Introduction
In the realm of financial markets, options trading offers investors the potential for substantial profits and the ability to mitigate risk. Calls and puts are two fundamental options strategies that allow traders to speculate on the future price movements of stocks, commodities, and other assets. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of calls and puts, exploring their history, basic concepts, and real-world applications. We will also examine the latest trends and developments in options trading, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate this complex and dynamic market.
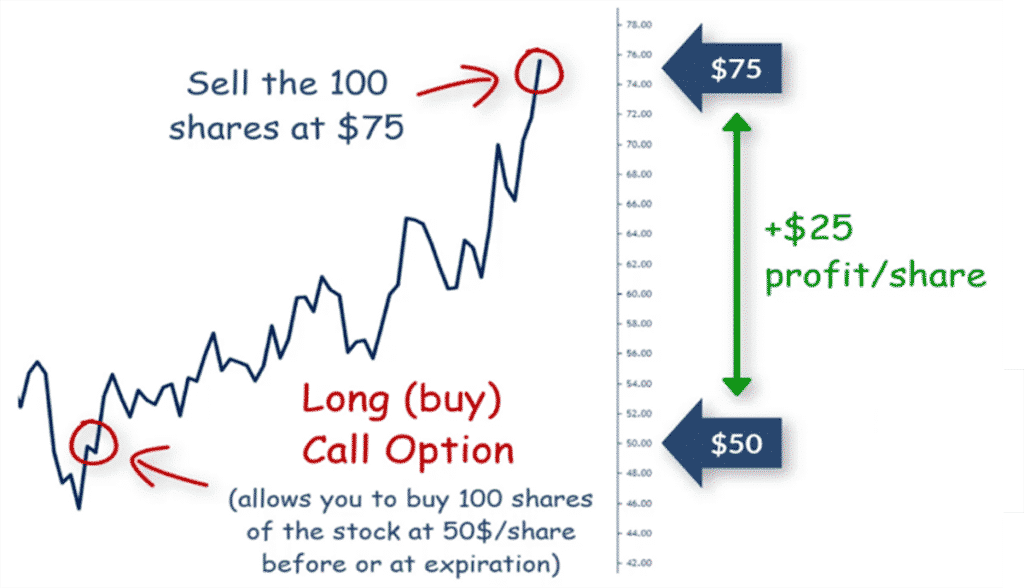
Image: 2ndskiesforex.com
Understanding Calls and Puts
A call option grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a specified price, known as the strike price, on or before a predetermined date, known as the expiration date. Conversely, a put option provides the holder the right to sell an underlying asset at a specified strike price on or before the expiration date.
Traders typically purchase call options if they expect the price of an underlying asset to increase, as it gives them the potential to buy the asset at a discounted price if their prediction holds true. On the other hand, put options are purchased when traders anticipate a decline in an underlying asset’s price, allowing them to sell the asset at a higher price if their forecast materializes.
Advantages and Limitations of Calls and Puts
Calls and puts offer distinct advantages for traders who seek both profit generation and risk management:
- Leverage: Call and put options provide a degree of leverage, allowing traders to control a large number of shares with a relatively small investment.
- Limited Risk: Unlike futures contracts, which obligate the holder to buy or sell a specific number of shares, calls and puts limit the potential loss to the premium paid for the options.
- Premiums: The premiums paid for calls and puts represent not only the value of the options but also the market’s expectation of the underlying asset’s price movement and volatility.
However, there are also limitations associated with call and put options:
- Time Decay: Call and put options have limited lifespans, and their value steadily declines as the expiration date approaches, especially if the underlying asset’s price remains unchanged or fluctuates within a narrow range.
- Complexity: Options trading involves numerous factors, including strike price, expiration date, and implied volatility, which can make it a complex endeavor for novice traders.
Applications of Calls and Puts
Calls and puts have a wide range of applications in financial markets:
- Speculation: Traders use calls and puts to speculate on the future direction of an underlying asset’s price. Call options are used for bullish bets, while put options are employed for bearish bets.
- Hedging: Calls and puts can be used to hedge against risk in other investments or portfolio positions. For example, an investor holding a stock position can purchase a put option to limit potential losses in case of a market downturn.
- Income Generation: Options premiums can generate income for traders who sell call and put options. This strategy involves selling the rights to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price, collecting the premium in exchange for the risk of being obligated to fulfill the contract if the predetermined conditions are met.

Image: acikubolex.web.fc2.com
Calls Puts Options Trading

Image: www.century.ae
Conclusion
Calls and puts are versatile financial instruments that offer traders the opportunity to amplify returns, manage risk, and generate income in financial markets. Understanding the intricacies of calls and puts, including their advantages, limitations, and applications, is essential for informed decision-making and successful trading. By leveraging this knowledge, you can explore the world of options trading with confidence, seeking both financial gains and the mitigation of potential losses.






