Understanding the Basics
An option contract is an agreement between two parties, giving the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on or before a specific date. If the value of the underlying fluctuates substantially, the buyer can execute their option to exploit the price differential, profiting from a smart trade.
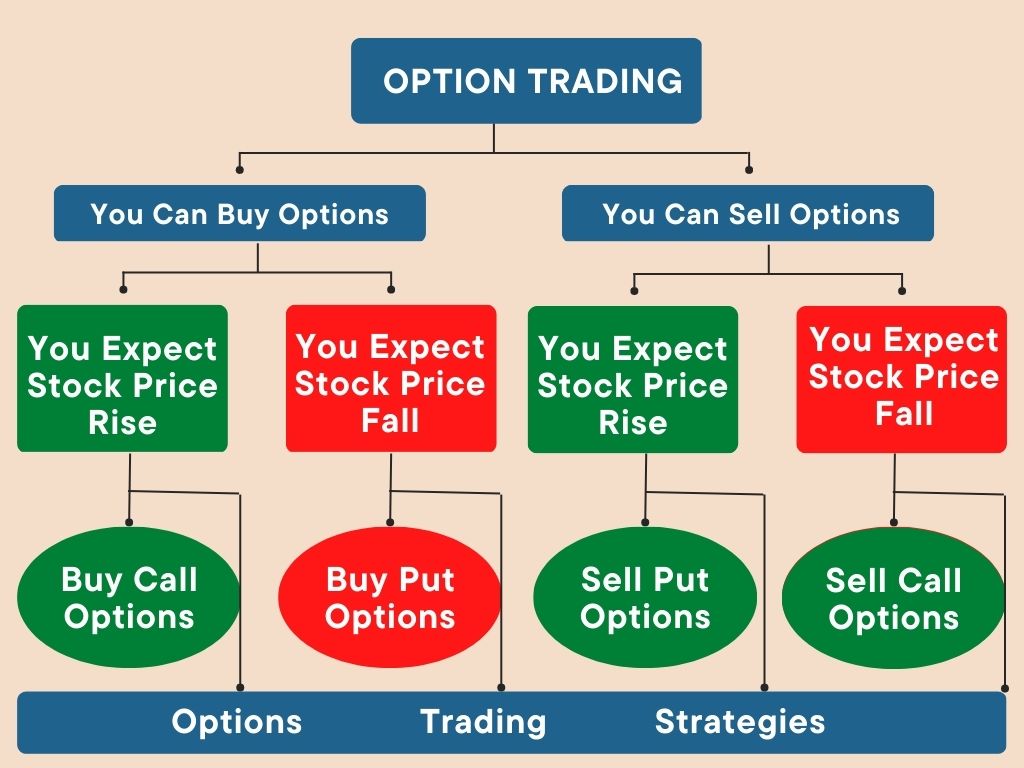
Image: www.ifmcinstitute.com
Anatomy of an Option Contract
An option contract is characterized by specific elements, including the type (call or put), strike price, maturity date, and premium paid by the buyer for the option. A call option allows the buyer to purchase the underlying asset while a put option conveys the right to sell. The strike price is the predetermined price at which the buyer can execute their option right, and the maturity date specifies the expiry time. The premium represents the cost to purchase the option contract, reflecting market factors.
How Options Work
Understanding the mechanics of option contracts is crucial. A call option grants the buyer the right to buy at a predefined price when the underlying asset price rises, offering profit potential in bullish markets. Conversely, a put option benefits from a decline in the underlying value, providing downside protection or profit from price depreciation.
Benefits and Considerations
Options offer unique advantages to traders:
- Leverage: Options amplify returns compared to spot trading, leveraging small investments for higher potential gains.
- Risk Management: They offer flexibility in managing risk by hedging against potential losses or locking in profits.
- Income Generation: Selling options can generate income through premiums, providing additional revenue streams.
However, it is essential to consider the potential risks:
- Loss of Premium: If the option expires unexecuted, the trader loses the premium paid upfront.
- Complex Strategies: Advanced option strategies can increase complexity, requiring a deep understanding and risk tolerance.
- Margin Requirements: When trading options, margin requirements may be higher than when trading the underlying asset.

Image: www.youtube.com
Market Analysis and Tips
Successful option trading involves comprehensive market analysis and strategies. Join specialized forums and monitor social media platforms to stay abreast of market trends, sentiment Shifts, and expert insights. Incorporate tools like technical analysis and Greeks (Delta, Gamma, Theta, etc.) to enhance your decision-making process.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a call and put option?
A: A call option grants the right to buy, while a put option provides the right to sell.
Q: Does an option buyer have to exercise their contract?
A: No, the buyer has the choice to let the option expire or execute it as they see fit.
Q: How is the option premium determined?
A: The premium reflects the intrinsic value, time value, volatility, and risk of the contract.
Q: What factors influence option values?
A: Underlying asset price, strike price, time to maturity, interest rates, and volatility.
What Is Contract In Option Trading
Conclusion
The intricacies of option contracts present intriguing opportunities but also dictate a prudent approach. A deep understanding and strategic implementation, keeping potential risks in mind, can empower traders to exploit market movements, manage risk effectively, and open doors to expanding their trading capabilities. Are you ready to delve into the world of options and start exploring its possibilities?






