The realm of financial markets presents an array of investment opportunities, each with its distinct characteristics and risk-reward dynamics. Futures and options, two derivative financial instruments, have garnered significant attention among traders due to their versatility and potential for profit generation. Understanding the fundamental differences between these instruments is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the financial landscape effectively. This article delves into the intricacies of futures and options, shedding light on their respective roles, advantages, and risks to empower traders with the knowledge necessary for informed decision-making.
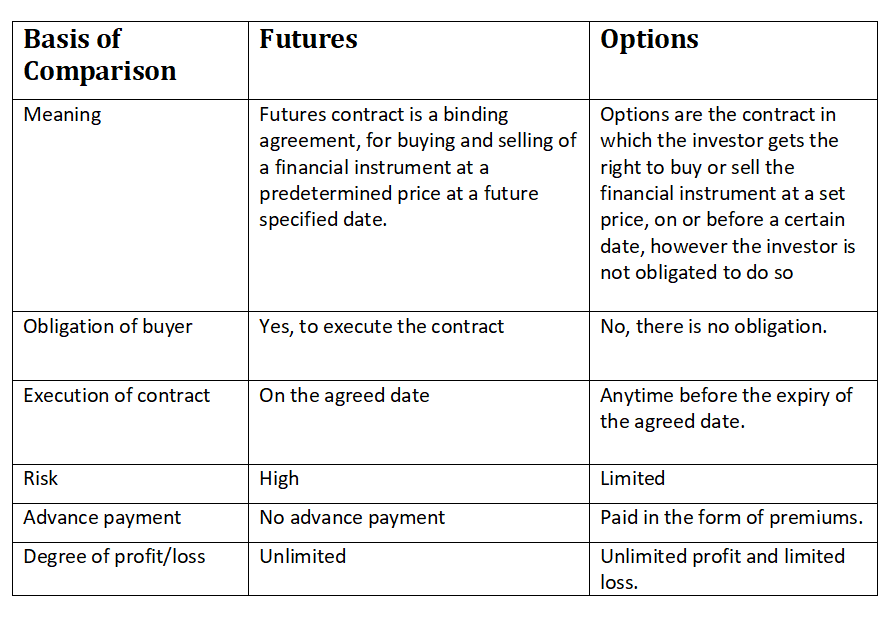
Image: www.5paisa.com
Futures: A Primer
Futures contracts are agreements between two parties to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on a predetermined future date. They are standardized contracts, meaning their terms, including the underlying asset, quantity, expiration date, and settlement price, are predefined and exchange-traded. Commodities, currencies, and equity indices are the most common underlying assets for futures contracts.
Leverage: A Double-Edged Sword
Futures offer the advantage of leverage, enabling traders to control a substantial underlying asset value with a relatively small initial investment. This aspect allows for both amplified profits and losses, making risk management paramount.
Margin Requirements: The Necessary Safety Net
Margin requirements are an integral aspect of futures trading. Traders are required to deposit a certain percentage of the contract’s value as margin, acting as collateral to cover potential losses. Margin calls may occur when losses exceed the initial margin, prompting traders to deposit additional funds or face contract liquidation.
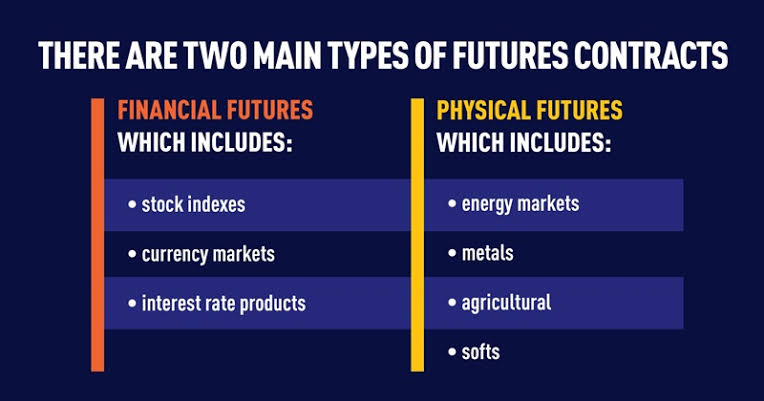
Image: buddymantra.com
Options: A Versatile Tool
Unlike futures, options contracts confer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price on or before a specific expiration date. This flexibility provides traders with a wider range of strategies, such as hedging, speculation, and income generation.
Types of Options: A Spectrum of Strategies
Options come in two primary forms: calls and puts. Call options confer the right to buy the underlying asset, while put options grant the right to sell. Traders can tailor their strategies by selecting the appropriate combination of option type, strike price, and expiration date.
Premiums: The Cost of Flexibility
Options have an intrinsic value, representing the potential profit if the contract is exercised before expiration. However, traders must pay a premium to acquire an option contract, which represents the market’s assessment of the likelihood of the contract being profitable.
Futures vs Options: A Comparative Analysis
The primary distinction between futures and options lies in their inherent obligations. Futures contracts carry an obligation to buy or sell the underlying asset, while options provide the right but not the obligation to do the same. This fundamental difference impacts the risk profile and potential returns associated with these instruments.
Hedging Strategies: Managing Risk
Futures and options both serve as valuable risk management tools. Hedgers use futures to lock in prices, reducing exposure to future price fluctuations in the underlying asset. Similarly, options can be employed to create customized hedging strategies, offering flexibility and tailored protection.
Speculative Opportunities: The Pursuit of Profits
Futures and options can be employed for speculative purposes, seeking profit from price movements in the underlying asset. Futures offer greater leverage, magnifying both potential gains and losses. Options, on the other hand, provide a controlled risk environment, limiting potential losses to the premium paid.
Income Generation: Harvesting Profits
Selling options can generate income through premiums received, known as option writing. Covered calls and cash-secured puts are common strategies employed by traders to generate income while potentially limiting downside risk.
Difference Between Trading Futures And Options
https://youtube.com/watch?v=WsTAgI2pyiM
Conclusion: Empowering Traders with Knowledge
Navigating the financial markets requires a thorough understanding of the available instruments and their nuances. This article has shed light on the differences between futures and options, highlighting their respective advantages and risks. By grasping these complexities, traders can make informed decisions, tailoring their strategies to their specific investment objectives and risk tolerance. Remember, knowledge is power, and in the realm of financial markets, it is the key to unlocking success.







