Navigating the Dynamic Options Market
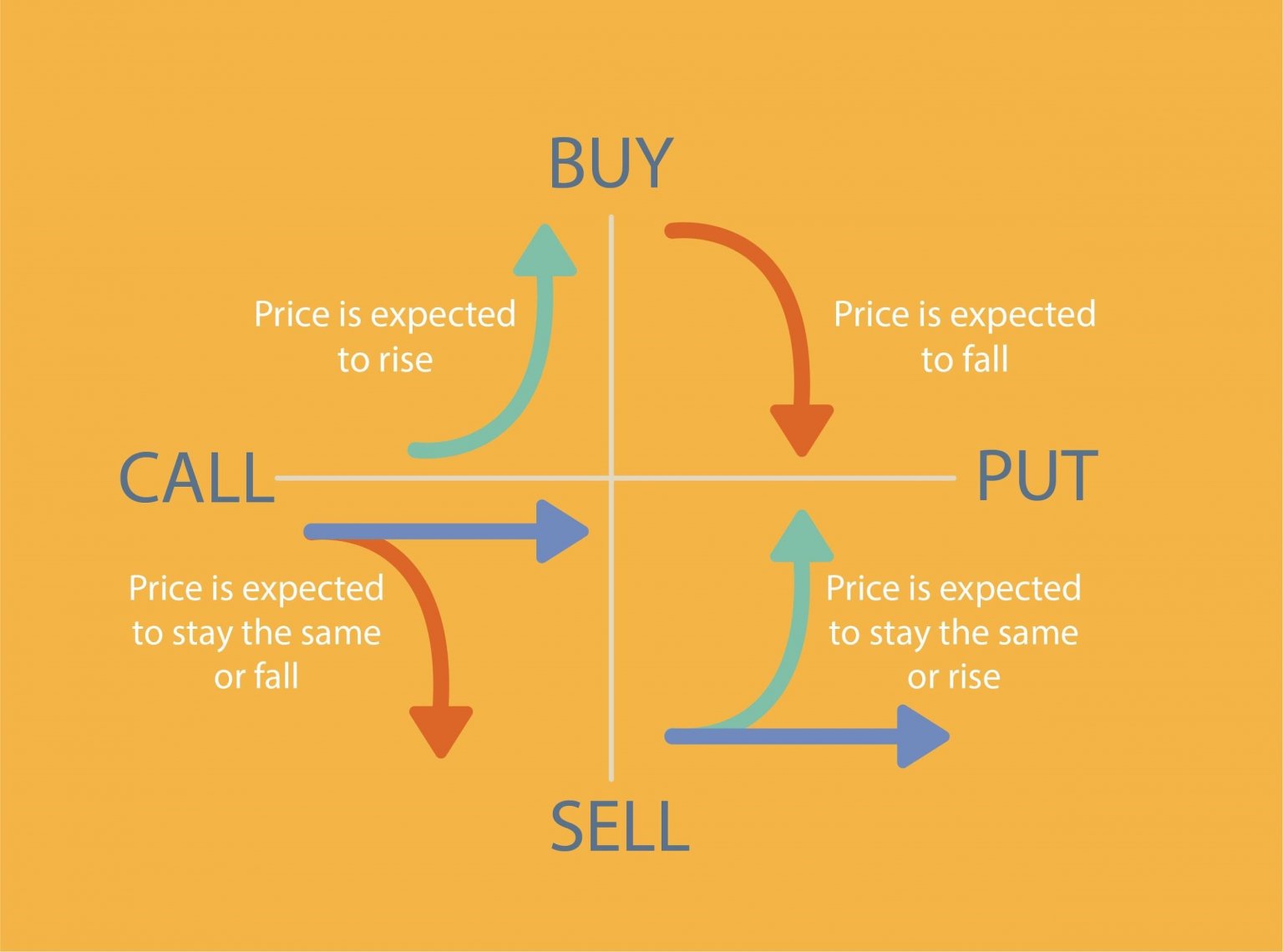
Image: www.markettradersdaily.com
In the realm of financial markets, options play a pivotal role, providing investors with the flexibility to manage risk, speculate on price movements, and potentially enhance returns. Yet, the intricate details of option trading can often leave beginners bewildered. This comprehensive guide will demystify the complex world of options, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate its nuances and harness its potential benefits.
Deconstructing Option Terminology
At the heart of option trading lies the concept of “rights.” An option conveys the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specific date (expiration date). There are two main types of options: calls and puts. Call options grant holders the right to buy an asset, while put options provide the right to sell. Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for comprehending the mechanics of option trading.
The Anatomy of an Option Contract
Each option contract encompasses several key components:
- Underlying Asset: The security (e.g., stock, ETF, commodity) that the option is based upon.
- Strike Price: The price at which the holder can exercise the option.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option expires and ceases to have value.
- Premium: The price paid to acquire the option.
The relationship between these components determines the value and potential outcome of an option trade.
Unveiling Option Strategies
Investors employ a myriad of option strategies, each tailored to specific investment objectives. Some common strategies include:
- Covered Call: Selling call options against a stock already owned, generating income from the premium while limiting upside potential.
- Protective Put: Buying put options to hedge against potential losses in a long stock position.
- Bull Call Spread: Buying a lower-strike call option and selling a higher-strike call option to limit risk and profit from moderate price increases.
- Bear Put Spread: Selling a lower-strike put option and buying a higher-strike put option to profit from price declines.
Understanding the nuances of these strategies is essential for effective option trading.
The Psychology of Option Trading
Option trading involves not only technical knowledge but also a deep understanding of human behavior. Options entice traders with the allure of potentially high returns, but this pursuit often leads to speculative excess and irrational decision-making. Exercise caution, trade with discipline, and recognize the inherent risks associated with options trading.
Harnessing Options for Investment Success
Approaching options trading strategically can enhance portfolio returns and mitigate risks. Key principles to embrace include:
- Due Diligence: Thoroughly research the underlying asset, market conditions, and your own risk tolerance before trading options.
- Risk Management: Options can amplify both profits and losses. Establish a clear trading plan and adhere to it diligently to limit exposure to excessive risk.
- Patience and Discipline: Successful option trading requires patience and discipline. Avoid impulsive trades and stay committed to your strategy over the long term.
Conclusion
Options provide traders with a powerful tool to enhance returns, manage risk, and express their market views. By understanding the fundamentals of option trading, practicing sound strategy, and exercising caution, you can navigate the dynamic options market with confidence and potentially reap its rewards. Remember, knowledge is your most valuable asset in the realm of options trading.

Image: blog.shoonya.com
Trading Option Meaning

Image: eazeetraders.com






