Navigating the Complexities of Insider Information and Market Advantage
Imagine a scenario where you overhear a private conversation about a major company’s upcoming acquisition. With this newfound knowledge, you rush to purchase stock in the target company, hoping to reap the windfall that follows the announcement. While tempting, such actions raise ethical and legal concerns, potentially falling into the realm of insider trading. But what if the information you acted upon was not illegally obtained but granted to you through your position as a company insider? Is exercising stock options based on this information considered insider trading? Join us as we delve into the complex world of insider trading and stock options, unraveling the intricacies that govern this delicate balance.
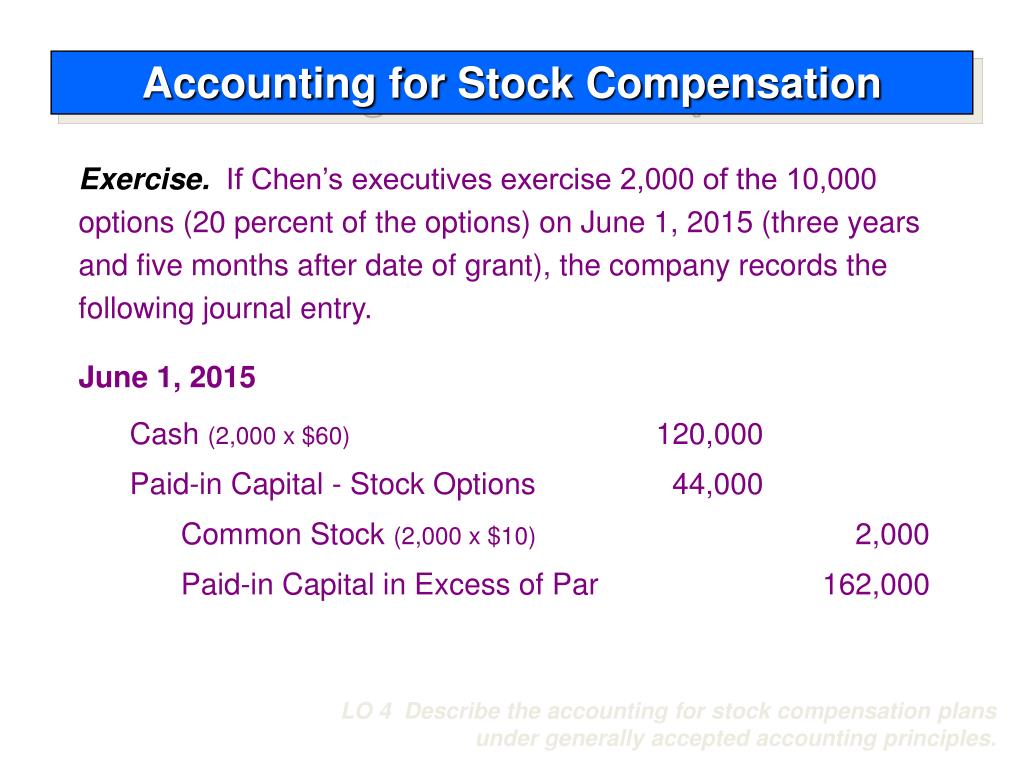
Image: exercisewalls.blogspot.com
Insider trading, in its most straightforward definition, refers to the buying or selling of stocks or other securities while possessing material nonpublic information about the company. This nonpublic information can range from financial performance updates to upcoming mergers or acquisitions. The core principle behind insider trading regulations is the prevention of unfair advantages, ensuring equal access to information for all market participants. However, the exercise of stock options by insiders presents a unique set of considerations, where the lines between acceptable and unacceptable actions can blur.
Stock options are employee compensation tools granted by companies to their employees, typically executives or key personnel. These options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to purchase a certain number of shares of the company’s stock at a set price, known as the exercise price. When the stock price rises above the exercise price, the holder can choose to exercise their options, profiting from the difference between the current stock price and the exercise price.
In the case of insiders, they may have access to material nonpublic information that could influence the stock’s price. Exercising stock options while in possession of such information raises questions about whether they are taking unfair advantage of their privileged knowledge. To address this concern, companies implement specific policies and regulations governing when insiders can exercise their stock options.
Insider trading regulations vary across jurisdictions, with different countries and regulatory bodies adopting their own frameworks. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) enforces insider trading laws. According to the SEC, insiders must exercise stock options within specific trading windows, typically before or after the release of earnings reports or other market-moving information. This ensures that insiders are not trading on nonpublic information.
In addition, companies may have their own internal policies governing insider trading. These policies often include blackout periods, during which insiders are prohibited from exercising stock options or trading company securities. Companies may also require insiders to report their stock option transactions to the company for review and approval.
While the exercise of stock options by insiders can be a complex matter, there are clear guidelines and regulations in place to prevent insider trading and ensure fair market practices. Companies have a responsibility to implement robust insider trading policies, and insiders must adhere to these rules to avoid violating the law and damaging market integrity.
Despite the regulations and policies aimed at preventing insider trading, cases do arise where individuals engage in illegal insider trading activities. In such cases, regulators and law enforcement agencies investigate and take appropriate actions, including imposing fines, sanctions, and even criminal charges.
Understanding the complexities of insider trading and stock options is essential for both insiders and market participants. Insider trading undermines the fairness of the market and can erode investor confidence. By adhering to the established rules and regulations, companies and insiders can help ensure a level playing field, where all investors have equal access to information and fair opportunities to participate in the market.
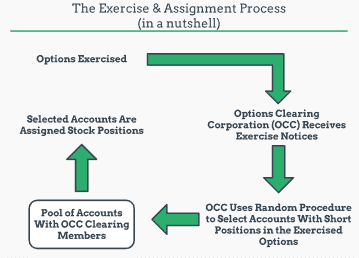
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Exercise Stock Options Insider Trading

Image: learn.valur.io






