Introduction:
Are you intrigued by the financial world and eager to explore new investment opportunities? Options trading might be the perfect avenue for you. In this extensive guide, we will delve into the fundamentals of options trading, equipping you with the knowledge and understanding necessary to embark on this exciting journey. Whether you’re a complete novice or have some familiarity with the concept, this article will provide valuable insights to help you navigate the intricate world of options trading.
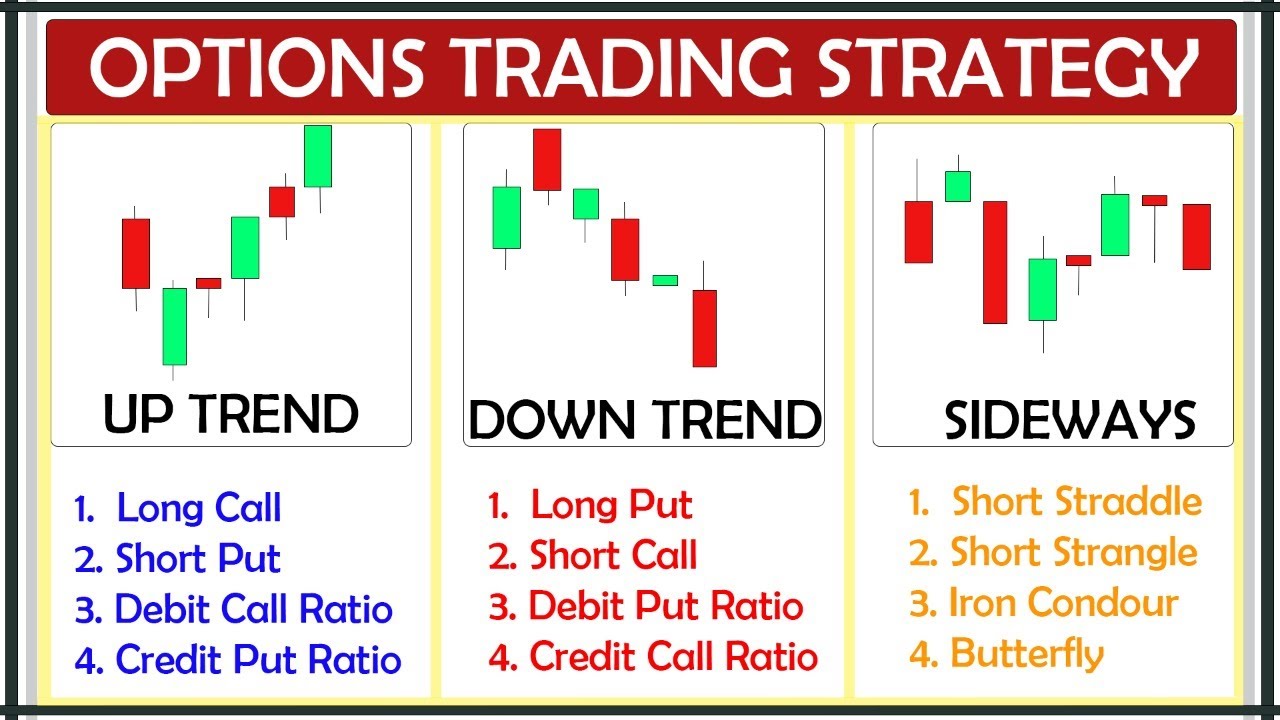
Image: www.youtube.com
Options have become increasingly popular as traders seek to enhance their portfolios and potentially generate substantial returns. These versatile instruments offer a unique combination of flexibility, leverage, and risk management tools.
What Are Options?
Essentially, options are financial contracts that grant buyers the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset, such as a stock or an index, at a specified price, known as the strike price, on or before a defined expiration date. The buyer of an option pays a premium to the seller, who assumes the obligation to fulfill the contract if the buyer chooses to exercise their right.
Options provide traders with a variety of advantages. They allow investors to speculate on the future price movements of an underlying asset without having to own it outright. This can be especially beneficial in situations where the trader expects a significant price movement but lacks the capital to purchase the underlying asset directly.
Types of Options
- **Call Options**: Grant the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset.
- **Put Options**: Grant the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset.
How Options Work
To illustrate how options work, let’s consider the following example. Suppose you believe that the stock price of a particular company will rise in the future. You can purchase a call option with a strike price of \$100 and an expiration date of 6 months. If the stock price rises above \$100 before the expiration date, you can exercise your right to buy the stock at the strike price, allowing you to profit from the price increase.
On the other hand, if the stock price falls below \$100, you will have the option to let the option expire worthless. In this case, you will lose the premium you paid for the option, but you will not be obligated to buy the underlying asset at the strike price.

Image: www.youtube.com
Factors Affecting Option Prices
- Price of the underlying asset
- Expiration date
- Strike price
- Volatility of the underlying asset
- Interest rates
Tips for Trading Options
To enhance your success in options trading, consider the following expert advice:
- Understand the risks: Options trading involves significant risk and can result in substantial losses. Ensure that you thoroughly comprehend the risks before entering into any trades.
- Start small: Begin with small trades until you become more familiar with the market and develop your trading skills.
- Use leverage cautiously: Leverage can amplify your potential profits but can also magnify your losses. Exercise caution when using leverage in your trades.
- Set clear goals: Define your trading objectives clearly and stick to them. Avoid making impulsive trades based solely on emotions.
- Manage your emotions: Trading can be stressful, and it’s crucial to control your emotions. Avoid letting fear or greed influence your decisions.
Trading Options 101 Youtube 2017

Image: pocketsense.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between a call option and a put option?
A: Call options give you the right to buy the underlying asset, while put options give you the right to sell.
Q: When is a good time to buy an option?
A: The optimal time to buy an option depends on your trading strategy and market conditions. Consider factors such as the price of the underlying asset, volatility, and your expectations for future price movements.
Q: Do I need a lot of money to trade options?
A: No, you don’t necessarily need a significant amount of money to trade options. You can start with small trades and gradually increase your investment as your experience and confidence grow.
Conclusion:
Options trading offers a multifaceted approach to the financial world, empowering traders with tools to enhance their portfolios and potentially generate substantial returns. By comprehensively understanding the concepts, strategies, and risks involved, you can equip yourself to make informed decisions and navigate the options market effectively. However, it’s imperative to approach options trading with caution, managing risks wisely and continuously educating yourself to enhance your trading acumen.
Are you eager to venture into the exciting realm of options trading? Share your questions, thoughts, and experiences in the comments below!






