The stock market can be a daunting place, filled with jargon and complex strategies. But for those seeking to diversify their portfolio and potentially maximize returns, there’s a whole new world of possibilities beyond simply buying and selling stocks: options trading. Imagine this: you’re at a café, sipping your latte and scrolling through your phone. Suddenly, you come across a news article about a promising new technology company that’s about to release its latest product. You’re intrigued, but you’re not sure if you want to invest in the company’s stock just yet. Enter options trading – a tool that allows you to speculate on the future price movement of a stock without actually owning the stock itself.
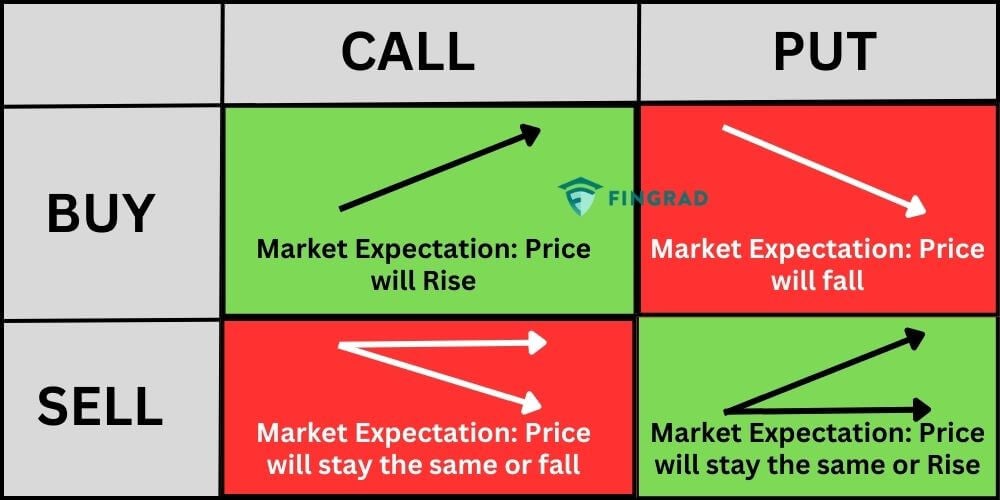
Image: tradebrains.in
Options trading, while seemingly mysterious, can be demystified with a little understanding. It’s a powerful tool that can offer both significant potential gains and substantial risks. Understanding how it works is crucial to navigating its intricacies and making informed decisions. This guide aims to provide you with a comprehensive overview of this intriguing financial instrument, empowering you to make informed choices about your investment strategy.
Demystifying Options Trading: What Are Options and How Do They Work?
In essence, options are contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset (like a stock) at a specific price (the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). Think of it like a ticket to a concert, giving you the right to attend but not forcing you to. The key difference here is that instead of a concert, we’re talking about the price of an asset.
There are two main types of options contracts:
- Call options give you the right to buy the underlying asset. You would buy a call option if you believe the price of the asset will go up.
- Put options give you the right to sell the underlying asset. You would buy a put option if you believe the price of the asset will go down.
The person who sells the option is known as the writer. They receive a premium for selling the option, which is basically the price you pay to buy the right to buy or sell the stock. This premium represents the potential risk the writer takes on by agreeing to your terms.
Examples of How Options Trading Can Be Used:
Let’s illustrate this with some real-world examples:
Scenario 1: The Bullish Investor
You believe the price of Apple stock will rise in the next few months. Instead of buying shares directly, you buy a call option on Apple stock with a strike price of $150 and an expiration date of June 2024. The current price of Apple stock is $145, and you pay a premium of $5 per share for the option. If the price of Apple stock rises to $160 by June 2024, you can exercise your option, buying the shares for $150 and immediately selling them in the market for $160, making a profit of $10 per share. Conversely, if the Apple stock price declines, your option will expire worthless, and you’ll lose only the premium paid.

Image: www.tradestation.com
Scenario 2: The Bearish Investor
You’re concerned about the future of Tesla stock and believe its price will decline. Instead of shorting the stock, which involves borrowing and selling shares, you can buy a put option on Tesla stock with a strike price of $250 and an expiration date of December 2024. The current price of Tesla stock is $260, and you pay a premium of $7 per share for the put option. If the price of Tesla stock falls to $230 by December 2024, you can exercise your option, selling the stock for $250 and buying it in the market for $230, netting a profit of $20 per share.
The Compelling Advantages of Options Trading
Options trading offers a unique set of advantages that make them an attractive tool for investors:
- Leverage: Options offer leverage, allowing you to control a large amount of stock with a smaller investment compared to buying or selling shares directly. A small investment in an option can potentially generate significant returns if the underlying asset moves in your favor. However, this leverage also magnifies potential losses.
- Flexibility and Diversification: Options provide flexibility in adjusting your investment strategy, allowing you to profit from both bullish and bearish market conditions. This flexibility makes them a valuable tool for diversifying your portfolio.
- Limited Risk: When you buy an option, your maximum loss is limited to the premium paid, unlike buying stock, where your potential loss is unlimited. This limited risk characteristic is a key advantage for risk-averse investors.
The Risks of Options Trading
Despite the attractive benefits, it’s crucial to acknowledge the substantial risks associated with options trading. Unfamiliarity with the mechanics of options can lead to significant losses, and the leverage factor can magnify these losses. Options trading requires a deep understanding of market dynamics, price movements, and time decay, and it’s essential to carefully research and learn the intricacies before venturing into this challenging world
Important Considerations for Options Traders
As you start your journey into options trading, remember these key principles:
- Start Small: Begin with small positions, gradually increasing your investment as you gain experience and confidence.
- Educate Yourself: Options are complex financial instruments, and a thorough understanding of their workings is essential for success.
- Manage Your Risk: Risk management is paramount. Establish stop-loss orders, set realistic profit targets, and diversify your portfolio across different options and underlying assets.
- Use a Brokerage Account: Choose a reputable brokerage account that offers options trading services and provides educational resources. They often have online platforms with tools that can streamline your trading experience.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of market news and developments. Follow reputable financial sources and economic indicators.
Frequently Asked Questions about Options Trading
Q: What are the benefits of trading options compared to buying shares?
Options offer leverage, allowing you to control a larger number of shares with a smaller investment than buying the actual shares. They also provide the potential to profit from market volatility, limited risk and potential for diversification of your portfolio.
Q: What are the risks associated with options trading?
Options trading is a risky endeavor, and losses can exceed the premium paid. The leverage factor, time decay and rapid price fluctuations can amplify losses. It’s crucial to understand the risks, manage them proactively, and educate yourself thoroughly.
Q: What are some key things to consider when choosing an options strategy?
Think about your investment goals, risk tolerance, market outlook, and the specific characteristics of the underlying asset. Research different options strategies, identify those that align with your objectives, and understand the risks associated with each strategy.
Q: What are some good resources for learning more about options trading?
There are a wealth of online and offline resources available for learning about options trading, including reputable websites, educational videos, books, and online courses. Look for materials from reputable financial institutions, universities, and experienced traders.
What’S Options Trading
Conclusion: Embark on Your Options Trading Journey
Options trading offers a world of possibilities, but it’s a complex field that requires careful planning, risk management, and ongoing learning. While it can be a rewarding avenue for investors seeking diversification and potential for high returns, remember that it’s essential to start small, educate yourself thoroughly, and manage your risk diligently. Are you ready to explore the realm of options trading? If so, start with these resources and gain the knowledge you need to make informed decisions.






