Have you ever wondered about the whispers of “options trading” in the financial world, a concept often shrouded in mystery and technical jargon? It’s a realm where savvy investors can harness the power of leverage to amplify their potential gains, but also face the risk of significant losses. This article unravels the world of stock market options, providing a comprehensive guide for both curious newcomers and seasoned investors seeking to expand their knowledge.
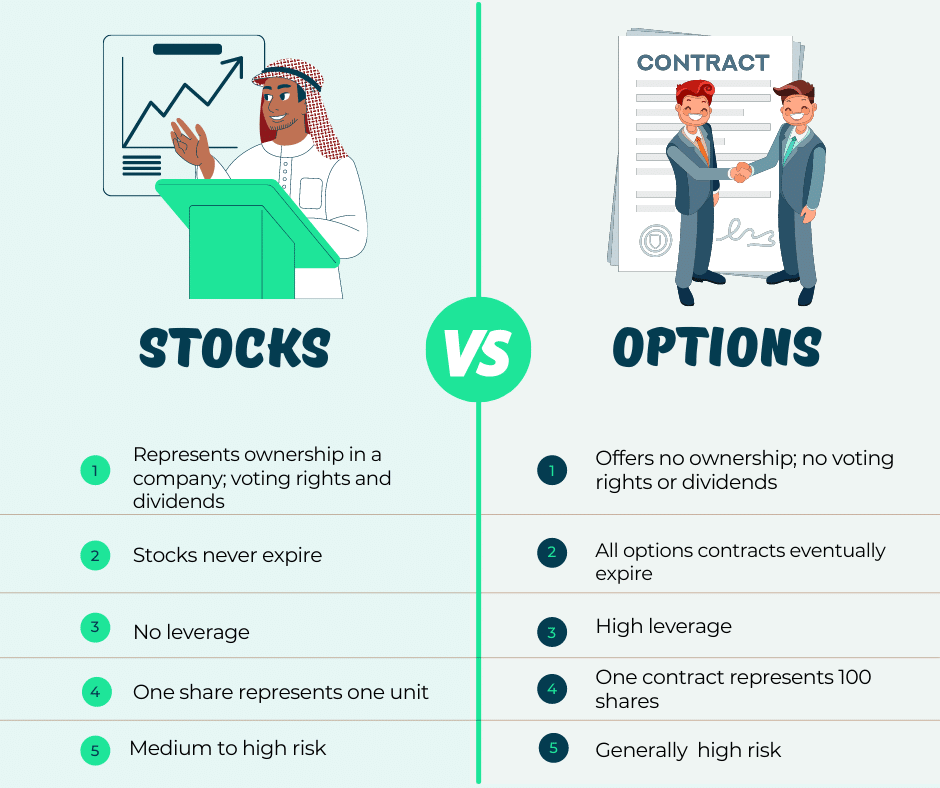
Image: idahc.com
Options trading is a complex yet fascinating aspect of the stock market, granting investors the right—but not the obligation—to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. While it presents the potential for amplified returns, understanding its intricacies is paramount to navigating its inherent risks. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting your financial journey, grasping the fundamentals of options trading empowers you to make informed decisions and potentially reap significant rewards.
Understanding the Basics: Options Defined
What are Options Contracts?
At its core, an options contract is an agreement that gives the buyer the right—not the obligation—to buy or sell an underlying asset, such as a stock, at a specific price (the strike price) within a set period (the expiration date). These contracts are traded on exchanges like the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), similar to how stocks are traded.
Types of Options: Calls and Puts
There are two primary types of options:
- Call Options: Give the buyer the right to purchase the underlying asset at the strike price. Call buyers hope the stock price rises, allowing them to exercise their option profitably by purchasing the stock at the lower strike price and selling it in the open market for a higher price.
- Put Options: Give the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. Put buyers hope the stock price falls, enabling them to exercise their option by purchasing the stock in the market (at a price lower than the strike) and immediately selling it to the option seller, pocketing the difference.

Image: mungfali.com
Delving Deeper: Understanding Options Terminology
To truly appreciate the intricacies of options trading, a grasp of its specialized vocabulary is crucial:
Strike Price: The Key Price Point
The strike price is the predetermined price at which the buyer can buy or sell the underlying asset when exercising the option. It’s like a set price point that the option buyer is aiming to achieve.
Expiration Date: The Time is of the Essence
The expiration date is the final day on which the option contract can be exercised. After this date, the option expires, and its value can plummet to zero.
Premium: The Price of the Right
The premium is the price the buyer pays for the option contract. It’s the cost of acquiring the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at the strike price. The premium is influenced by factors such as the underlying asset’s price, volatility, time until expiration, and interest rates.
Intrinsic Value: The Potential Gain
The intrinsic value of an option is the difference between the strike price and the current market price of the underlying asset. For a call option, it’s the difference between the current market price and the strike price, and for a put option, it’s the difference between the strike price and the current market price. Intrinsic value is the minimum value an option can have, as the buyer can always exercise the option if they stand to gain financially.
Time Value: The Uncertainty Factor
Time value is the portion of the option premium that represents the possibility of the underlying asset’s price moving in the buyer’s favor before expiration. It’s the value tied to the uncertainty of future price movements. The longer the time until expiration, the higher the potential for movement, and thus the higher the time value.
Strategies: Navigating the Options Landscape
Options trading provides a myriad of strategies, catering to diverse investment goals and risk appetites. Here’s a peek at some of the most common strategies:
Covered Call Writing: Generating Income While Owning Stock
Investors who believe the price of a stock will remain relatively stable or even rise slightly might consider selling a covered call. In this strategy, the investor sells a call option on a stock they already own. If the stock price stays below the strike price, the investor gets to keep the premium they received for selling the call. However, if the stock price rises above the strike price, the call buyer will exercise their option, forcing the investor to sell their stock at the strike price. This limits potential upside gain but generates income from the premium.
Cash-Secured Put Writing: A Potential for Profit
Cash-secured put writing involves selling a put option on a stock while holding sufficient cash to cover the purchase of the stock at the strike price if the option is exercised. If the stock price stays above the strike price, the investor keeps the premium received for selling the put. If the stock price falls below the strike price, the option is exercised, forcing the investor to buy the stock at the strike price. This strategy can potentially generate income but also exposes investors to significant losses if the stock price falls sharply.
Straddle: Betting on Volatility
A straddle strategy involves simultaneous buying of a call and a put option on the same underlying asset with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy profits if the underlying asset’s price moves drastically in either direction—up or down—due to increased volatility. It’s less profitable if the price stays relatively stable, making it a risky strategy for investors hoping to capitalize on significant price fluctuations.
Strangle: A More Flexible Approach to Volatility
A strangle strategy is similar to a straddle but involves buying a call option and a put option with different strike prices. The call’s strike price is above the current market price, and the put’s strike price is below the current market price. This allows the investor to profit from a greater range of price movements compared to a straddle but at a lower cost.
The Risks of Options Trading: Navigating Volatility and Losses
While options trading offers the potential for significant gains, it’s essential to recognize and understand the inherent risks involved. The leverage associated with options can amplify both gains and losses, making responsible risk management crucial.
Amplified Losses: Understanding Leverage
Options leverage allows investors to control a larger position in the underlying asset with a smaller investment. This amplifies potential gains, but it also amplifies losses. A small movement in the underlying asset’s price can result in substantial gains or losses on an options position.
Expiration Risk: The Pressure of Time
The expiration date is a crucial factor in options trading. As the expiration date approaches, the time value of an option decreases, putting pressure on the option buyer to make a decision—exercise the option or let it expire worthless.
Volatility Risk: Riding the Waves of Uncertainty
Options are sensitive to price volatility. Increased volatility can work in favor of the option buyer, boosting the potential for profit if the price moves in their direction. But it can also work against them, leading to significant losses.
Making Informed Decisions: Practical Tips for Success
To navigate the world of options trading effectively, adopt these strategies and consider these crucial factors:
Thorough Research and Planning
Never enter an options trade without conducting thorough research. Understand the underlying asset, its current price, historical price movements, and relevant news and events. Develop a well-defined trading strategy based on your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Start Small and Gradually Increase Your Exposure
Begin with a small amount of capital and gradually increase your exposure as you gain experience and confidence. Avoid overextending yourself and prioritize risk management.
Master Risk Management Strategies
Options trading is inherently risky. Develop and implement effective risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, using margin accounts cautiously, and diversifying your portfolio.
Stay Informed: Keep Track of Market Trends
The stock market is constantly changing. Stay up-to-date on market trends, economic indicators, and industry news that can impact the prices of assets you’re trading.
Consider Professional Guidance
If you’re new to options trading, consider consulting a financial advisor or options trading specialist. They can help you understand the complexities of options trading, develop a suitable strategy, and provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Stock Market Options Trading
Conclusion: A Journey of Learning and Potential
Options trading presents a dynamic and potentially rewarding realm within the stock market. While it involves a degree of complexity and risk, proper understanding, research, and responsible risk management can empower investors to capitalize on opportunities for amplified returns. Embrace the journey of learning, starting small, and constantly refining your knowledge to harness the potential that options trading offers.






