Breaking Down the Basics: What’s the Difference?
When delving into the realm of options trading, comprehending the concepts of net credit and net debit is crucial for navigating this complex financial landscape. Let’s dive into the intricacies of these terms to illuminate their significance and guide you toward informed trading decisions.
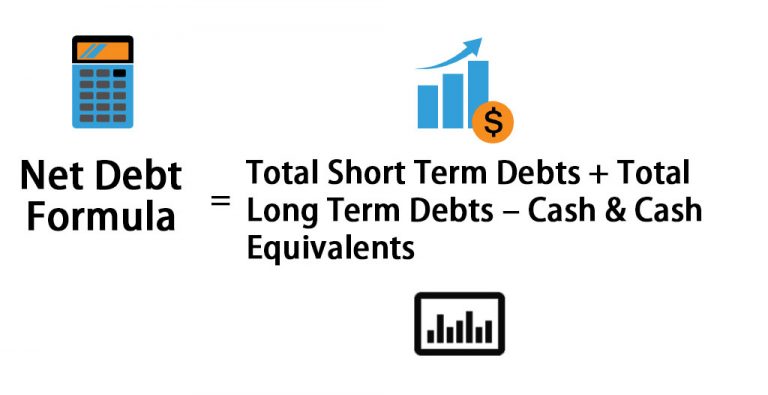
Image: www.educba.com
In the world of options trading, net credit refers to a scenario where you receive a premium payment (known as a credit) upon selling an option contract. When you enter a net debit transaction, you pay a premium (known as a debit) to acquire an option contract. Simply put, net credit implies receiving money upfront, while net debit signifies paying money upfront in options trading.
Net Credit: A Closer Examination
When engaging in net credit trading, you are essentially selling an option contract to another party, granting them the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price. In return, they compensate you with a premium payment. This premium payment signifies the amount of money you receive upfront for selling the option contract. Net credit transactions are often employed when traders anticipate a stable or declining market and believe the option will not be exercised.
Net Debit: Delving into the Details
In contrast, net debit trading involves purchasing an option contract from another party, gaining the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price. For this privilege, you pay a premium to the seller upfront. The rationale behind net debit transactions often lies in anticipation of price movements that favor exercising the option contract. By paying a premium, you secure the potential to profit from favorable market conditions.
Understanding the Impact: Strategic Implications
The decision between net credit and net debit strategies hinges on the trader’s market outlook and risk tolerance. Net credit transactions carry less risk as the trader receives a premium upfront. However, the potential profits are also capped at this premium amount. Conversely, net debit transactions offer the chance for greater profits but come with higher risk as the trader must pay a premium upfront.
Traders opt for net credit strategies when they anticipate minimal price fluctuations or believe the option will expire worthless. On the other hand, net debit strategies are often favored when traders anticipate significant price movements that could result in the profitable exercise of the option contract.
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Net Credit Vs Net Debit In Options Trading
![Net Credit Sales - [ Definition, Example, Formula Calculation ] - Guide](https://www.stockmaster.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/net-credit-sales.jpg)
Image: www.stockmaster.com
Navigating Options Trading: Key Takeaways
To navigate the complexities of options trading effectively, it’s essential to remember that net credit involves receiving a premium for selling an option contract, while net debit entails paying a premium to acquire an option contract. Traders should carefully consider market conditions and their risk tolerance when deciding between net credit and net debit strategies.
Additionally, it’s crucial to seek guidance from experienced financial professionals and thoroughly understand the risks involved before engaging in options trading. By mastering the nuances of net credit and net debit, traders can position themselves to make informed decisions and potentially reap the rewards of this dynamic financial arena.






