Introduction
The world of investing is vast and complex, and the option to trade can be a high-risk, confusing proposition for beginners. But don’t be deterred! With the right guidance, you can simplify the option trading process, grasp the basics, and potentially enhance your financial strategies.

Image: kingtradingsystems.com
Options, in the realm of finance, are contracts granting the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price (known as the strike price) on or before a predetermined date (expiration date). This flexibility can lead to substantial gains but also carries inherent risk, so it’s crucial to approach options trading with a comprehensive understanding.
Basic Concepts
Understanding the basic concepts of options trading is the foundation for successful navigation.
-
Call Option: Gives the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset.
-
Put Option: Grants the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset.
-
Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires.
-
Strike Price: The price at which the buyer can buy or sell the underlying asset.
-
Premium: The price paid by the buyer to acquire the option contract.
Types of Options
Options are classified based on the underlying asset:
-
Stock Options: The underlying asset is a stock.
-
Index Options: The underlying asset is a market index, like the S&P 500.
-
Commodity Options: The underlying asset is a commodity, such as gold or oil.
Trading Options
To trade options, you need a brokerage account that permits options trading. The process involves:
-
Selecting the Option: Identify the type of option (call or put), expiration date, and strike price.
-
Placing the Order: Specify the number of contracts, price, and type of order (limit or market).
-
Exercising the Option: If the option is profitable, you can exercise it before the expiration date.

Image: www.youtube.com
Strategies for Beginners
For beginners, employing simple yet effective strategies can elevate the probability of success:
-
Covered Call: Sell a call option against an underlying asset you own, generating premium income and limiting potential profits.
-
Cash-Secured Put: Sell a put option backed by cash in your account, earning premium and potentially acquiring the underlying asset at a lower price.
-
Bull Call Spread: Buy a deep in-the-money call option (low strike price) and simultaneously sell an out-of-the-money call option (higher strike price) with the same expiration date.
Options Trading For Beginners & Dummies
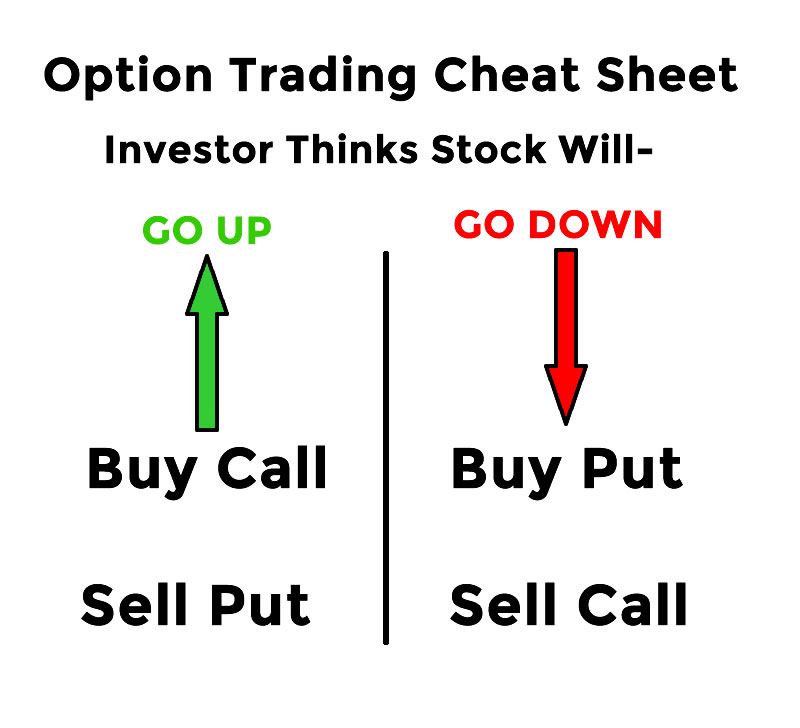
Image: alphabetastock.com
Conclusion
Options trading can introduce powerful tools for financial growth, but bear in mind the inherent risk involved. By comprehending the basics, exploring the different types of options, and adopting prudent strategies, you can unlock the potential of options trading while mitigating risks. Remember, education is paramount in the financial realm; seek guidance, explore educational resources, and continue refining your trading skills over time.






