The financial world offers a vast array of investment opportunities, including options and futures trading. While both instruments share similarities, they also possess distinct characteristics that cater to diverse risk appetites and investment objectives. This article delves into the intricacies of options vs. futures trading, providing a comprehensive guide to help investors make informed decisions.

Image: tradeoptionswithme.com
Introducing Options and Futures: The Basics
Options contracts grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specified date. Futures contracts, on the other hand, obligate the buyer to purchase or the seller to deliver the underlying asset at a set price on a future date. Both instruments offer investors the potential for leverage, allowing them to control significant positions with a relatively small capital outlay.
Key Differentiators: A Deeper Dive
Expiration: Options contracts have a finite lifespan, expiring on a specific date. Futures contracts, however, continue trading until the delivery date or are closed out earlier.
Obligations: Option holders can choose to exercise their right to buy or sell the underlying asset, but they are not obligated to do so. Futures contracts, on the other hand, create a binding commitment for both parties.
Customization: Options contracts are highly customizable, allowing investors to tailor strike prices, expiration dates, and option types (calls or puts) to meet their specific requirements. Futures contracts, while less flexible, offer standardized contract specifications.
Margin Requirements: Options trading typically requires lower margin requirements than futures trading, making them more accessible to retail investors with limited capital.
Applications and Strategies
Options Trading: Options contracts are often used for hedging portfolios, speculating on future price movements, and generating income through premiums. Popular strategies include covered calls, protective puts, and straddles.
Futures Trading: Futures contracts are commonly employed for hedging against price fluctuations, fulfilling physical delivery obligations, and speculating on commodity or financial market trends. Strategies such as calendar spreads, basis trades, and arbitrage are prevalent.
Image: www.5paisa.com
Risks and Considerations
Understanding the inherent risks associated with options and futures trading is crucial. Options trading involves potentially unlimited losses if price movements do not align with expectations, while futures trading carries the risk of substantial losses due to market volatility and margin requirements.
Choosing the Right Instrument
The choice between options and futures trading depends on an investor’s risk tolerance, investment objectives, and individual circumstances. Options offer greater flexibility and income-generating potential but come with higher potential losses. Futures provide lower upfront costs and the ability to gain exposure to underlying assets, but they also carry the burden of potential unlimited losses.
Option Vs Future Trading
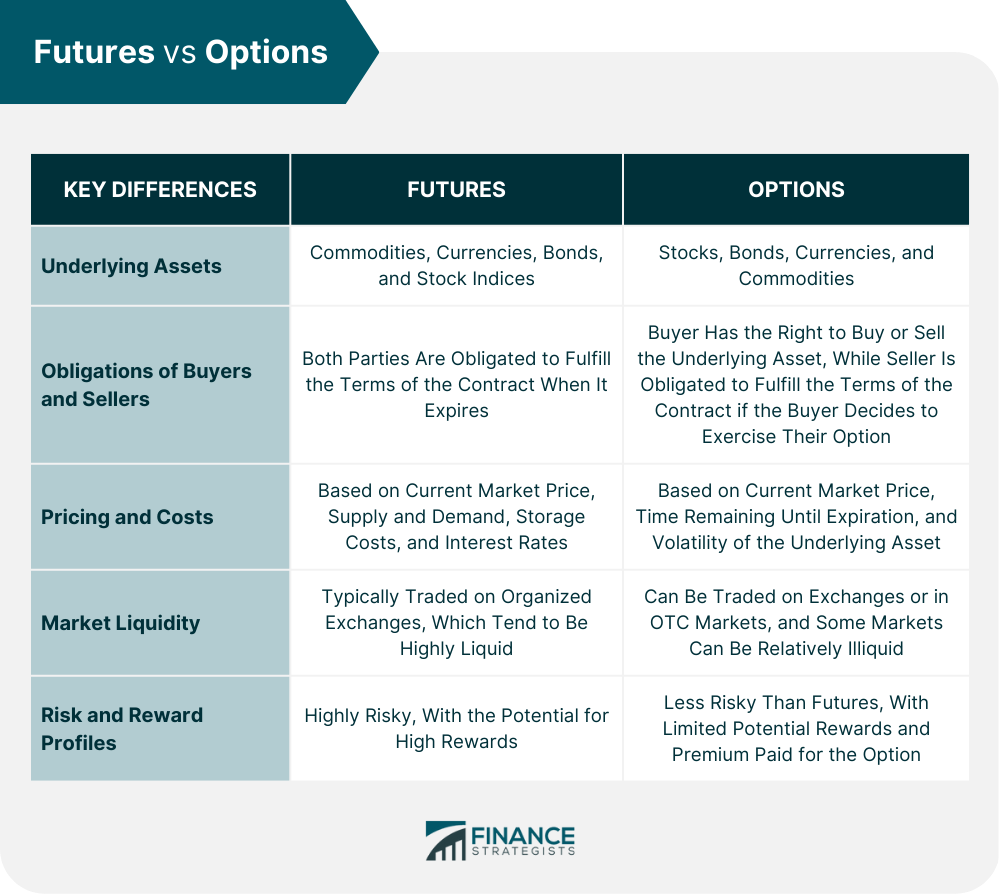
Image: www.financestrategists.com
Conclusion
Options and futures trading offer distinct opportunities for investors seeking to manage risk, speculate on market movements, or generate income. By understanding the intricacies and differences between these instruments, investors can make informed decisions that align with their investment goals and risk appetites. Whether it’s protecting portfolios, capitalizing on volatility, or diversifying investments, options, and futures trading provide valuable tools for savvy investors.






