Introduction

Image: tradebrains.in
In the fast-paced world of finance, options trading has emerged as a powerful tool with the potential to amplify gains and provide hedging strategies. However, navigating the complexities of options trading requires a deep understanding of its intricacies and potential pitfalls. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the essential knowledge and insights you need to make informed decisions when venturing into the world of options trading.
Delving into the World of Options
An option contract grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (in the case of call options) or sell (in the case of put options) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specific time frame (expiration date). Unlike futures contracts, which obligate a buy or sell, options provide flexibility and the option to let the contract expire worthless.
Understanding the Underlying Assets
Options can be traded on various underlying assets, predominantly including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies. Comprehending the characteristics and behavior of the underlying asset is paramount in making sound trading decisions. For instance, options on volatile stocks carry a higher premium than those on less volatile ones.
Options Premiums and Greeks
The price of an option, known as its premium, is influenced by several factors, including the underlying asset’s price, volatility, time to expiration, and interest rates. Understanding the interplay of these factors is essential for accurate option pricing.
Additionally, Greek letters (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, theta, and vega) are used to measure the sensitivity of an option’s premium to changes in underlying price and other variables. These Greeks provide valuable insights for risk and profit analysis.
Types of Options Trading Strategies
Options trading offers a diverse range of strategies, each designed for specific market conditions and risk-reward preferences. Common strategies include:
- Covered calls: Selling a call option while owning the underlying asset.
- Protective puts: Buying a put option to protect against a decline in the underlying asset’s value.
- Iron condors: Combining long and short call and put options at different strike prices.
- Straddles and strangles: Simultaneously buying or selling both call and put options at different strike prices.
Assessing Risk and Managing Emotions
Options trading carries inherent risks. It’s crucial to establish realistic risk tolerance levels and manage emotions effectively. Sticking to a predetermined trading plan and refraining from impulsive decisions can help mitigate potential losses.
Seeking Professional Guidance
While this guide provides a comprehensive overview, it’s always recommended to consult with a qualified financial advisor or options specialist before engaging in actual trading. They can provide personalized guidance and assist in developing a tailored trading strategy that aligns with individual financial goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusion
Options trading presents both opportunities and risks. By arming yourself with a solid understanding of the concepts outlined in this guide, you can unlock the potential of options to supplement your investment portfolio. Embarking on this journey with informed decisions and a well-rounded knowledge base will empower you to navigate the complexities of options trading with greater confidence and efficiency.
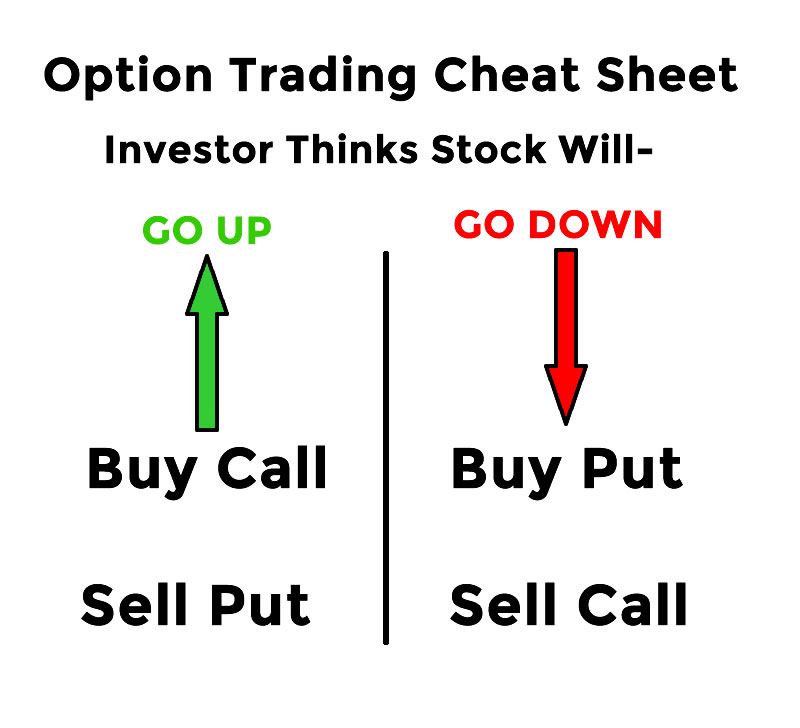
Image: alphabetastock.com
What To Know Before Trading Options






