Unveiling the World of Options
The world of investing can be daunting, especially when navigating the realm of options trading. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding the ins and outs of options trading is crucial. This comprehensive guide, inspired by Investopedia, will unravel the complexities of options trading, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed investment decisions.
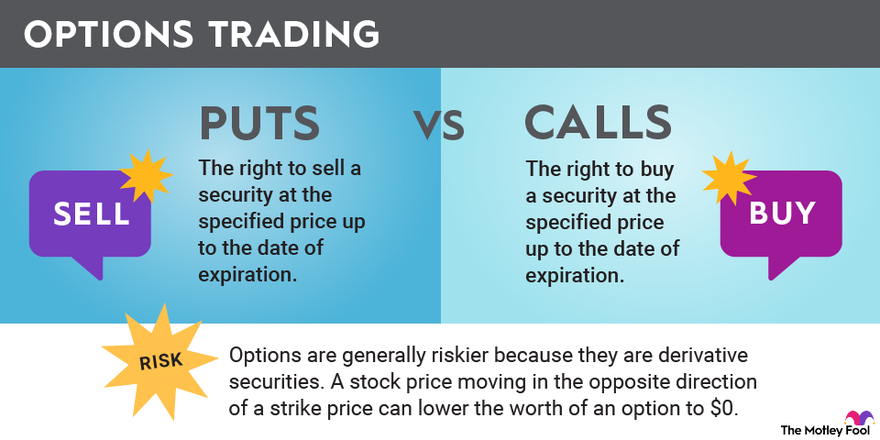
Image: www.fool.com
What are Options?
Options are financial contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a specified price (exercise price) on or before a certain date (expiration date). This flexibility offers traders the potential to profit from upward (call) or downward (put) price movements of the underlying asset.
Historical Roots
The concept of options trading dates back to ancient Greece, where merchants used them to hedge against price fluctuations in their commodities. The formalization of options contracts occurred in the 17th century, with the Amsterdam Stock Exchange introducing standardized options contracts in 1602. Over the centuries, options trading has evolved into a sophisticated and widely used tool in modern financial markets.
Understanding Options Mechanics
At its core, an option contract involves three key parties: the buyer, the seller (writer), and the clearinghouse. The buyer pays a premium to the seller in exchange for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price. The seller receives the premium and takes on the obligation to deliver or purchase the asset if the option is exercised.

Image: fipocuqofe.web.fc2.com
Call and Put Options
Call options give the buyer the right to purchase the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date. If the market price of the underlying asset rises above the strike price, the buyer can exercise the call option, buying the asset at a profit.
Put options, on the other hand, provide the buyer with the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date. If the market price of the underlying asset falls below the strike price, the buyer can exercise the put option, selling the asset at a profit.
Benefits and Risks of Options Trading
Options trading offers investors several benefits, including:
- Increased Investment Flexibility: Options provide traders with the ability to take both long and short positions, allowing them to speculate on both上昇 and下降 trends.
- Enhanced Market Positioning: Options can be used to hedge or mitigate risk by locking in a specific price for a future purchase or sale.
- Leverage and Efficiency: Options allow investors to control a substantial underlying asset value with a relatively small investment amount, offering potential for significant returns.
However, it’s important to note that options trading also carries inherent risks:
- Loss of Premium: If the underlying asset price does not move in the desired direction or the option contract expires worthless, the buyer may lose the entire premium paid for the option.
- Limited Timeframe: Options have a limited lifetime, and if they are not exercised or sold before the expiration date, they become worthless.
- Unforeseen Market Events: Unexpected events such as wars, political unrest, or economic crises can impact option values.
Expert Advice and Tips
To navigate the world of options trading effectively, consider these expert tips:
- Thorough Research: Delve into the fine print of option contracts, understand the complexities of the underlying asset, and stay informed about market news and sentiment.
- Clearly Defined Strategy: Develop a clear investment plan that outlines your goals, risk tolerance, and exit strategy.
- Risk Management: Determine your risk appetite and manage it attentively. Consider using techniques such as stop-loss orders or position sizing to safeguard your investments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between a call option and a put option?
A: Call options give the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset, while put options provide the right to sell it.
Q: How much does it cost to trade options?
A: The cost of an option is determined by several factors, including the underlying asset price, volatility, interest rates, and the time remaining until expiration.
Q: Can I make money by selling options?
A: Yes, selling (or writing) options can generate income if the underlying asset behaves in a way that makes the option contract expire worthless.
Options Trading Explained Investopedia
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CoveredCall-943af7ec4a354a05aaeaac1d494e160a.png)
Image: www.investopedia.com
Conclusion
Options trading offers a diverse range of investment opportunities and opportunities for capital growth. By comprehending the fundamentals, potential rewards, and inherent risks, you can unlock the potential of this dynamic market. Embark on your journey into the realm of options trading with confidence, knowing that you have the knowledge and insights to navigate this exciting landscape.






