active during market open hours, resulting in higher commissions. Consider trading during off-peak hours to potentially secure lower commissions.
- Negotiate with your broker: Some brokers may be willing to negotiate commissions, especially if you are a high-volume trader. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your broker and discuss potential discounts.
- Consider using limit orders: When placing an order, use limit orders instead of market orders. Using limit orders puts you in charge of the maximum commission you’re willing to pay for the trade.
FAQs on Charges in Options Trading
Q: What is the typical commission structure for options trading?
A: Commission structures vary between brokers, but most charge either a flat fee per contract or a percentage of the contract value.
Q: How are assignment fees determined?
A: Assignment fees are typically a small fee charged by the OCC and vary based on the underlying asset and the strike price of the option.
Q: Can I negotiate fees with my broker?
A: Yes, some brokers may be willing to negotiate commissions, especially for high-volume traders. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your broker to discuss potential discounts.
Charges On Options Trading
Conclusion
Understanding charges on options trading is key to maximizing your profits. Traders can make informed decisions, minimize fees, and navigate the options market effectively by being aware of these fees.
Are you interested in learning more about options trading and how to minimize charges? Let us know in the comments below.






