Options trading has gained immense popularity in recent years, captivating the interest of both seasoned investors and novice enthusiasts alike. This dynamic market, characterized by its multifaceted nature and potential for significant returns, offers a compelling opportunity to speculate on the future direction of assets. However, the complexities of options trading necessitate a thorough understanding of its intricacies to navigate successfully.

Image: www.entrepreneurshipsecret.com
What is Options Trading?
Options contracts are financial instruments that confer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. These contracts offer a unique blend of flexibility and risk management, enabling traders to capitalize on price movements while limiting potential losses. Depending on the trader’s objective, options can be either bought or sold, creating opportunities for both bullish and bearish market scenarios.
Types of Options Contracts
The options market encompasses two primary types of contracts: calls and puts. Call options grant the buyer the right to purchase the underlying asset at the specified strike price, while put options provide the right to sell. Each contract is characterized by its unique set of risk and reward profiles, catering to different trading strategies and risk appetites.
Factors Influencing Options Trading Activity
The activity in the options market is driven by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Underlying Asset Price: The price of the underlying asset exerts a significant influence on options trading activity. As the price fluctuates, so does the demand for options contracts that provide exposure to potential price movements.
- Volatility: The volatility of the underlying asset’s price is a crucial factor in determining options premiums. Higher volatility implies greater uncertainty in future price movements, leading to higher premiums for options contracts.
- Time to Expiration: The time remaining until the expiration date of an options contract impacts its value. Options with longer time to expiration generally command higher premiums due to the increased potential for price fluctuations.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates can influence options pricing by affecting the cost of borrowing and the perceived value of future cash flows. Changes in interest rates can impact the relative attractiveness of options strategies and the overall trading volume.
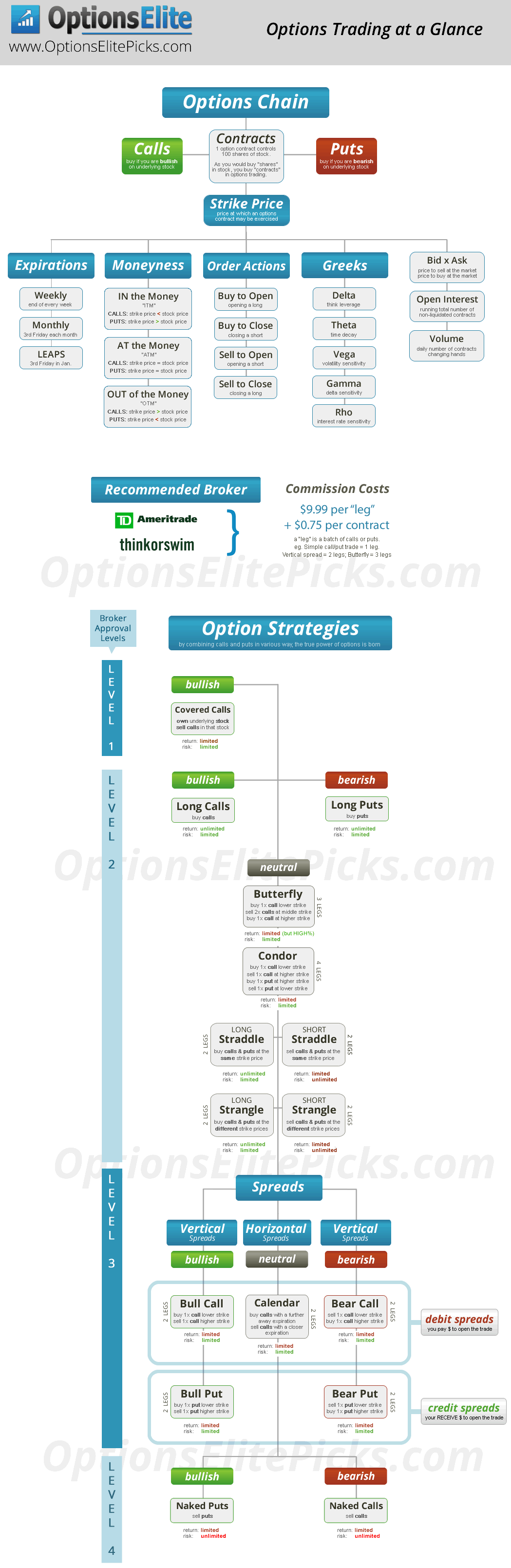
Image: thestockmarketwatch.com
Understanding Options Premiums
The price of an options contract is known as its premium. This premium represents the upfront cost incurred by the buyer of the contract. The premium is determined by a combination of factors, including the factors mentioned above, as well as the prevailing market sentiment and the supply and demand dynamics for the specific options contract.
Recent Trends in Options Trading Activity
The options market has witnessed several notable trends in recent times:
- Growth in Retail Participation: The advent of user-friendly trading platforms and the increasing availability of educational resources have fueled a surge in retail participation in options trading.
- Rise of Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): The introduction of options ETFs has provided investors with a convenient and diversified way to gain exposure to options strategies, further expanding the market’s reach.
- Increased Volatility Trading: The rise of complex volatility trading strategies, such as those employed by hedge funds and quantitative trading firms, has contributed to increased volatility in options markets.
Strategies for Successful Options Trading
Engaging in options trading requires a well-defined strategy and a comprehensive understanding of risk management principles. Some common strategies include:
- Covered Call Writing: This strategy involves selling call options against an underlying asset that the trader already owns. It generates income from the premium received and limits potential upside in the stock.
- Protective Put Buying: By purchasing put options, traders can protect their long positions in stocks from potential downside risks.
- Collar Strategy: This strategy combines the sale of a call option with the purchase of a put option at a higher strike price. It provides limited upside potential while protecting against large losses.
Options Trading Activity
Conclusion
Options trading activity is a vibrant and complex arena that offers both potential rewards and risks. By delving into the intricacies of options contracts, understanding the factors that influence their pricing, and adopting sound trading strategies, investors can navigate this market with greater confidence and position themselves for financial success. Whether you are a seasoned trader or just starting to explore the world of options, continued education and a commitment to risk management are paramount in this ever-evolving field.






