Introduction
Navigating the complexities of option trading often involves grappling with tax intricacies. Understanding the tax rate on option trading is paramount for informed decision-making and optimal financial outcomes. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of option trading taxation, providing a comprehensive guide to help you strategize effectively.
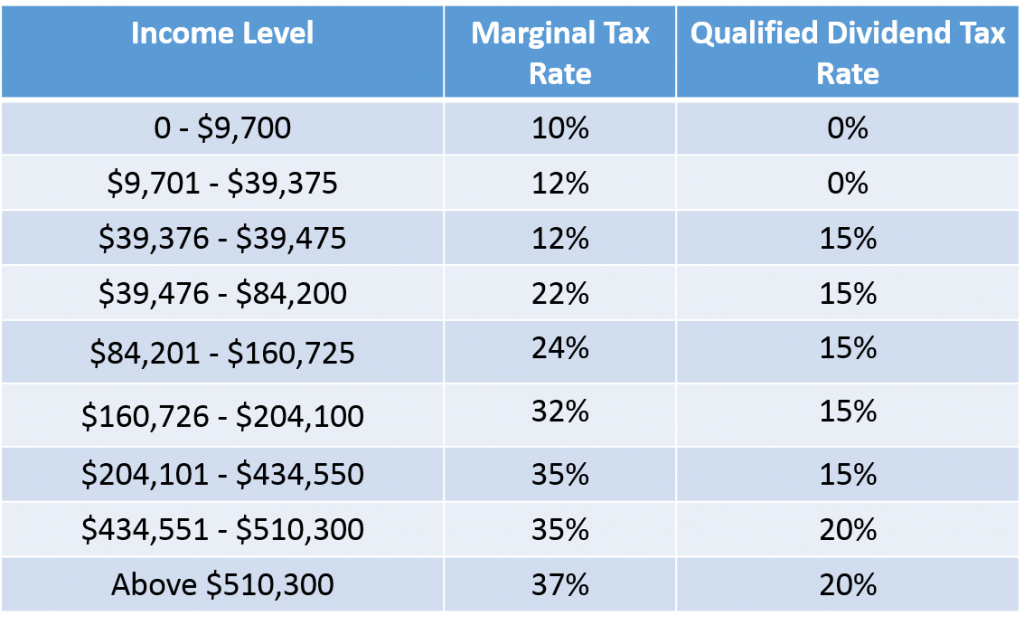
Image: findwes.com
In the world of finance, options have emerged as a popular instrument, allowing traders to leverage their knowledge and potentially reap significant rewards. However, alongside the potential gains lies the responsibility to navigate the tax implications associated with option trading. Failing to do so can lead to unintended consequences and missed opportunities.
Tax Treatment of Option Trading
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) classifies options as either short-term or long-term investments based on the holding period. Short-term options, held for less than a year, are subject to short-term capital gains tax rates, while long-term options, held for a year or more, benefit from lower long-term capital gains tax rates.
Short-Term Options
Short-term option profits are taxed as ordinary income, meaning they are added to your regular income for the year. The tax rate applied to short-term gains is typically determined by your income tax bracket. In general, higher income earners pay higher tax rates.
Long-Term Options
Long-term option profits are eligible for more favorable tax rates. Depending on your income tax bracket, you may be subject to a 0%, 15%, or 20% long-term capital gains tax rate. Typically, lower income earners qualify for the lower tax rates.
Image: forexnautilussystem.blogspot.com
Understanding the Wash Sale Rule
The wash sale rule is a crucial tax regulation that impacts option traders. This rule prohibits you from claiming a tax loss on the sale of an option if you have purchased a “substantially identical” option within 30 days before or after the sale.
The purpose of the wash sale rule is to prevent traders from artificially generating losses to offset capital gains. If a wash sale occurs, the loss is disallowed, and the holding period for the replacement option begins on the date of purchase, not the date of the original option.
Tax Considerations for Options Strategies
Option traders often employ various strategies to generate income. Some common strategies include covered calls, cash-secured puts, and straddles. It’s important to understand the tax implications of each strategy before implementing it.
For instance, covered calls involve selling call options against shares you already own. The premium received from the sale of the call options is taxed as short-term capital gain, regardless of whether the underlying shares are sold or not. Cash-secured puts, on the other hand, entail selling put options while holding sufficient cash to purchase the underlying asset if the option is exercised. The premium received from selling the put option is taxed as short-term capital gain.
Tips for Minimizing Option Trading Taxes
While you cannot avoid paying taxes on option trading profits, there are strategies to minimize your tax burden:
- Hold options long-term: By holding options for a year or more, you qualify for more favorable long-term capital gains tax rates.
- Utilize tax-advantaged accounts: Investing in options within IRAs or 401(k) accounts allows for tax-deferred or tax-free growth of your investments.
- Manage your gains and losses strategically: Offset short-term capital gains with long-term capital losses to reduce your overall tax liability.
FAQs on Option Trading Taxes
- Q: What is the difference between short-term and long-term option taxes?
A: Short-term option profits are taxed as ordinary income, while long-term option profits are taxed at lower capital gains rates. - Q: What is the wash sale rule?
A: The wash sale rule prevents traders from claiming a tax loss on the sale of an option if they purchase a substantially identical option within 30 days. - Q: How are covered calls taxed?
A: Premiums received from selling covered calls are taxed as short-term capital gains. - Q: Can I use tax-advantaged accounts for option trading?
A: Yes, you can invest in options within IRAs or 401(k) accounts for tax-deferred or tax-free growth. - Q: How can I minimize my option trading taxes?
A: Hold options long-term, utilize tax-advantaged accounts, and strategically manage your gains and losses to reduce your tax liability.
Tax Rate On Option Trading
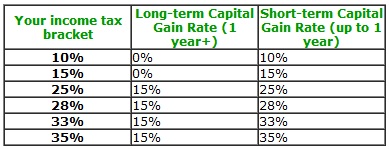
Image: www.sharesexplained.com
Conclusion
Understanding the tax rate on option trading is crucial for successful navigation of the financial markets. By meticulously managing your option trades and adhering to tax regulations, you can optimize your financial outcomes while remaining compliant. If you have any further questions or require personalized advice, it is highly recommended to seek professional guidance from an experienced financial advisor or tax professional.
Are you an avid reader keen on delving deeper into the world of finance and taxation? If so, we invite you to explore our website for a wealth of informative articles and resources tailored to your interests. Join our engaged community of finance enthusiasts and stay up-to-date on the latest market trends. We value your feedback and welcome any questions you may have. Your insights and participation help us continuously improve our content and provide you with the best possible experience. Stay connected and let’s embark on this financial journey together!






