Introduction
Step into the dynamic world of options trading, where financial strategies take center stage. At its core lies the concept of calls and puts, two essential tools that empower traders to navigate market fluctuations like seasoned captains. Whether you’re a financial novice or a seasoned investor, understanding these options will grant you the knowledge to tailor your trading strategies and make informed decisions.
Deciphering the Options Puzzle: Calls and Puts
Picture this: you’re in a bustling marketplace, surrounded by vendors pedaling their goods. Some offer options to buy a specific product at a predetermined price, while others sell options to sell that same product. That, in essence, is the essence of calls and puts in options trading.
In options trading, the owner of a call option holds the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a specified price (the strike price) on or before a certain date (the expiration date). This empowers them with the flexibility to purchase the asset at a potentially favorable price if the market value rises beyond the strike price.

Image: tradebrains.in
On the flip side, the seller of a call option agrees to sell the underlying asset to the buyer at the strike price if they exercise their right to buy. In this setup, the seller receives a premium for granting the buyer this option and stands to profit if the market value remains below the strike price.
Puts, on the other hand, grant the holder the right to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price on or before expiration. When the market value falls below the strike price, the put gives the buyer the advantage of selling the asset at a potentially favorable price.
Conversely, the seller of a put option takes on the obligation to buy the underlying asset from the buyer if they exercise their right to sell. The seller collects a premium for granting this option and benefits when the market value remains above the strike price.
Examples to Illuminate: A Closer Look at Calls and Puts
Let’s illustrate these concepts with real-world examples. Suppose you believe the stock price of Apple will rise in the coming months. You could purchase a call option with a strike price of $150, giving you the right to buy Apple shares at $150, regardless of their actual market value at expiration. If the market price climbs to $170, you can exercise your option and buy the shares for $150, resulting in a profit of $20 per share.
Conversely, if you anticipate a decline in Apple’s stock price, you could buy a put option with a strike price of $150. Should the market price indeed drop to $130, you can capitalize on this downturn by selling the shares at the $150 strike price, netting a profit of $20 per share.
Exploring the Mechanics of Calls and Puts in Options Trading
Understanding the underlying mechanics of calls and puts empowers traders to execute effective strategies. The premium is the price paid to acquire an option, which includes compensation for the option seller’s risk of fulfilling the contract.
Traders must carefully consider expiration dates and strike prices when making their choices. The expiration date determines how long the option remains active, while the strike price influences the potential profit or loss.
Strategies for Success: Utilizing Calls and Puts
Seasoned traders often combine calls and puts to develop sophisticated strategies that capitalize on market movements. Some common approaches include:
- Covered Call: Selling a call option against an existing long position in the underlying asset, generating additional income while limiting potential upside.
- Protective Put: Buying a put option against an existing long position in the underlying asset, providing downside protection in case of price declines.
- Collar Strategy: Combining a call option with a put option at different strike prices, defining boundaries for potential gains and losses while capturing premium.
/call-and-put-options-definitions-and-examples-1031124-v5-8566395195f0403aaf5b4ad9e5cc9364.png)
Image: elearningensup.gifafrique.com
Unveiling Market Movements: The Influence of Calls and Puts
The trading activity in calls and puts can offer valuable insights into market sentiment. A surge in call option buying suggests bullish sentiment, while increased put option trading indicates bearish expectations. Monitoring these activities can help traders gauge market direction and adjust their strategies accordingly.
What Are Calls And Puts In Options Trading
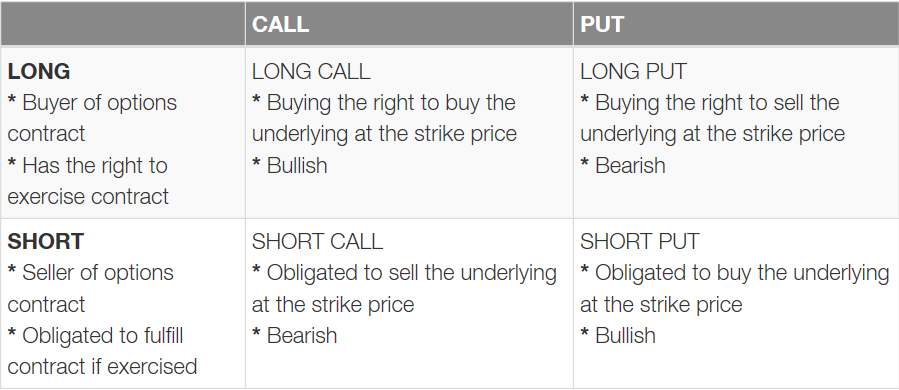
Image: tickertape.tdameritrade.com
Conclusion
Exploring the realm of options trading with calls and puts equips you with versatile tools to navigate market fluctuations and pursue tailored trading strategies. By comprehending the mechanics, nuances, and applications of these options, you can empower your investment decisions with informed choices and maximize your potential returns. Remember to stay attuned to market trends, continuously refine your knowledge, and approach trading with a prudent and well-informed mindset. The journey into options trading is an ongoing odyssey, promising both challenges and opportunities. By harnessing your understanding, you can effectively navigate the waters of market volatility and potentially reap the rewards that await you.






