Imagine this: you’re sitting at home, sipping your coffee, when you hear on the news that a certain tech company is about to unveil a groundbreaking new product. You know this could send ripples through the market, potentially boosting the company’s stock price. But instead of simply buying shares, you decide to explore an alternative path – the world of options trading. This seemingly complex strategy holds the potential to amplify your gains, but it also carries risks you need to understand. This article delves into the fascinating world of options, unpacking its intricacies to empower you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.

Image: www.strike.money
Options are financial derivatives that give you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. This right to buy is called a “call option,” while the right to sell is known as a “put option.” Options trading is a powerful tool that allows you to tailor your risk and reward profiles, offering a degree of control that traditional stock buying doesn’t. Whether you’re an experienced investor or someone who’s just starting out, understanding the nuances of options can open doors to new strategies and opportunities.
Delving into the Realm of Options: A Deeper Look
Let’s break down the core concepts that define the world of options:
1. Understanding Strike Prices and Expiration Dates
The foundation of options trading lies in the strike price and the expiration date. The strike price is the predetermined price at which you can buy or sell the underlying asset. The expiration date marks the final day you can exercise your option. Think of it like a contract that gives you a specific price and a specific deadline. For example, a call option with a strike price of $100 and an expiration date of January 2024 grants you the right to buy the underlying stock at $100 anytime before January 2024.
2. Exploring the Spectrum of Options: Calls and Puts
- Call Options: A call option grants you the right to buy the underlying asset at a specific price (the strike price). You would buy a call option if you believe the price of the underlying asset will rise. If it does, you can exercise your option, buy the asset at the strike price, and sell it in the market at the higher current price, realizing a profit.
- Put Options: A put option grants you the right to sell the underlying asset at a specific price (the strike price). You would buy a put option if you anticipate the price of the underlying asset to decline. If it does, you can exercise your option, sell the asset at the strike price, and buy it back in the market at the lower current price, pocketing the difference.
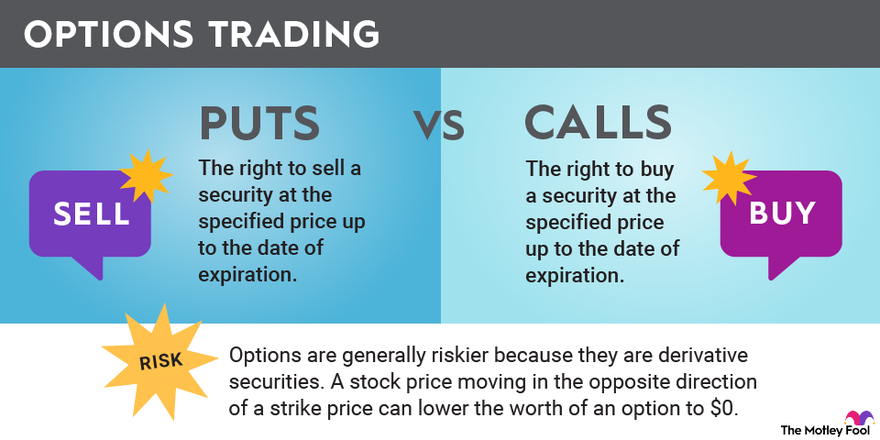
Image: www.fool.com
3. Navigating the Risks and Rewards: The Underlying Asset
The value of an option is directly linked to the price of the underlying asset. The more the underlying asset’s price moves in your favor, the more valuable your option becomes. However, the opposite is true as well. The further the price moves against you, the less valuable your option becomes. This is why it’s crucial to choose the right option for your risk tolerance and investment goals.
4. Understanding the Premium: The Price of Your Right
When you buy an option, you pay a premium, which is the cost of acquiring the right to buy or sell the underlying asset. The premium is determined by factors like the price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time to expiration, and market volatility. The higher the premium, the more you are paying for the right, but also the greater the potential profit or loss.
5. Time Decay: The Ticking Clock
One of the unique aspects of options is time decay. As time passes, the value of an option naturally decreases. This is because the time you have to exercise your option shrinks, reducing its inherent potential. This means that options with shorter timeframes are more susceptible to time decay and therefore have higher premiums.
6. Market Volatility: The Wild Ride
Market volatility is the degree of price fluctuations in the underlying asset. Options are sensitive to volatility, meaning they become more valuable as volatility increases. This is because with increased volatility, the chance of large price movements, potentially in your favor, rises. However, this amplified potential reward comes with amplified risk as well.
7. A Glimpse into the Applications: Unveiling Real-World Uses
Beyond the theoretical framework, options find practical applications across various domains. Some of the common uses include:
- Speculating on Price Movements: Options allow you to take a directional bet on the price of an underlying asset. You can profit from both upwards and downwards movements, without having to actually buy the asset itself.
- Hedging Existing Positions: Options can be used to mitigate potential losses on existing positions. For instance, if you own a stock and are concerned about its price falling, you can buy a put option to limit your downside risk.
- Generating Income: Options can be used to generate income through selling premium. By selling calls or puts, you can collect the premium paid for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset.
Navigating the Options Landscape: Expert Guidance and Actionable Tips
The world of options trading can seem daunting at first. But with the right understanding and approach, you can use this powerful tool to your advantage. Here are some expert insights and actionable tips to get you started:
1. Start Small and Focus on Education:
Don’t jump into options trading with a large sum of money. Instead, start with a small amount and focus on learning the basics. There are numerous resources available online and in libraries that can provide you with the knowledge you need. Remember, understanding the fundamentals is crucial for success.
2. Assess Your Risk Tolerance:
Before you start trading options, make sure you understand the risks involved. Options are leveraged instruments, meaning they can amplify both your profits and losses. Be realistic about your risk appetite and avoid taking on more risk than you can comfortably handle.
3. Diversify Your Portfolio:
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your portfolio by investing in different asset classes and strategies. This can help to reduce your overall risk and improve your chances of success.
Example Of Option Trading
Concluding Thoughts: The Power of Informed Decisions
Options trading offers a unique and versatile approach to investment. By understanding the basics and applying the right strategies, you can take advantage of the potential for amplified returns and gain greater control over your risk. This journey into the world of options can be both challenging and rewarding. Remember, continuous learning, research, and a well-defined strategy are key to navigating this dynamic landscape.






