Introduction
The world of finance is vast and ever-evolving, with a myriad of investment strategies and instruments available. Options trading, a versatile derivative strategy, has gained significant prominence in recent years, offering investors unique opportunities to manage risk, leverage market movements, and potentially enhance returns.

Image: speedtrader.com
In essence, options are contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price within a predetermined time frame. This flexibility makes options trading suitable for various investment objectives, from hedging against market volatility to profiting from price fluctuations.
Types of Options
There are two primary types of options: calls and puts.
Call Options
A call option gives the buyer the right to purchase the underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) by the expiration date. Call options are often employed by investors who believe the underlying asset’s price will rise and want to capitalize on potential gains beyond the strike price.
Put Options
Conversely, a put option awards the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price by the expiration date. Put options are utilized when investors anticipate a decline in the asset’s price and seek to profit from that move.
Option Features
In addition to their respective functions, call and put options share specific characteristics including:
- Premium: The price paid by the buyer of the option, granting them the contractual rights associated with the option.
- Strike Price: The agreed-upon price at which the buyer may execute the option to buy (call) or sell (put).
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires, annulling any unexercised rights.
Options Trading Strategies
The versatility of options facilitates a wide array of trading strategies, each with its unique risk and reward profile. Some prevalent strategies include:
- Covered Call Writing: Selling a call option against an existing holding of the underlying asset, aiming to generate additional income through premium revenue.
- Protective Put Writing: Selling a put option to protect an underlying asset from potential price declines.
- Bullish Spread: Purchasing a call option at a lower strike price while simultaneously selling a call option at a higher strike price.
- Bearish Spread: Acquiring a put option at a higher strike price and simultaneously selling a put option at a lower strike price.
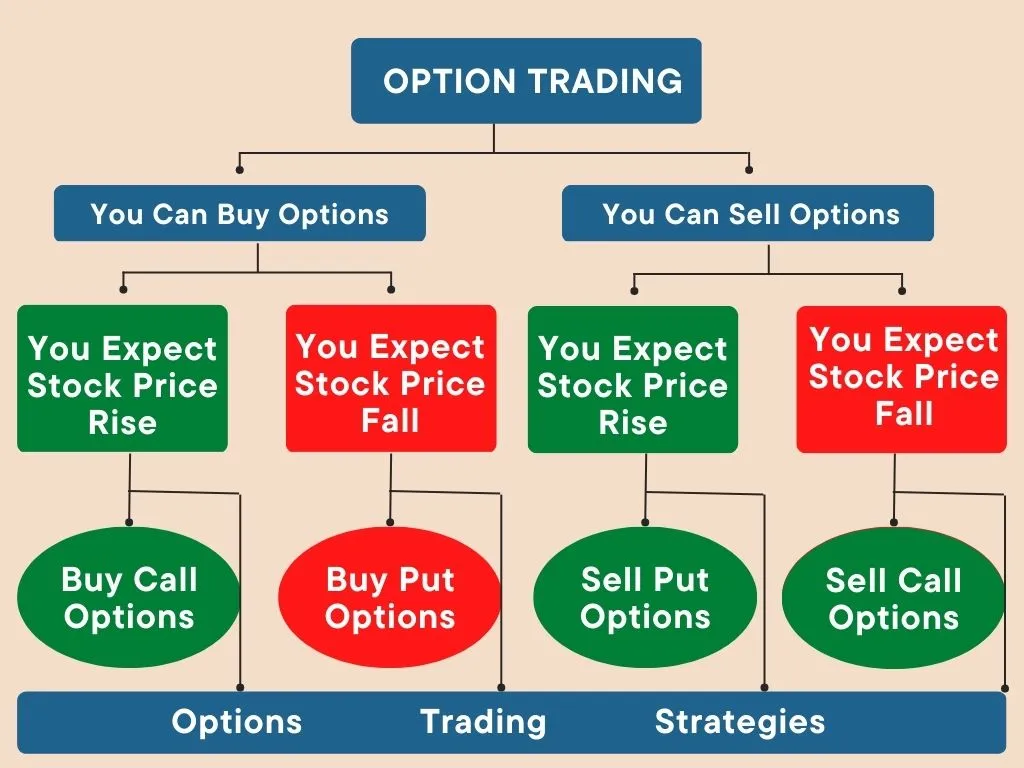
Image: changehero.io
Tips and Expert Advice
Navigating the complexities of options trading requires a thorough understanding of market dynamics, sound risk management practices, and a disciplined approach. Here are some tips and pieces of expert advice:
- Educate Yourself: Comprehending the intricacies of options trading is crucial before initiating trades. Dedicate time to research, consult experts, and gain a firm grasp of option terminology and strategies.
- Manage Risk: Options trading involves inherent risk, so employ proper risk management techniques like position sizing, stop-loss orders, and diversification.
- Consider Time Decay: Options premiums erode over time, particularly as expiration approaches. Factor in time decay when evaluating potential trades.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between an option and a futures contract?
A: Unlike options, which grant the right but not the obligation to buy or sell, futures contracts obligate the holder to purchase (or deliver) the underlying asset at a specified future date and price.
Q: What factors influence option prices?
A: Option prices are influenced by several variables, including the underlying asset’s price, volatility, time to expiration, and prevailing market conditions such as interest rates and macroeconomic trends.
Type Of Option Trading
Image: apkpure.com
Conclusion
Options trading presents a vast and versatile landscape, providing investors with a range of opportunities and complex strategies. While the potential rewards can be significant, it is imperative to remember that options trading carries inherent risks. By embracing a disciplined and informed approach, investors can harness the power of options to enhance their portfolio performance and mitigate potential losses.






