Introduction
In the bustling world of finance, where traders grapple with intricate investment strategies, the distinction between day trading and ordinary trading can be crucial. Day trading, characterized by its intense activity and focus on short-term price fluctuations, has traditionally been a distinct category with its own set of rules and regulations. However, a lesser-known fact is that trading options does not qualify as day trading, offering traders a unique path to participate in the options market without triggering the day-trading designation. This article will delve into the nuances of this distinction, exploring the implications for traders and shedding light on the advantages and considerations associated with trading options.

Image: www.youtube.com
Understanding Day Trading
Day trading is a high-frequency trading strategy that involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day, typically with the intention of closing all positions by the end of the market’s business hours. This approach hinges on rapid decision-making and the ability to capitalize on small price movements, often utilizing leverage to amplify profits. Day traders rely on technical analysis and other short-term indicators to identify trading opportunities and manage risk.
Options Trading vs. Day Trading
Options are financial contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (in the case of call options) or sell (in the case of put options) an underlying asset at a specified price on or before a certain date. Unlike stocks or futures, which represent direct ownership or trading of the underlying asset, options provide an indirect exposure to the market while offering flexibility and potential leverage.
Crucially, trading options does not constitute day trading, even if it involves multiple trades within a single market day. This is due to the unique nature of options contracts, which are not considered securities but rather standardized derivatives. As such, they fall outside the regulatory framework governing day trading, which is primarily concerned with ensuring market stability and preventing excessive speculation in certain securities markets.
Benefits of Trading Options
The exclusion of options trading from the day-trading classification offers several advantages to traders. First and foremost, it eliminates the regulatory burdens and restrictions associated with day trading. Day traders are subject to specific capital requirements, margin restrictions, and reporting obligations, which can be daunting for retail traders.
Secondly, trading options provides greater flexibility compared to day trading. Options traders are not constrained by the end-of-day closing requirement applicable to day traders. This allows them to hold positions overnight or for longer periods, adapting their strategies to different market conditions and time horizons.
Thirdly, options can act as a buffer against market volatility, offering greater downside protection compared to direct investment in the underlying asset. This is particularly relevant for traders seeking risk mitigation strategies while still participating in market movements.
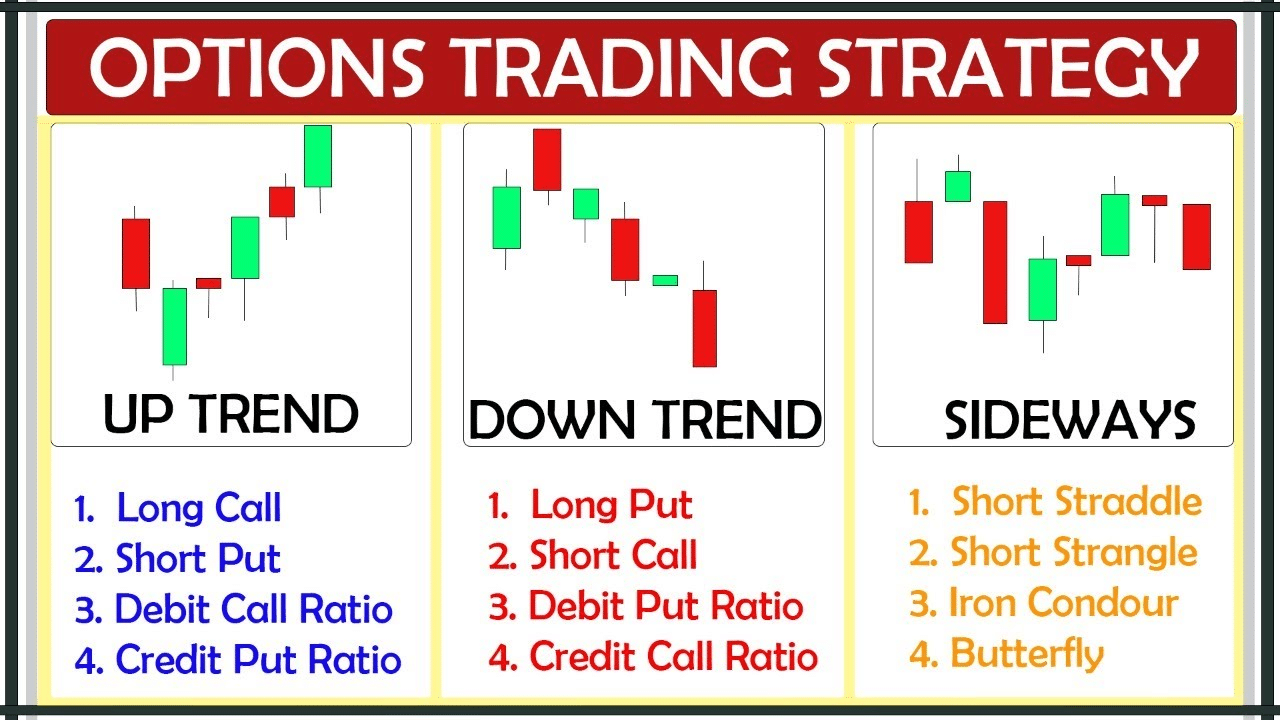
Image: investgrail.com
Considerations for Options Traders
While trading options offers unique advantages, it is not without considerations. Options contracts have their own complexities and risks, including time decay, volatility, and the potential for significant losses. Traders should thoroughly understand options mechanics, pricing models, and risk management techniques before engaging in this market.
Furthermore, it is important to note that while trading options does not constitute day trading, it can still be subject to specific broker regulations and margin requirements. Traders should familiarize themselves with their broker’s policies regarding options trading to avoid any misunderstandings or account restrictions.
Trading Options Dont Count As Day Trade

Image: www.redfox-trading.com
Conclusion
Trading options provides traders with an alternative path to participate in the financial markets without triggering the day-trading designation. This distinction offers several benefits, including exemption from day-trading regulations, greater flexibility, and potential risk mitigation. However, it is crucial for traders to approach options trading with caution, recognizing its inherent risks and complexities. By understanding the nuances of options trading and carefully considering potential implications, traders can harness the advantages of this market while managing their risks effectively.






